EMD-17049
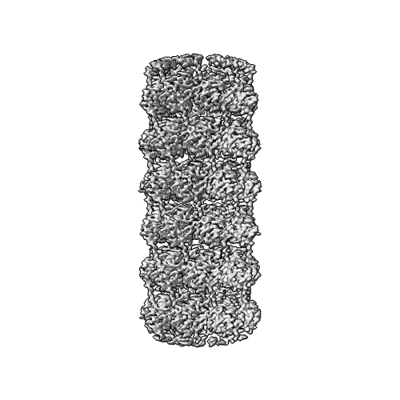
Virus-like Particle based on PVY coat protein with dC40 deletion with stacked-ring architecture
EMD-17049
Helical reconstruction3.5 Å
 Deposition: 07/04/2023
Deposition: 07/04/2023Map released: 24/01/2024
Last modified: 31/01/2024
Sample Organism:
Potato virus Y strain NTN
Sample: Virus-like particle from dC40 coat protein
Fitted models: 8opd (Avg. Q-score: 0.489)
Raw data: EMPIAR-11546
Deposition Authors: Kavcic L ,
Kezar A
,
Kezar A  ,
Podobnik M
,
Podobnik M 
Sample: Virus-like particle from dC40 coat protein
Fitted models: 8opd (Avg. Q-score: 0.489)
Raw data: EMPIAR-11546
Deposition Authors: Kavcic L
 ,
Kezar A
,
Kezar A  ,
Podobnik M
,
Podobnik M 
From structural polymorphism to structural metamorphosis of the coat protein of flexuous filamentous potato virus Y.
Kavcic L  ,
Kezar A
,
Kezar A  ,
Koritnik N
,
Koritnik N  ,
Znidaric MT,
Klobucar T
,
Znidaric MT,
Klobucar T  ,
Vicic Z
,
Vicic Z  ,
Merzel F,
Holden E,
Benesch JLP
,
Merzel F,
Holden E,
Benesch JLP  ,
Podobnik M
,
Podobnik M 
(2024) Commun Chem , 7 , 14 - 14
 ,
Kezar A
,
Kezar A  ,
Koritnik N
,
Koritnik N  ,
Znidaric MT,
Klobucar T
,
Znidaric MT,
Klobucar T  ,
Vicic Z
,
Vicic Z  ,
Merzel F,
Holden E,
Benesch JLP
,
Merzel F,
Holden E,
Benesch JLP  ,
Podobnik M
,
Podobnik M 
(2024) Commun Chem , 7 , 14 - 14
Abstract:
The structural diversity and tunability of the capsid proteins (CPs) of various icosahedral and rod-shaped viruses have been well studied and exploited in the development of smart hybrid nanoparticles. However, the potential of CPs of the wide-spread flexuous filamentous plant viruses remains to be explored. Here, we show that we can control the shape, size, RNA encapsidation ability, symmetry, stability and surface functionalization of nanoparticles through structure-based design of CP from potato virus Y (PVY). We provide high-resolution insight into CP-based self-assemblies, ranging from large polymorphic or monomorphic filaments to smaller annular, cubic or spherical particles. Furthermore, we show that we can prevent CP self-assembly in bacteria by fusion with a cleavable protein, enabling controlled nanoparticle formation in vitro. Understanding the remarkable structural diversity of PVY CP not only provides possibilities for the production of biodegradable nanoparticles, but may also advance future studies of CP's polymorphism in a biological context.
The structural diversity and tunability of the capsid proteins (CPs) of various icosahedral and rod-shaped viruses have been well studied and exploited in the development of smart hybrid nanoparticles. However, the potential of CPs of the wide-spread flexuous filamentous plant viruses remains to be explored. Here, we show that we can control the shape, size, RNA encapsidation ability, symmetry, stability and surface functionalization of nanoparticles through structure-based design of CP from potato virus Y (PVY). We provide high-resolution insight into CP-based self-assemblies, ranging from large polymorphic or monomorphic filaments to smaller annular, cubic or spherical particles. Furthermore, we show that we can prevent CP self-assembly in bacteria by fusion with a cleavable protein, enabling controlled nanoparticle formation in vitro. Understanding the remarkable structural diversity of PVY CP not only provides possibilities for the production of biodegradable nanoparticles, but may also advance future studies of CP's polymorphism in a biological context.
