Bis(5'-adenosyl)-triphosphatase
The FHIT protein is a diadenosine P1, P3-triphosphate (ApppA) hydrolase that cleaves diadenosine P1, P3-triphosphate to yield AMP and ADP which is found in animals and fungi. In humans the FHIT gene is found at 3p14.2 and is thought to act as a tumour suppressor gene involved in many human cancers. It belongs to one branch of the Histidine triad (HIT) superfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins which have a conserved His-X-His-X-His-X-X (where X is a hydrophobic amino acid) motif. This was originally thought to be a zinc-ion binding site but is now believed to be the alpha-phosphate binding site [PMID:9323207]. The other branch of this superfamily consists of the HINT (histidine triad nucleotide-binding) proteins, the proposed ancestor of FHIT, galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase, and other nucleotide binding proteins [PMID:9323207].
Dinocleoside polyphoshate hydrolases require millimolar Mn(II) Mg(II) or Ca(II) for optimum activity and are inhibited by Ni(II) Zn(II) and Cd(II).
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P49789
 (3.6.1.29)
(3.6.1.29)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
5fit
- FHIT-SUBSTRATE ANALOG
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.428.10
 (see all for 5fit)
(see all for 5fit)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.6.1.29)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A catalytic mechanism for FHIT proteins (and possibly other members of the HIT superfamily) has been proposed [PMID:9164465]. His96 is activated as a nucleophile by His94 so that the ND1 atom can attack the alpha phosphate group of the substrate as it enters the binding pocket. This causes the inversion of the alpha phosphate position to form a trigonal bipyramidal pentacovalent transition state from which the products are formed either by hydrolysis or transfer of the phosphoramidate bond.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (5fit) | ||
| His94 (main-C) | His94A (main-C) | Activates His96 to act as a nucleophile. | increase electrophilicity, increase nucleophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His98 | His98A | Plays an important role in the hydrolysis of the AMP-Im intermediate. This step requires a proton transfer to the departing imidazole, and His98 is in position to transfer a proton to the leaving group. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Gln83 | Gln83A | Acts to stabilise the negatively charged transition state. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His96 | His96A | Acts as the catalytic nucleophile. | nucleophile, nucleofuge, metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, hydrolysisReferences
- Huang K et al. (2005), European J Org Chem, 2005, 5198-5206. pH-Dependence in the Hydrolytic Action of the Human Fragile Histidine Triad. DOI:10.1002/ejoc.200500499.
- Zhou X et al. (2013), Biochemistry, 52, 3588-3600. Kinetic Mechanism of Human Histidine Triad Nucleotide Binding Protein 1. DOI:10.1021/bi301616c. PMID:23614568.
- Guranowski A et al. (2008), FEBS Lett, 582, 3152-3158. Fhit proteins can also recognize substrates other than dinucleoside polyphosphates. DOI:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.07.060. PMID:18694747.
- Huang K et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 7637-7642. The Mechanism of Action of the Fragile Histidine Triad, Fhit: Isolation of a Covalent Adenylyl Enzyme and Chemical Rescue of H96G-Fhit†. DOI:10.1021/bi049762n. PMID:15182206.
- Trapasso F et al. (2003), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 100, 1592-1597. Designed FHIT alleles establish that Fhit-induced apoptosis in cancer cells is limited by substrate binding. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0437915100. PMID:12574506.
- Brenner C et al. (1997), Nat Struct Biol, 4, 231-238. Crystal structures of HINT demonstrate that histidine triad proteins are GalT-related nucleotide-binding proteins. DOI:10.1038/nsb0397-231. PMID:9164465.
- Lima CD et al. (1997), Science, 278, 286-290. Structure-Based Analysis of Catalysis and Substrate Definition in the HIT Protein Family. DOI:10.1126/science.278.5336.286. PMID:9323207.

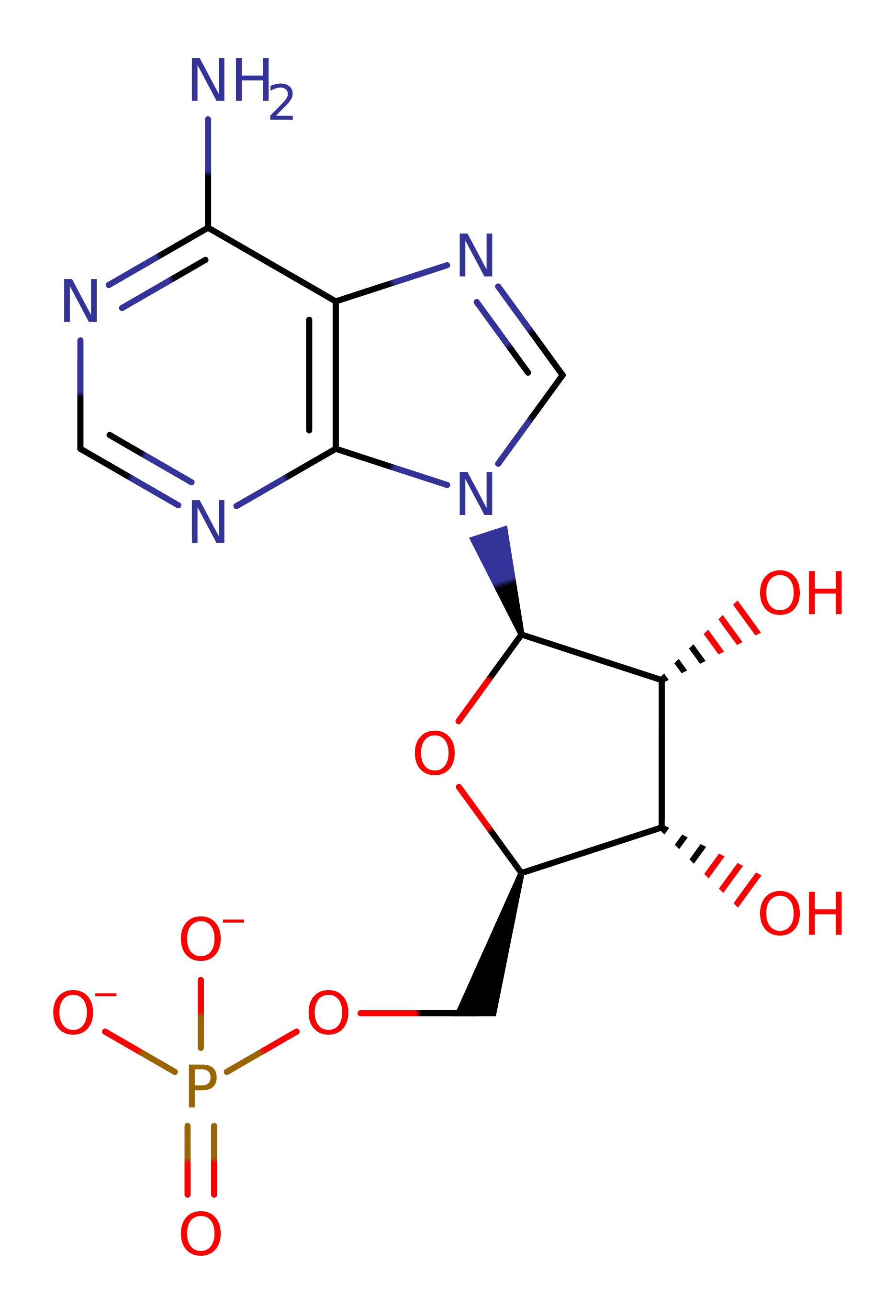
Step 1. His96 attacks the alpha phosphate of the substrate in a nucleophilic attack which proceeds via a trigonal bipimrimidal pentavalent transition state, which inverts the position of the alpha phosphate, and results in the elimination of ADP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His98A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His94A (main-C) | increase nucleophilicity |
| His98A | proton donor |
| His96A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer
Step 2. His98 deprotonates water, which attacks the phosphate of the covalently bound AMP, eliminating His96 and proceeding via a pentavalent transition state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His98A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His96A | metal ligand |
| His94A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| His98A | proton acceptor |
| His96A | nucleofuge |




 Download:
Download: