EMD-16671
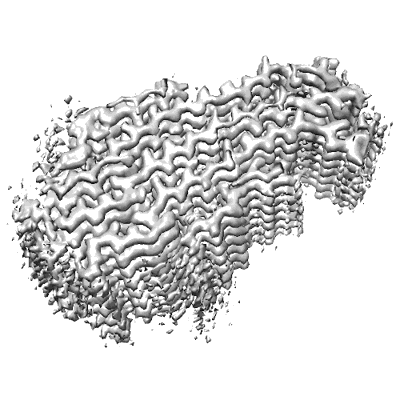
Cryo-EM structure of the Nup98(298-327) fibril
EMD-16671
Helical reconstruction2.67 Å
 Deposition: 09/02/2023
Deposition: 09/02/2023Map released: 21/02/2024
Last modified: 22/05/2024
Sample Organism:
Homo sapiens
Sample: Nup98(298-327)
Fitted models: 8ci8 (Avg. Q-score: 0.609)
Deposition Authors: Ibanez de Opakua A ,
Cima-Omori S,
Dienemann C
,
Cima-Omori S,
Dienemann C  ,
Zweckstetter M
,
Zweckstetter M 
Sample: Nup98(298-327)
Fitted models: 8ci8 (Avg. Q-score: 0.609)
Deposition Authors: Ibanez de Opakua A
 ,
Cima-Omori S,
Dienemann C
,
Cima-Omori S,
Dienemann C  ,
Zweckstetter M
,
Zweckstetter M 
Impact of distinct FG nucleoporin repeats on Nup98 self-association.
Ibanez de Opakua A  ,
Pantoja CF
,
Pantoja CF  ,
Cima-Omori MS
,
Cima-Omori MS  ,
Dienemann C
,
Dienemann C  ,
Zweckstetter M
,
Zweckstetter M 
(2024) Nat Commun , 15 , 3797 - 3797
 ,
Pantoja CF
,
Pantoja CF  ,
Cima-Omori MS
,
Cima-Omori MS  ,
Dienemann C
,
Dienemann C  ,
Zweckstetter M
,
Zweckstetter M 
(2024) Nat Commun , 15 , 3797 - 3797
Abstract:
Nucleoporins rich in phenylalanine/glycine (FG) residues form the permeability barrier within the nuclear pore complex and are implicated in several pathological cellular processes, including oncogenic fusion condensates. The self-association of FG-repeat proteins and interactions between FG-repeats play a critical role in these activities by forming hydrogel-like structures. Here we show that mutation of specific FG repeats of Nup98 can strongly decrease the protein's self-association capabilities. We further present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of a Nup98 peptide fibril with higher stability per residue compared with previous Nup98 fibril structures. The high-resolution structure reveals zipper-like hydrophobic patches which contain a GLFG motif and are less compatible for binding to nuclear transport receptors. The identified distinct molecular properties of different regions of the nucleoporin may contribute to spatial variations in the self-association of FG-repeats, potentially influencing transport processes through the nuclear pore.
Nucleoporins rich in phenylalanine/glycine (FG) residues form the permeability barrier within the nuclear pore complex and are implicated in several pathological cellular processes, including oncogenic fusion condensates. The self-association of FG-repeat proteins and interactions between FG-repeats play a critical role in these activities by forming hydrogel-like structures. Here we show that mutation of specific FG repeats of Nup98 can strongly decrease the protein's self-association capabilities. We further present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of a Nup98 peptide fibril with higher stability per residue compared with previous Nup98 fibril structures. The high-resolution structure reveals zipper-like hydrophobic patches which contain a GLFG motif and are less compatible for binding to nuclear transport receptors. The identified distinct molecular properties of different regions of the nucleoporin may contribute to spatial variations in the self-association of FG-repeats, potentially influencing transport processes through the nuclear pore.
