Formate C-acetyltransferase
Pyruvate formate-lyase catlayses the CoA-dependent, reversible cleavage of pyruvate into acetyal-CoA and formation. This enzyme is required for anaerobic glucose fermentation, utilised by various species of microorganism.
The resting state of this enzyme has a glycyl radical, this radical is created by the action of a radical SAM superfamily activating protein (PFL-AE) and is quenched in an oxygenated atmosphere leading to enzyme inactivation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P09373
 (2.3.1.54)
(2.3.1.54)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2pfl
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF PFL FROM E.COLI
(2.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.70.20
 (see all for 2pfl)
(see all for 2pfl)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.54)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The resting state of the enzyme involves the glycyl radical, as determined by spectroscopic studies. The backbone radical is kinetically stable, but extremely susceptible to reactions with molecular oxygen. This is thought to be involved in regulating the enzymes function within the anaerobic metabolism, and the regulation of the pathway more generally.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2pfl) | ||
| Cys419 | Cys418A | Forms a covalent intermediate with the substrate, | hydrogen radical acceptor, hydrogen radical donor, covalently attached, leaving group (radical), hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, radical combinant |
| Cys420 | Cys419A | Acts as a hydrogen atom relay. | hydrogen radical acceptor, hydrogen radical donor, hydrogen radical relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp334 | Trp333A | Stabilises the radical species formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, radical stabiliser |
| Gly735 (main) | Gly734A (main) | In the ground state of the enzyme this is a glycyl radical. It initiates the reaction by abstracting a hydrogen atom from Cys419. | hydrogen radical acceptor, hydrogen radical donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, hydrogen relay, bimolecular homolytic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, unimolecular homolytic elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, bimolecular homolytic substitution, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Himo F et al. (1998), J Am Chem Soc, 120, 11449-11455. Catalytic Mechanism of Pyruvate Formate-Lyase (PFL). A Theoretical Study. DOI:10.1021/ja9820947.
- Lucas Mde F et al. (2005), J Am Chem Soc, 127, 6902-6909. Theoretical Study of the Suicide Inhibition Mechanism of the Enzyme Pyruvate Formate Lyase by Methacrylate. DOI:10.1021/ja047699j. PMID:15869314.
- Guo J et al. (2004), J Phys Chem B, 108, 15347-15354. Catalytic Mechanism of Pyruvate−Formate Lyase Revisited. DOI:10.1021/jp0478054.
- Lucas MdF et al. (2003), J Phys Chem B, 107, 5751-5757. Pyruvate Formate Lyase: A New Perspective. DOI:10.1021/jp0223096.
- Zhang W et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 4123-4130. Inactivation of Pyruvate Formate-Lyase by Dioxygen: Defining the Mechanistic Interplay of Glycine 734 and Cysteine 419 by Rapid Freeze-Quench EPR†. DOI:10.1021/bi002589k.
- Plaga W et al. (2000), FEBS Lett, 466, 45-48. Modification of Cys-418 of pyruvate formate-lyase by methacrylic acid, based on its radical mechanism. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01752-4. PMID:10648809.
- Leppänen VM et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 733-744. Pyruvate formate lyase is structurally homologous to type I ribonucleotide reductase. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80098-7. PMID:10425676.
- Becker A et al. (1999), Nat Struct Biol, 6, 969-975. Structure and mechanism of the glycyl radical enzyme pyruvate formate-lyase. DOI:10.1038/13341. PMID:10504733.
- Eklund H et al. (1999), Structure, 7, R257-R262. Glycyl radical enzymes: a conservative structural basis for radicals. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)80019-2. PMID:10574800.

Step 1. The glycyl radical abstracts a hydrogen from Cys419, which in turn abstracts a hydrogen from Cys418.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen radical relay |
| Trp333A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys418A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys419A | hydrogen radical donor, hydrogen radical acceptor |
| Cys418A | hydrogen radical donor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, hydrogen relay
Step 2. Cys418 initiates a homolytic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the pyruvate substrate in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp333A | radical stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | radical combinant |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 3. The newly formed radical collapses, eliminating a carbon dioxyl radical.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp333A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, ingold: unimolecular homolytic elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 4. The carbon dioxyl radical abstracts a hydrogen from Cys419 forming the formate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp333A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys419A | hydrogen radical donor |
Chemical Components
hydrogen transfer, radical propagation, overall product formed, intermediate terminatedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp333A | radical stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys419A | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 6. CoA initiates a homolytic attack upon the carbonyl carbon of the acyl-Cys418 in a substitution reaction, eliminating Cys418, which abstracts a hydrogen from Cys419.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Trp333A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | leaving group (radical) |
| Cys419A | hydrogen radical donor |
| Cys418A | hydrogen radical acceptor |
Chemical Components
radical propagation, hydrogen transfer, ingold: bimolecular homolytic substitution, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated
Step 7. Cys419 abstracts a hydrogen from Gly734, regenerating the glycyl radical ground state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys419A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Trp333A | radical stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys418A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly734A (main) | hydrogen radical donor |
| Cys419A | hydrogen radical acceptor |

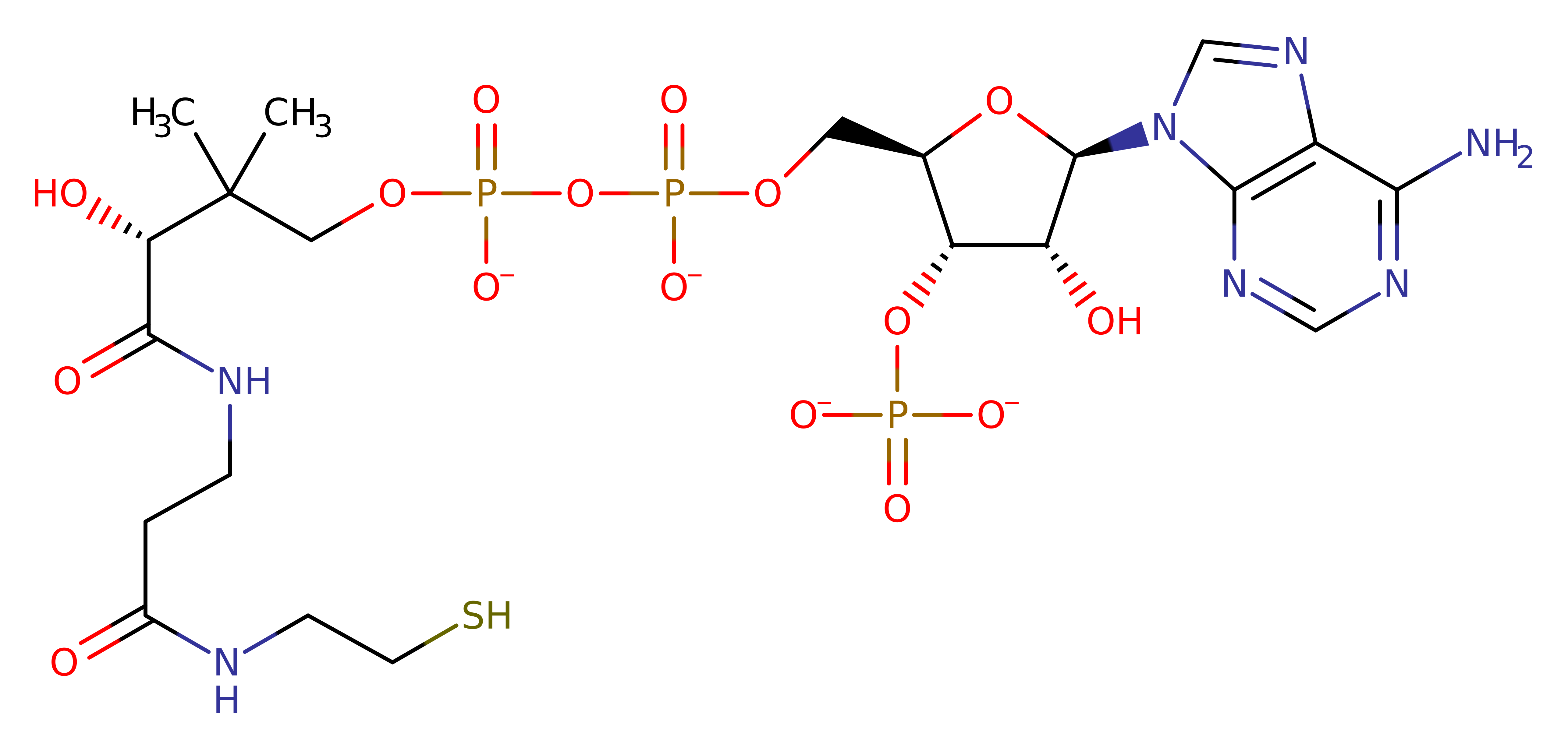



 Download:
Download: