EMD-37423
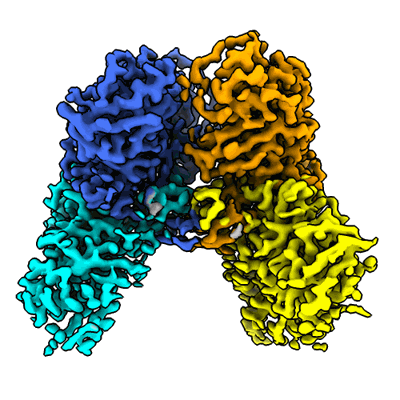
CryoEM structure of non-structural protein 1 tetramer from ZIKA virus
EMD-37423
Single-particle2.99 Å
 Deposition: 09/09/2023
Deposition: 09/09/2023Map released: 22/05/2024
Last modified: 09/10/2024
Sample Organism:
dengue virus type 4
Sample: ZIKA virus non-structural protein 1 tetramer
Fitted models: 8wbf (Avg. Q-score: 0.548)
Deposition Authors: Jiao HZ, Pan Q ,
Hu HL
,
Hu HL
Sample: ZIKA virus non-structural protein 1 tetramer
Fitted models: 8wbf (Avg. Q-score: 0.548)
Deposition Authors: Jiao HZ, Pan Q
 ,
Hu HL
,
Hu HL
The step-by-step assembly mechanism of secreted flavivirus NS1 tetramer and hexamer captured at atomic resolution.
Pan Q  ,
Jiao H
,
Jiao H  ,
Zhang W
,
Zhang W  ,
Chen Q
,
Chen Q  ,
Zhang G
,
Zhang G  ,
Yu J
,
Yu J  ,
Zhao W
,
Zhao W  ,
Hu H
,
Hu H 
(2024) Sci Adv , 10 , eadm8275 - eadm8275
 ,
Jiao H
,
Jiao H  ,
Zhang W
,
Zhang W  ,
Chen Q
,
Chen Q  ,
Zhang G
,
Zhang G  ,
Yu J
,
Yu J  ,
Zhao W
,
Zhao W  ,
Hu H
,
Hu H 
(2024) Sci Adv , 10 , eadm8275 - eadm8275
Abstract:
Flaviviruses encode a conserved, membrane-associated nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) with replication and immune evasion functions. The current knowledge of secreted NS1 (sNS1) oligomers is based on several low-resolution structures, thus hindering the development of drugs and vaccines against flaviviruses. Here, we revealed that recombinant sNS1 from flaviviruses exists in a dynamic equilibrium of dimer-tetramer-hexamer states. Two DENV4 hexameric NS1 structures and several tetrameric NS1 structures from multiple flaviviruses were solved at atomic resolution by cryo-EM. The stacking of the tetrameric NS1 and hexameric NS1 is facilitated by the hydrophobic β-roll and connector domains. Additionally, a triacylglycerol molecule located within the central cavity may play a role in stabilizing the hexamer. Based on differentiated interactions between the dimeric NS1, two distinct hexamer models (head-to-head and side-to-side hexamer) and the step-by-step assembly mechanisms of NS1 dimer into hexamer were proposed. We believe that our study sheds light on the understanding of the NS1 oligomerization and contributes to NS1-based therapies.
Flaviviruses encode a conserved, membrane-associated nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) with replication and immune evasion functions. The current knowledge of secreted NS1 (sNS1) oligomers is based on several low-resolution structures, thus hindering the development of drugs and vaccines against flaviviruses. Here, we revealed that recombinant sNS1 from flaviviruses exists in a dynamic equilibrium of dimer-tetramer-hexamer states. Two DENV4 hexameric NS1 structures and several tetrameric NS1 structures from multiple flaviviruses were solved at atomic resolution by cryo-EM. The stacking of the tetrameric NS1 and hexameric NS1 is facilitated by the hydrophobic β-roll and connector domains. Additionally, a triacylglycerol molecule located within the central cavity may play a role in stabilizing the hexamer. Based on differentiated interactions between the dimeric NS1, two distinct hexamer models (head-to-head and side-to-side hexamer) and the step-by-step assembly mechanisms of NS1 dimer into hexamer were proposed. We believe that our study sheds light on the understanding of the NS1 oligomerization and contributes to NS1-based therapies.
