EMD-16894
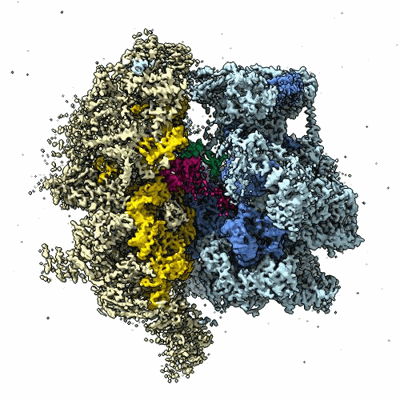
55S mammalian mitochondrial ribosome with mtRF1 and P-site tRNA
EMD-16894
Single-particle3.6 Å
 Deposition: 23/03/2023
Deposition: 23/03/2023Map released: 14/06/2023
Last modified: 26/06/2024
Sample Organism:
Sus scrofa,
Homo sapiens
Sample: 55S mammalian mitochondrial ribosome with mtRF1 and P-site tRNA
Fitted models: 8oin (Avg. Q-score: 0.384)
Deposition Authors: Saurer M ,
Leibundgut M
,
Leibundgut M  ,
Scaiola A
,
Scaiola A  ,
Schoenhut T,
Ban N
,
Schoenhut T,
Ban N 
Sample: 55S mammalian mitochondrial ribosome with mtRF1 and P-site tRNA
Fitted models: 8oin (Avg. Q-score: 0.384)
Deposition Authors: Saurer M
 ,
Leibundgut M
,
Leibundgut M  ,
Scaiola A
,
Scaiola A  ,
Schoenhut T,
Ban N
,
Schoenhut T,
Ban N 
Molecular basis of translation termination at noncanonical stop codons in human mitochondria.
Saurer M  ,
Leibundgut M
,
Leibundgut M  ,
Nadimpalli HP
,
Nadimpalli HP  ,
Scaiola A
,
Scaiola A  ,
Schonhut T
,
Schonhut T  ,
Lee RG
,
Lee RG  ,
Siira SJ
,
Siira SJ  ,
Rackham O
,
Rackham O  ,
Dreos R
,
Dreos R  ,
Lenarcic T
,
Lenarcic T  ,
Kummer E
,
Kummer E  ,
Gatfield D
,
Gatfield D  ,
Filipovska A
,
Filipovska A  ,
Ban N
,
Ban N 
(2023) Science , 380 , 531 - 536
 ,
Leibundgut M
,
Leibundgut M  ,
Nadimpalli HP
,
Nadimpalli HP  ,
Scaiola A
,
Scaiola A  ,
Schonhut T
,
Schonhut T  ,
Lee RG
,
Lee RG  ,
Siira SJ
,
Siira SJ  ,
Rackham O
,
Rackham O  ,
Dreos R
,
Dreos R  ,
Lenarcic T
,
Lenarcic T  ,
Kummer E
,
Kummer E  ,
Gatfield D
,
Gatfield D  ,
Filipovska A
,
Filipovska A  ,
Ban N
,
Ban N 
(2023) Science , 380 , 531 - 536
Abstract:
The genetic code that specifies the identity of amino acids incorporated into proteins during protein synthesis is almost universally conserved. Mitochondrial genomes feature deviations from the standard genetic code, including the reassignment of two arginine codons to stop codons. The protein required for translation termination at these noncanonical stop codons to release the newly synthesized polypeptides is not currently known. In this study, we used gene editing and ribosomal profiling in combination with cryo-electron microscopy to establish that mitochondrial release factor 1 (mtRF1) detects noncanonical stop codons in human mitochondria by a previously unknown mechanism of codon recognition. We discovered that binding of mtRF1 to the decoding center of the ribosome stabilizes a highly unusual conformation in the messenger RNA in which the ribosomal RNA participates in specific recognition of the noncanonical stop codons.
The genetic code that specifies the identity of amino acids incorporated into proteins during protein synthesis is almost universally conserved. Mitochondrial genomes feature deviations from the standard genetic code, including the reassignment of two arginine codons to stop codons. The protein required for translation termination at these noncanonical stop codons to release the newly synthesized polypeptides is not currently known. In this study, we used gene editing and ribosomal profiling in combination with cryo-electron microscopy to establish that mitochondrial release factor 1 (mtRF1) detects noncanonical stop codons in human mitochondria by a previously unknown mechanism of codon recognition. We discovered that binding of mtRF1 to the decoding center of the ribosome stabilizes a highly unusual conformation in the messenger RNA in which the ribosomal RNA participates in specific recognition of the noncanonical stop codons.
