EMD-19064
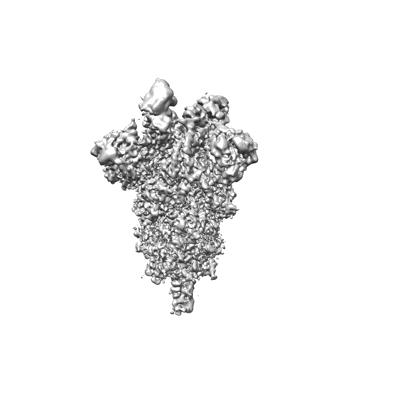
CryoEM reconstruction of SARS-CoV-2 spike in complex with nanobody tri-TMH (partially open conformation)
EMD-19064
Single-particle3.28 Å
 Deposition: 07/12/2023
Deposition: 07/12/2023Map released: 31/01/2024
Last modified: 17/04/2024
Sample Organism:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2,
Vicugna pacos
Sample: SARS-CoV-2 spike in complex with nanobody tri-TMH
Deposition Authors: Rissanen I ,
Hannula L
,
Hannula L  ,
Huiskonen JT
,
Huiskonen JT 
Sample: SARS-CoV-2 spike in complex with nanobody tri-TMH
Deposition Authors: Rissanen I
 ,
Hannula L
,
Hannula L  ,
Huiskonen JT
,
Huiskonen JT 
Nanobody engineering for SARS-CoV-2 neutralization and detection.
Hannula L  ,
Kuivanen S
,
Kuivanen S  ,
Lasham J
,
Lasham J  ,
Kant R
,
Kant R  ,
Kareinen L
,
Kareinen L  ,
Bogacheva M
,
Bogacheva M  ,
Strandin T
,
Strandin T  ,
Sironen T
,
Sironen T  ,
Hepojoki J
,
Hepojoki J  ,
Sharma V
,
Sharma V  ,
Saviranta P
,
Saviranta P  ,
Kipar A
,
Kipar A  ,
Vapalahti O
,
Vapalahti O  ,
Huiskonen JT
,
Huiskonen JT  ,
Rissanen I
,
Rissanen I 
(2024) Microbiol Spectr , 12 , e0419922 - e0419922
 ,
Kuivanen S
,
Kuivanen S  ,
Lasham J
,
Lasham J  ,
Kant R
,
Kant R  ,
Kareinen L
,
Kareinen L  ,
Bogacheva M
,
Bogacheva M  ,
Strandin T
,
Strandin T  ,
Sironen T
,
Sironen T  ,
Hepojoki J
,
Hepojoki J  ,
Sharma V
,
Sharma V  ,
Saviranta P
,
Saviranta P  ,
Kipar A
,
Kipar A  ,
Vapalahti O
,
Vapalahti O  ,
Huiskonen JT
,
Huiskonen JT  ,
Rissanen I
,
Rissanen I 
(2024) Microbiol Spectr , 12 , e0419922 - e0419922
Abstract:
In response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the quest for coronavirus inhibitors has inspired research on a variety of small proteins beyond conventional antibodies, including robust single-domain antibody fragments, i.e., "nanobodies." Here, we explore the potential of nanobody engineering in the development of antivirals and diagnostic tools. Through fusion of nanobody domains that target distinct binding sites, we engineered multimodular nanobody constructs that neutralize wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and the Alpha and Delta variants at high potency, with IC50 values as low as 50 pM. Despite simultaneous binding to distinct epitopes, Beta and Omicron variants were more resistant to neutralization by the multimodular nanobodies, which highlights the importance of accounting for antigenic drift in the design of biologics. To further explore the applications of nanobody engineering in outbreak management, we present an assay based on fusions of nanobodies with fragments of NanoLuc luciferase that can detect sub-nanomolar quantities of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in a single step. Our work showcases the potential of nanobody engineering to combat emerging infectious diseases.
In response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the quest for coronavirus inhibitors has inspired research on a variety of small proteins beyond conventional antibodies, including robust single-domain antibody fragments, i.e., "nanobodies." Here, we explore the potential of nanobody engineering in the development of antivirals and diagnostic tools. Through fusion of nanobody domains that target distinct binding sites, we engineered multimodular nanobody constructs that neutralize wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and the Alpha and Delta variants at high potency, with IC50 values as low as 50 pM. Despite simultaneous binding to distinct epitopes, Beta and Omicron variants were more resistant to neutralization by the multimodular nanobodies, which highlights the importance of accounting for antigenic drift in the design of biologics. To further explore the applications of nanobody engineering in outbreak management, we present an assay based on fusions of nanobodies with fragments of NanoLuc luciferase that can detect sub-nanomolar quantities of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in a single step. Our work showcases the potential of nanobody engineering to combat emerging infectious diseases.
