EMD-26067
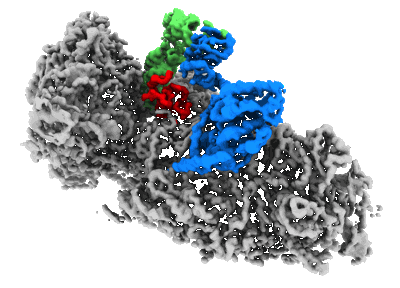
CryoEM structure of the human 40S small ribosomal subunit in complex with translation initiation factors eIF1A and eIF5B.
EMD-26067
Single-particle3.2 Å
 Deposition: 26/01/2022
Deposition: 26/01/2022Map released: 27/04/2022
Last modified: 12/06/2024
Sample Organism:
Homo sapiens
Sample: human 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with eIF1A and eIF5B
Fitted models: 7tql (Avg. Q-score: 0.412)
Deposition Authors: Lapointe CP ,
Grosely R
,
Grosely R
Sample: human 40S ribosomal subunit in complex with eIF1A and eIF5B
Fitted models: 7tql (Avg. Q-score: 0.412)
Deposition Authors: Lapointe CP
 ,
Grosely R
,
Grosely R
eIF5B and eIF1A reorient initiator tRNA to allow ribosomal subunit joining.
Lapointe CP  ,
Grosely R,
Sokabe M,
Alvarado C,
Wang J
,
Grosely R,
Sokabe M,
Alvarado C,
Wang J  ,
Montabana E,
Villa N,
Shin BS,
Dever TE
,
Montabana E,
Villa N,
Shin BS,
Dever TE  ,
Fraser CS,
Fernandez IS
,
Fraser CS,
Fernandez IS  ,
Puglisi JD
,
Puglisi JD 
(2022) Nature , 607 , 185 - 190
 ,
Grosely R,
Sokabe M,
Alvarado C,
Wang J
,
Grosely R,
Sokabe M,
Alvarado C,
Wang J  ,
Montabana E,
Villa N,
Shin BS,
Dever TE
,
Montabana E,
Villa N,
Shin BS,
Dever TE  ,
Fraser CS,
Fernandez IS
,
Fraser CS,
Fernandez IS  ,
Puglisi JD
,
Puglisi JD 
(2022) Nature , 607 , 185 - 190
Abstract:
Translation initiation defines the identity and quantity of a synthesized protein. The process is dysregulated in many human diseases1,2. A key commitment step is when the ribosomal subunits join at a translation start site on a messenger RNA to form a functional ribosome. Here, we combined single-molecule spectroscopy and structural methods using an in vitro reconstituted system to examine how the human ribosomal subunits join. Single-molecule fluorescence revealed when the universally conserved eukaryotic initiation factors eIF1A and eIF5B associate with and depart from initiation complexes. Guided by single-molecule dynamics, we visualized initiation complexes that contained both eIF1A and eIF5B using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The resulting structure revealed how eukaryote-specific contacts between the two proteins remodel the initiation complex to orient the initiator aminoacyl-tRNA in a conformation compatible with ribosomal subunit joining. Collectively, our findings provide a quantitative and architectural framework for the molecular choreography orchestrated by eIF1A and eIF5B during translation initiation in humans.
Translation initiation defines the identity and quantity of a synthesized protein. The process is dysregulated in many human diseases1,2. A key commitment step is when the ribosomal subunits join at a translation start site on a messenger RNA to form a functional ribosome. Here, we combined single-molecule spectroscopy and structural methods using an in vitro reconstituted system to examine how the human ribosomal subunits join. Single-molecule fluorescence revealed when the universally conserved eukaryotic initiation factors eIF1A and eIF5B associate with and depart from initiation complexes. Guided by single-molecule dynamics, we visualized initiation complexes that contained both eIF1A and eIF5B using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The resulting structure revealed how eukaryote-specific contacts between the two proteins remodel the initiation complex to orient the initiator aminoacyl-tRNA in a conformation compatible with ribosomal subunit joining. Collectively, our findings provide a quantitative and architectural framework for the molecular choreography orchestrated by eIF1A and eIF5B during translation initiation in humans.
