EMD-10706
Cryo-EM structure of a Phenuiviridae L protein
EMD-10706
Single-particle3.78 Å
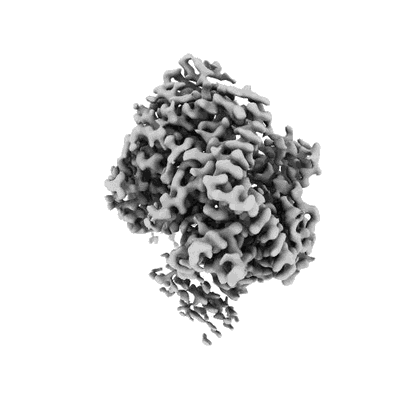 Deposition: 26/02/2020
Deposition: 26/02/2020Map released: 08/04/2020
Last modified: 22/05/2024
Sample Organism:
SFTS virus AH12
Sample: Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus L Protein
Fitted models: 6y6k (Avg. Q-score: 0.522)
Deposition Authors: Vogel D ,
Thorkelsson SR
,
Thorkelsson SR
Sample: Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus L Protein
Fitted models: 6y6k (Avg. Q-score: 0.522)
Deposition Authors: Vogel D
 ,
Thorkelsson SR
,
Thorkelsson SR
Structural and functional characterization of the severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus L protein.
Vogel D  ,
Thorkelsson SR,
Quemin ERJ,
Meier K
,
Thorkelsson SR,
Quemin ERJ,
Meier K  ,
Kouba T
,
Kouba T  ,
Gogrefe N,
Busch C,
Reindl S,
Gunther S
,
Gogrefe N,
Busch C,
Reindl S,
Gunther S  ,
Cusack S
,
Cusack S  ,
Grunewald K
,
Grunewald K  ,
Rosenthal M
,
Rosenthal M 
(2020) Nucleic Acids Res , 48 , 5749 - 5765
 ,
Thorkelsson SR,
Quemin ERJ,
Meier K
,
Thorkelsson SR,
Quemin ERJ,
Meier K  ,
Kouba T
,
Kouba T  ,
Gogrefe N,
Busch C,
Reindl S,
Gunther S
,
Gogrefe N,
Busch C,
Reindl S,
Gunther S  ,
Cusack S
,
Cusack S  ,
Grunewald K
,
Grunewald K  ,
Rosenthal M
,
Rosenthal M 
(2020) Nucleic Acids Res , 48 , 5749 - 5765
Abstract:
The Bunyavirales order contains several emerging viruses with high epidemic potential, including Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV). The lack of medical countermeasures, such as vaccines and antivirals, is a limiting factor for the containment of any virus outbreak. To develop such antivirals a profound understanding of the viral replication process is essential. The L protein of bunyaviruses is a multi-functional and multi-domain protein performing both virus transcription and genome replication and, therefore, is an ideal drug target. We established expression and purification procedures for the full-length L protein of SFTSV. By combining single-particle electron cryo-microscopy and X-ray crystallography, we obtained 3D models covering ∼70% of the SFTSV L protein in the apo-conformation including the polymerase core region, the endonuclease and the cap-binding domain. We compared this first L structure of the Phenuiviridae family to the structures of La Crosse peribunyavirus L protein and influenza orthomyxovirus polymerase. Together with a comprehensive biochemical characterization of the distinct functions of SFTSV L protein, this work provides a solid framework for future structural and functional studies of L protein-RNA interactions and the development of antiviral strategies against this group of emerging human pathogens.
The Bunyavirales order contains several emerging viruses with high epidemic potential, including Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV). The lack of medical countermeasures, such as vaccines and antivirals, is a limiting factor for the containment of any virus outbreak. To develop such antivirals a profound understanding of the viral replication process is essential. The L protein of bunyaviruses is a multi-functional and multi-domain protein performing both virus transcription and genome replication and, therefore, is an ideal drug target. We established expression and purification procedures for the full-length L protein of SFTSV. By combining single-particle electron cryo-microscopy and X-ray crystallography, we obtained 3D models covering ∼70% of the SFTSV L protein in the apo-conformation including the polymerase core region, the endonuclease and the cap-binding domain. We compared this first L structure of the Phenuiviridae family to the structures of La Crosse peribunyavirus L protein and influenza orthomyxovirus polymerase. Together with a comprehensive biochemical characterization of the distinct functions of SFTSV L protein, this work provides a solid framework for future structural and functional studies of L protein-RNA interactions and the development of antiviral strategies against this group of emerging human pathogens.
Secondary citations:
- Afonine PV, Poon BK, Read RJ, Sobolev OV, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A & Adams PD. (2018) Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, 74, 531 - 544
- & Scheres SH. (2012) RELION: implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J Struct Biol, 180, 519 - 530
