EMD-30573
A proof of concept for neutralizing antibody-guided vaccine design against SARS-CoV-2
EMD-30573
Single-particle3.9 Å
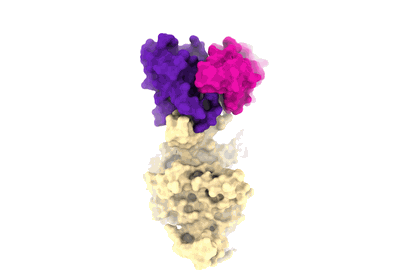 Deposition: 23/09/2020
Deposition: 23/09/2020Map released: 07/04/2021
Last modified: 16/10/2024
Sample Organism:
Homo sapiens,
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Sample: FC05 Fab binds to SARS-CoV-2 Spike
Fitted models: 7d4g (Avg. Q-score: 0.285)
Deposition Authors: Cao L ,
Wang X
,
Wang X
Sample: FC05 Fab binds to SARS-CoV-2 Spike
Fitted models: 7d4g (Avg. Q-score: 0.285)
Deposition Authors: Cao L
 ,
Wang X
,
Wang X
A proof of concept for neutralizing antibody-guided vaccine design against SARS-CoV-2.
Zhang L,
Cao L  ,
Gao XS,
Zheng BY,
Deng YQ,
Li JX,
Feng R,
Bian Q,
Guo XL,
Wang N,
Qiu HY,
Wang L,
Cui Z,
Ye Q,
Chen G,
Lu KK,
Chen Y,
Chen YT,
Pan HX,
Yu J,
Yao W,
Zhu BL,
Chen J,
Liu Y,
Qin CF,
Wang X,
Zhu FC
,
Gao XS,
Zheng BY,
Deng YQ,
Li JX,
Feng R,
Bian Q,
Guo XL,
Wang N,
Qiu HY,
Wang L,
Cui Z,
Ye Q,
Chen G,
Lu KK,
Chen Y,
Chen YT,
Pan HX,
Yu J,
Yao W,
Zhu BL,
Chen J,
Liu Y,
Qin CF,
Wang X,
Zhu FC
(2021) Natl Sci Rev , 8 , nwab053 - nwab053
 ,
Gao XS,
Zheng BY,
Deng YQ,
Li JX,
Feng R,
Bian Q,
Guo XL,
Wang N,
Qiu HY,
Wang L,
Cui Z,
Ye Q,
Chen G,
Lu KK,
Chen Y,
Chen YT,
Pan HX,
Yu J,
Yao W,
Zhu BL,
Chen J,
Liu Y,
Qin CF,
Wang X,
Zhu FC
,
Gao XS,
Zheng BY,
Deng YQ,
Li JX,
Feng R,
Bian Q,
Guo XL,
Wang N,
Qiu HY,
Wang L,
Cui Z,
Ye Q,
Chen G,
Lu KK,
Chen Y,
Chen YT,
Pan HX,
Yu J,
Yao W,
Zhu BL,
Chen J,
Liu Y,
Qin CF,
Wang X,
Zhu FC
(2021) Natl Sci Rev , 8 , nwab053 - nwab053
Abstract:
Mutations and transient conformational movements of the receptor binding domain (RBD) that make neutralizing epitopes momentarily unavailable present immune escape routes for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). To mitigate viral escape, we developed a cocktail of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) targeting epitopes located on different domains of spike (S) protein. Screening of a library of monoclonal antibodies generated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of COVID-19 convalescent patients yielded potent NAbs, targeting the N-terminal domain (NTD) and RBD domain of S, effective at nM concentrations. Remarkably, a combination of RBD-targeting NAbs and NTD-binding NAbs, FC05, enhanced the neutralization potency in cell-based assays and an animal model. Results of competitive surface plasmon resonance assays and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of antigen-binding fragments bound to S unveil determinants of immunogenicity. Combinations of immunogens, identified in the NTD and RBD of S, when immunized in rabbits and macaques, elicited potent protective immune responses against SARS-CoV-2. More importantly, two immunizations of this combination of NTD and RBD immunogens provided complete protection in macaques against a SARS-CoV-2 challenge, without observable antibody-dependent enhancement of infection. These results provide a proof of concept for neutralization-based immunogen design targeting SARS-CoV-2 NTD and RBD.
Mutations and transient conformational movements of the receptor binding domain (RBD) that make neutralizing epitopes momentarily unavailable present immune escape routes for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). To mitigate viral escape, we developed a cocktail of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) targeting epitopes located on different domains of spike (S) protein. Screening of a library of monoclonal antibodies generated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of COVID-19 convalescent patients yielded potent NAbs, targeting the N-terminal domain (NTD) and RBD domain of S, effective at nM concentrations. Remarkably, a combination of RBD-targeting NAbs and NTD-binding NAbs, FC05, enhanced the neutralization potency in cell-based assays and an animal model. Results of competitive surface plasmon resonance assays and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of antigen-binding fragments bound to S unveil determinants of immunogenicity. Combinations of immunogens, identified in the NTD and RBD of S, when immunized in rabbits and macaques, elicited potent protective immune responses against SARS-CoV-2. More importantly, two immunizations of this combination of NTD and RBD immunogens provided complete protection in macaques against a SARS-CoV-2 challenge, without observable antibody-dependent enhancement of infection. These results provide a proof of concept for neutralization-based immunogen design targeting SARS-CoV-2 NTD and RBD.
