HIV-1 reverse transcriptase
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) is a component of gag-pol polyprotein encoded by the human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) genome. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase contains both DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H (RNase H) activities to convert the viral genomic RNA to double-stranded DNA, which is then integrated into the host genome and replicated along with the infected host cells. Understanding the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase catalytic mechanism is key for discovery of potent drugs and development of more effective, less toxic drugs and multi-drug combinations.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P03366
 (2.7.7.-, 2.7.7.7, 2.7.7.49, 3.1.-.-, 3.1.13.2, 3.1.26.13, 3.4.23.16)
(2.7.7.-, 2.7.7.7, 2.7.7.49, 3.1.-.-, 3.1.13.2, 3.1.26.13, 3.4.23.16)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 BH10 (Virus)

- PDB
-
1rtd
- STRUCTURE OF A CATALYTIC COMPLEX OF HIV-1 REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE: IMPLICATIONS FOR NUCLEOSIDE ANALOG DRUG RESISTANCE
(3.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.70.270
 (see all for 1rtd)
(see all for 1rtd)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.7.49)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase mechanism consists of two main steps: deprotonation of the 3'-primer terminus by Asp185 followed by nucleophilic attack of the 3'OH towards the alpha-phosphate of the incoming deoxy-nucleotide (dNTP). The pyrophosphate leaving group is then protonated by Lys220.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1rtd) | ||
| Asp784 | Asp185A(E) | Asp185 is responsible for the deprotonation of primer's 3'OH group | metal ligand, proton acceptor |
| Asp709 | Asp110A(E) | Asp110 coordinates the Mg2+ metal ions | metal ligand |
| Asp785 | Asp186A(E) | Asp186 coordinates the Mg2+ metal ions | metal ligand |
| Val710 (main-C) | Val111A(E) (main-C) | Val111 coordinates the Mg2+ metal ions | metal ligand |
| Lys819 | Lys220A(E) | Lys220 acts as a general acid for the protonation of pyrophosphate leaving group | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, coordination to a metal ion, overall product formed, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionReferences
- Rungrotmongkol T et al. (2014), Medchemcomm, 5, 593-. QM/MM simulations indicate that Asp185 is the likely catalytic base in the enzymatic reaction of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. DOI:10.1039/c3md00319a.
- Castro C et al. (2009), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 16, 212-218. Nucleic acid polymerases use a general acid for nucleotidyl transfer. DOI:10.1038/nsmb.1540. PMID:19151724.
- Castro C et al. (2007), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 104, 4267-4272. Two proton transfers in the transition state for nucleotidyl transfer catalyzed by RNA- and DNA-dependent RNA and DNA polymerases. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0608952104. PMID:17360513.
- Rungrotmongkol T et al. (2007), J Mol Graph Model, 26, 1-13. Active site dynamics and combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) modelling of a HIV-1 reverse transcriptase/DNA/dTTP complex. DOI:10.1016/j.jmgm.2006.09.004. PMID:17046299.
- Huang H et al. (1998), Science, 282, 1669-1675. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. DOI:10.1126/science.282.5394.1669. PMID:9831551.

Step 1. Asp185 acts a general base to deprotonate the 3'-OH primer terminus. Active site residues serve as ligand to coordinate the metal ions Mg2+.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp185A(E) | proton acceptor, metal ligand |
| Asp110A(E) | metal ligand |
| Asp186A(E) | metal ligand |
| Val111A(E) (main-C) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, coordination to a metal ion
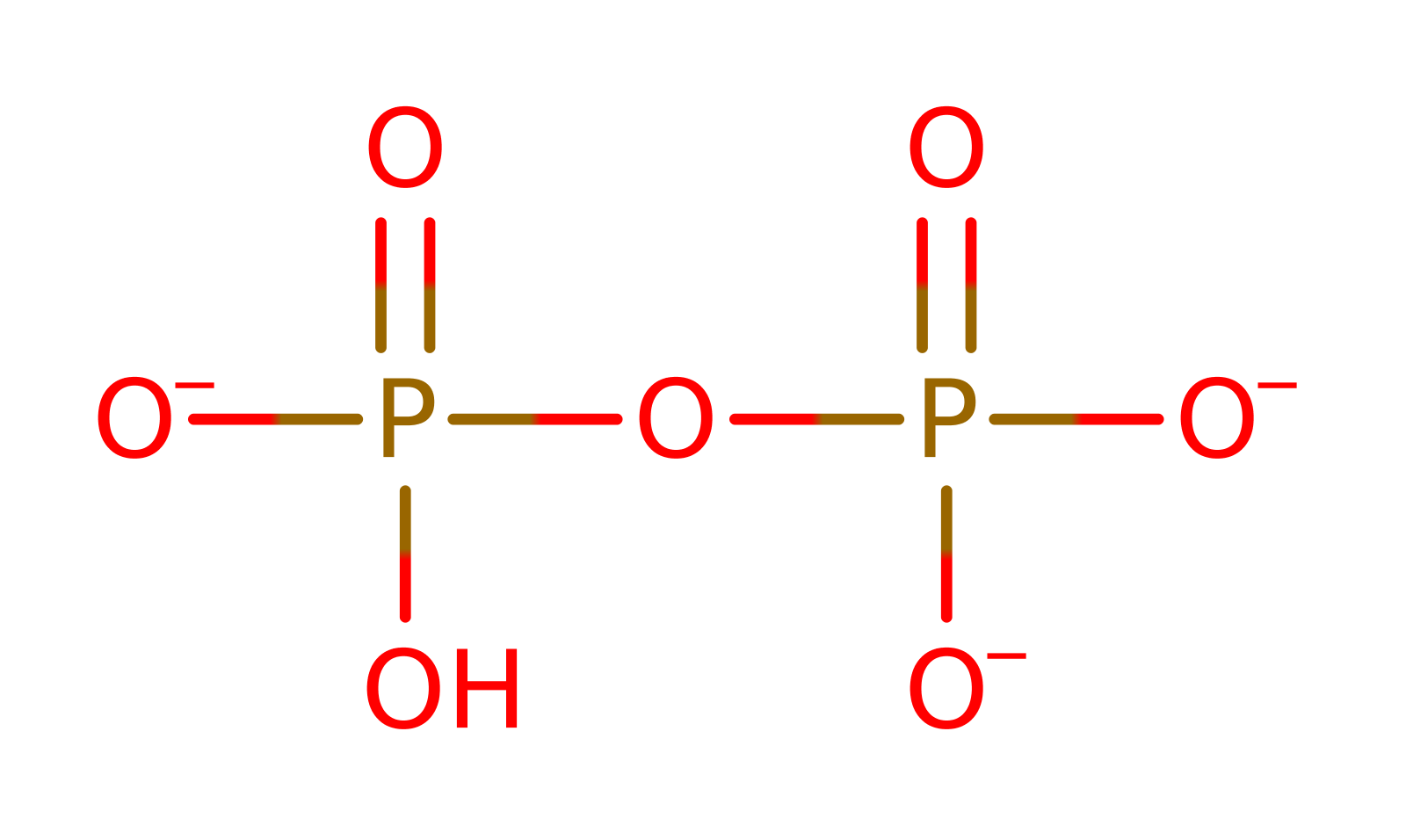
Step 2. Resulting hydroxide 3'-O performs nucleophilic attack towards the alpha-phosphate, leading to polymerization of nucleotides and hydrolysis of pyrophosphate. The pyrophosphate leaving group is protonated by Lys220.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp185A(E) | metal ligand |
| Asp110A(E) | metal ligand |
| Asp186A(E) | metal ligand |
| Val111A(E) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Lys220A(E) | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: