EMD-17616
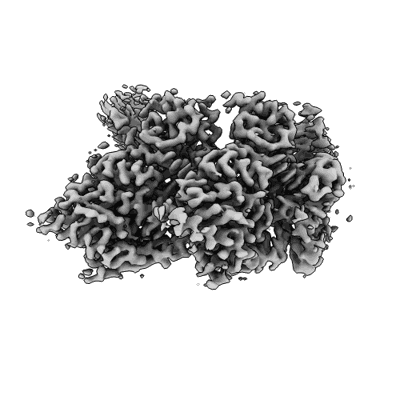
Local refinement of dimeric human metapneumovirus (HMPV) N-RNA
EMD-17616
Single-particle3.1 Å
 Deposition: 12/06/2023
Deposition: 12/06/2023Map released: 06/12/2023
Last modified: 20/03/2024
Sample Organism:
Human metapneumovirus (strain CAN97-83),
Escherichia coli
Sample: Human metapneumovirus N-RNA
Fitted models: 8pdo (Avg. Q-score: 0.555)
Deposition Authors: Whitehead JD ,
Decool H
,
Decool H  ,
Leyrat C
,
Leyrat C  ,
Carrique L
,
Carrique L  ,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M
,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M 
Sample: Human metapneumovirus N-RNA
Fitted models: 8pdo (Avg. Q-score: 0.555)
Deposition Authors: Whitehead JD
 ,
Decool H
,
Decool H  ,
Leyrat C
,
Leyrat C  ,
Carrique L
,
Carrique L  ,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M
,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M 
Structure of the N-RNA/P interface indicates mode of L/P recruitment to the nucleocapsid of human metapneumovirus.
Whitehead JD  ,
Decool H
,
Decool H  ,
Leyrat C
,
Leyrat C  ,
Carrique L
,
Carrique L  ,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M
,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M 
(2023) Nat Commun , 14 , 7627 - 7627
 ,
Decool H
,
Decool H  ,
Leyrat C
,
Leyrat C  ,
Carrique L
,
Carrique L  ,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M
,
Fix J,
Eleouet JF,
Galloux M,
Renner M 
(2023) Nat Commun , 14 , 7627 - 7627
Abstract:
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a major cause of respiratory illness in young children. The HMPV polymerase (L) binds an obligate cofactor, the phosphoprotein (P). During replication and transcription, the L/P complex traverses the viral RNA genome, which is encapsidated within nucleoproteins (N). An essential interaction between N and a C-terminal region of P tethers the L/P polymerase to the template. This N-P interaction is also involved in the formation of cytoplasmic viral factories in infected cells, called inclusion bodies. To define how the polymerase component P recognizes N-encapsidated RNA (N-RNA) we employed cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and molecular dynamics simulations, coupled to activity assays and imaging of inclusion bodies in cells. We report a 2.9 Å resolution structure of a triple-complex between multimeric N, bound to both RNA and the C-terminal region of P. Furthermore, we also present cryo-EM structures of assembled N in different oligomeric states, highlighting the plasticity of N. Combined with our functional assays, these structural data delineate in molecular detail how P attaches to N-RNA whilst retaining substantial conformational dynamics. Moreover, the N-RNA-P triple complex structure provides a molecular blueprint for the design of therapeutics to potentially disrupt the attachment of L/P to its template.
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a major cause of respiratory illness in young children. The HMPV polymerase (L) binds an obligate cofactor, the phosphoprotein (P). During replication and transcription, the L/P complex traverses the viral RNA genome, which is encapsidated within nucleoproteins (N). An essential interaction between N and a C-terminal region of P tethers the L/P polymerase to the template. This N-P interaction is also involved in the formation of cytoplasmic viral factories in infected cells, called inclusion bodies. To define how the polymerase component P recognizes N-encapsidated RNA (N-RNA) we employed cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and molecular dynamics simulations, coupled to activity assays and imaging of inclusion bodies in cells. We report a 2.9 Å resolution structure of a triple-complex between multimeric N, bound to both RNA and the C-terminal region of P. Furthermore, we also present cryo-EM structures of assembled N in different oligomeric states, highlighting the plasticity of N. Combined with our functional assays, these structural data delineate in molecular detail how P attaches to N-RNA whilst retaining substantial conformational dynamics. Moreover, the N-RNA-P triple complex structure provides a molecular blueprint for the design of therapeutics to potentially disrupt the attachment of L/P to its template.
