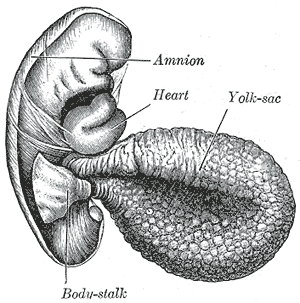
A sac-like expansion of the ventral wall of the intestine, narrowed into a yolk stalk near the body[Hyman's]. Membranous sac attached to an embryo, providing early nourishment in the form of yolk in bony fishes, sharks, reptiles, birds, and primitive mammals. It functions as the developmental circulatory system of the human embryo, before internal circulation begins. In the mouse, the yolk sac is the first site of blood formation, generating primitive macrophages and erythrocytes[WP].
class Information
consider splitting class
uberon
Yolk sac
- One of the extraembryonic fetal membranes that balloons out from the fetal midgut. [TFD][VHOG]
- the extraembryonic tissue membrane, formed from the visceral endoderm and the extraembryonic mesoderm, which is located ventral to the embryonic disc and is connected to the presumptive midgut of the embryo; the yolk that it contains is the site of embryonic hematopoiesis and vitelline circulation is involved in early embryonic circulation; it is the origin of the primordial germ cells
Structures homologous to the four extraembryonic membranes of reptiles and birds appear in mammals: amnion, chorion, yolk sac, and allantois.[well established][VHOG]
In therians, a structure homologous to the yolk sac is is present, but contains no yolk platelets. Instead it is filled with fluid [ISBN:0073040584 (Vertebrates, Kardong)]
class Relations
- extraembryonic tissueuberon
- extraembryonic membraneuberon
- epithelial sacuberon
- has developmental contribution fromrosomeendodermuberon
- has developmental contribution fromrosomesplanchnic layer of lateral plate mesodermuberon
- has developmental contribution fromrosomeendodermuberon
- has developmental contribution fromrosomesplanchnic layer of lateral plate mesodermuberon