EMD-17006
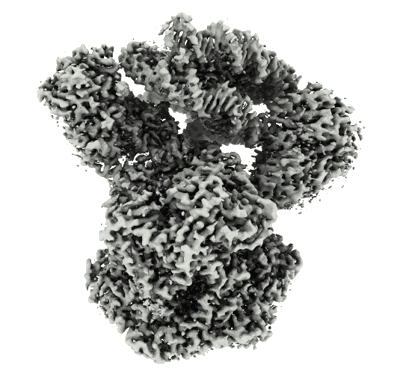
CryoEM Structure INO80core Hexasome complex composite map state1
EMD-17006
Single-particle2.8 Å
 Deposition: 04/04/2023
Deposition: 04/04/2023Map released: 26/07/2023
Last modified: 24/07/2024
Sample Organism:
Thermochaetoides thermophila,
Homo sapiens,
synthetic construct
Sample: INO80 core module in complex with hexasome
Fitted models: 8oo7 (Avg. Q-score: 0.556)
Deposition Authors: Zhang M ,
Jungblut A
,
Jungblut A  ,
Hoffmann T
,
Hoffmann T  ,
Eustermann S
,
Eustermann S 
Sample: INO80 core module in complex with hexasome
Fitted models: 8oo7 (Avg. Q-score: 0.556)
Deposition Authors: Zhang M
 ,
Jungblut A
,
Jungblut A  ,
Hoffmann T
,
Hoffmann T  ,
Eustermann S
,
Eustermann S 
Hexasome-INO80 complex reveals structural basis of noncanonical nucleosome remodeling.
Zhang M  ,
Jungblut A
,
Jungblut A  ,
Kunert F
,
Kunert F  ,
Hauptmann L
,
Hauptmann L  ,
Hoffmann T
,
Hoffmann T  ,
Kolesnikova O
,
Kolesnikova O  ,
Metzner F
,
Metzner F  ,
Moldt M,
Weis F
,
Moldt M,
Weis F  ,
DiMaio F
,
DiMaio F  ,
Hopfner KP
,
Hopfner KP  ,
Eustermann S
,
Eustermann S 
(2023) Science , 381 , 313 - 319
 ,
Jungblut A
,
Jungblut A  ,
Kunert F
,
Kunert F  ,
Hauptmann L
,
Hauptmann L  ,
Hoffmann T
,
Hoffmann T  ,
Kolesnikova O
,
Kolesnikova O  ,
Metzner F
,
Metzner F  ,
Moldt M,
Weis F
,
Moldt M,
Weis F  ,
DiMaio F
,
DiMaio F  ,
Hopfner KP
,
Hopfner KP  ,
Eustermann S
,
Eustermann S 
(2023) Science , 381 , 313 - 319
Abstract:
Loss of H2A-H2B histone dimers is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes, but how the cellular machinery functions in the context of noncanonical nucleosomal particles remains largely elusive. In this work, we report the structural mechanism for adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent chromatin remodeling of hexasomes by the INO80 complex. We show how INO80 recognizes noncanonical DNA and histone features of hexasomes that emerge from the loss of H2A-H2B. A large structural rearrangement switches the catalytic core of INO80 into a distinct, spin-rotated mode of remodeling while its nuclear actin module remains tethered to long stretches of unwrapped linker DNA. Direct sensing of an exposed H3-H4 histone interface activates INO80, independently of the H2A-H2B acidic patch. Our findings reveal how the loss of H2A-H2B grants remodelers access to a different, yet unexplored layer of energy-driven chromatin regulation.
Loss of H2A-H2B histone dimers is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes, but how the cellular machinery functions in the context of noncanonical nucleosomal particles remains largely elusive. In this work, we report the structural mechanism for adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent chromatin remodeling of hexasomes by the INO80 complex. We show how INO80 recognizes noncanonical DNA and histone features of hexasomes that emerge from the loss of H2A-H2B. A large structural rearrangement switches the catalytic core of INO80 into a distinct, spin-rotated mode of remodeling while its nuclear actin module remains tethered to long stretches of unwrapped linker DNA. Direct sensing of an exposed H3-H4 histone interface activates INO80, independently of the H2A-H2B acidic patch. Our findings reveal how the loss of H2A-H2B grants remodelers access to a different, yet unexplored layer of energy-driven chromatin regulation.
Secondary citations:
- Afonine PV, Poon BK, Read RJ, Sobolev OV, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A & Adams PD. (2018) Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, 74, 531 - 544
- Kimanius D, Zickert G, Nakane T, Adler J, Lunz S, Schonlieb CB, Oktem O & Scheres SHW. (2021) New tools for automated cryo-EM single-particle analysis in RELION-4.0. 478, 4169 - 4185
- & Croll TI. (2018) ISOLDE: a physically realistic environment for model building into low-resolution electron-density maps. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, 74, 519 - 530
- Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG & Cowtan K. (2010) Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, 66, 486 - 501
