EMD-28619
Cryo-EM structure of HIV-1 BG505 DS-SOSIP ENV trimer bound to VRC34.01-MM28 FAB
EMD-28619
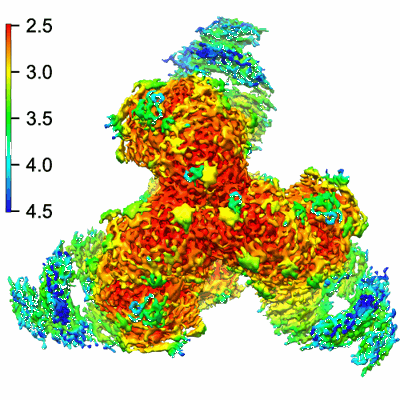
Single-particle2.7 Å
 Deposition: 19/10/2022
Deposition: 19/10/2022Map released: 27/09/2023
Last modified: 13/11/2024
Sample Organism:
Human immunodeficiency virus 1,
Homo sapiens
Sample: BG505 DS-SOSIP VRC34.01-MM28 FAB COMPLEX
Fitted models: 8euw (Avg. Q-score: 0.553)
Deposition Authors: Pletnev S, Kwong P
Sample: BG505 DS-SOSIP VRC34.01-MM28 FAB COMPLEX
Fitted models: 8euw (Avg. Q-score: 0.553)
Deposition Authors: Pletnev S, Kwong P
Antibody-directed evolution reveals a mechanism for enhanced neutralization at the HIV-1 fusion peptide site.
Banach BB,
Pletnev S,
Olia AS,
Xu K,
Zhang B,
Rawi R  ,
Bylund T,
Doria-Rose NA
,
Bylund T,
Doria-Rose NA  ,
Nguyen TD,
Fahad AS,
Lee M
,
Nguyen TD,
Fahad AS,
Lee M  ,
Lin BC,
Liu T,
Louder MK
,
Lin BC,
Liu T,
Louder MK  ,
Madan B,
McKee K,
O'Dell S,
Sastry M,
Schon A,
Bui N,
Shen CH,
Wolfe JR,
Chuang GY,
Mascola JR,
Kwong PD
,
Madan B,
McKee K,
O'Dell S,
Sastry M,
Schon A,
Bui N,
Shen CH,
Wolfe JR,
Chuang GY,
Mascola JR,
Kwong PD  ,
DeKosky BJ
,
DeKosky BJ 
(2023) Nat Commun , 14 , 7593 - 7593
 ,
Bylund T,
Doria-Rose NA
,
Bylund T,
Doria-Rose NA  ,
Nguyen TD,
Fahad AS,
Lee M
,
Nguyen TD,
Fahad AS,
Lee M  ,
Lin BC,
Liu T,
Louder MK
,
Lin BC,
Liu T,
Louder MK  ,
Madan B,
McKee K,
O'Dell S,
Sastry M,
Schon A,
Bui N,
Shen CH,
Wolfe JR,
Chuang GY,
Mascola JR,
Kwong PD
,
Madan B,
McKee K,
O'Dell S,
Sastry M,
Schon A,
Bui N,
Shen CH,
Wolfe JR,
Chuang GY,
Mascola JR,
Kwong PD  ,
DeKosky BJ
,
DeKosky BJ 
(2023) Nat Commun , 14 , 7593 - 7593
Abstract:
The HIV-1 fusion peptide (FP) represents a promising vaccine target, but global FP sequence diversity among circulating strains has limited anti-FP antibodies to ~60% neutralization breadth. Here we evolve the FP-targeting antibody VRC34.01 in vitro to enhance FP-neutralization using site saturation mutagenesis and yeast display. Successive rounds of directed evolution by iterative selection of antibodies for binding to resistant HIV-1 strains establish a variant, VRC34.01_mm28, as a best-in-class antibody with 10-fold enhanced potency compared to the template antibody and ~80% breadth on a cross-clade 208-strain neutralization panel. Structural analyses demonstrate that the improved paratope expands the FP binding groove to accommodate diverse FP sequences of different lengths while also recognizing the HIV-1 Env backbone. These data reveal critical antibody features for enhanced neutralization breadth and potency against the FP site of vulnerability and accelerate clinical development of broad HIV-1 FP-targeting vaccines and therapeutics.
The HIV-1 fusion peptide (FP) represents a promising vaccine target, but global FP sequence diversity among circulating strains has limited anti-FP antibodies to ~60% neutralization breadth. Here we evolve the FP-targeting antibody VRC34.01 in vitro to enhance FP-neutralization using site saturation mutagenesis and yeast display. Successive rounds of directed evolution by iterative selection of antibodies for binding to resistant HIV-1 strains establish a variant, VRC34.01_mm28, as a best-in-class antibody with 10-fold enhanced potency compared to the template antibody and ~80% breadth on a cross-clade 208-strain neutralization panel. Structural analyses demonstrate that the improved paratope expands the FP binding groove to accommodate diverse FP sequences of different lengths while also recognizing the HIV-1 Env backbone. These data reveal critical antibody features for enhanced neutralization breadth and potency against the FP site of vulnerability and accelerate clinical development of broad HIV-1 FP-targeting vaccines and therapeutics.
