Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase
Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) is an enzyme that catalyses the synthesis of epinephrine from norepinephrine (NE) utilizing the cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) as a methyl donor. Epinephrine is a naturally occurring hormone that increases cardiac output and raises glucose levels in the blood.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P11086
 (2.1.1.28)
(2.1.1.28)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1hnn
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN PNMT COMPLEXED WITH SK&F 29661 AND ADOHCY(SAH)
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.150
 (see all for 1hnn)
(see all for 1hnn)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.1.28)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
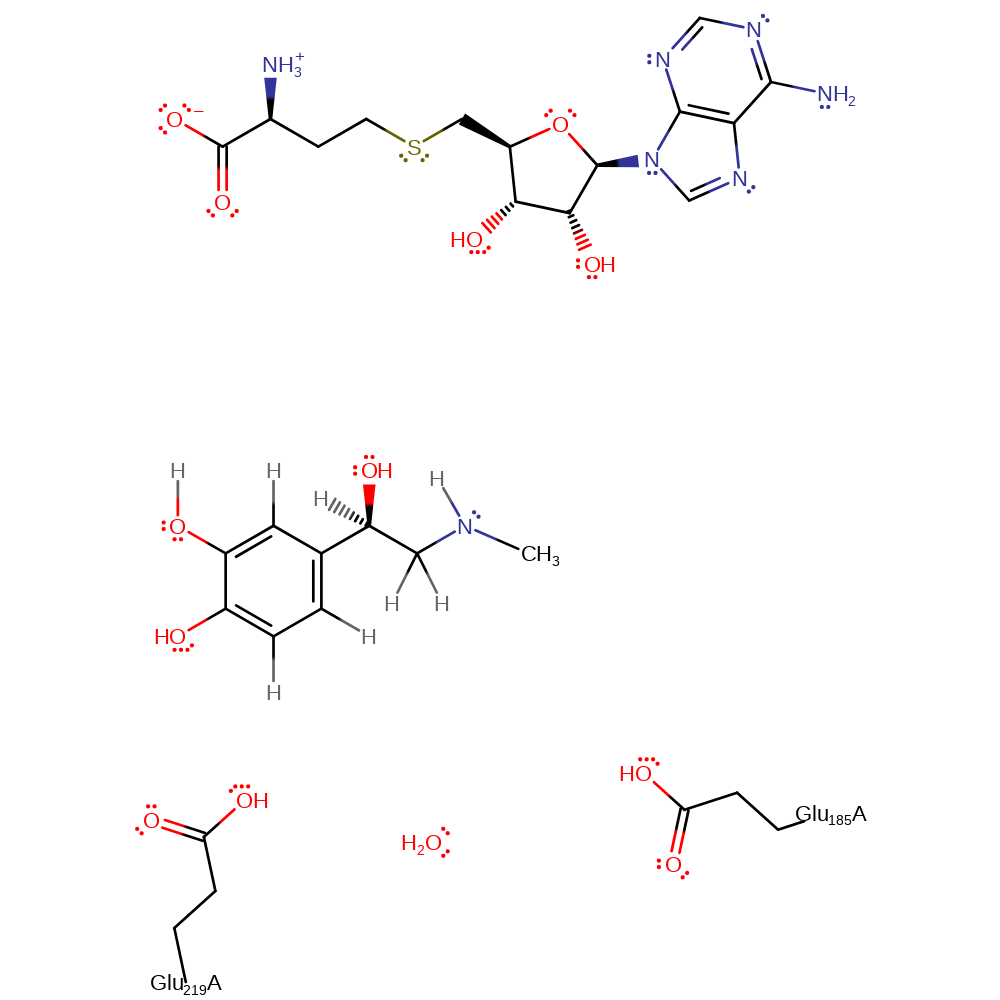
Phenyl ethanolamine N-methyltransferase catalyses the synthesis of epinephrine. This reaction has three major steps: The first step is the deprotonation of protonation of protonated norepinephrine, the second and the rate limiting step is the methyl transferring step and the last step is the deprotonation of the methylated norepinephrine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hnn) | ||
| Glu219 | Glu219A | Acts as a nucleophile and deprotonates AdoHcy in the last step of catalysis. | proton acceptor |
| Glu185 | Glu185A | Acts as a nucleophile and deprotonates Noradrenaline in the first step of catalysis. | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, rate-determining step, overall reactant usedReferences
- Hou QQ et al. (2012), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1824, 533-541. QM/MM studies on the catalytic mechanism of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.01.017. PMID:22326747.
- Mahmoodi N et al. (2020), J Am Chem Soc, 142, 14222-14233. Transition-State Analogues of Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/jacs.0c05446. PMID:32702980.

Step 1. The amine of Noradrenaline is deprotonated by Glu185 via a bridging water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu185A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. SN2 nucleophilic attack from the amine to AdoHcyn. This causes transfer of methyl group from AdoHcyn to NE.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, rate-determining stepCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu219A | proton acceptor |






 Download:
Download: