Camphor 5-monooxygenase
Camphor 5-monooxygenase is involved in the pathway of (R)-camphor degradation, which is part of terpene metabolism. It is a B-class cytochrome P450, one of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of proteins.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00183
 (1.14.15.1)
(1.14.15.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas putida (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1yrc
- X-ray Crystal Structure of hydrogenated Cytochrome P450cam
(1.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.630.10
 (see all for 1yrc)
(see all for 1yrc)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (1), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.14.15.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Putidaredoxin donates a single electron to the Fe(III) centre of the heme cofactor, forming Fe(II), which in turn donates the electron to the dioxygen substrate .Putidaredoxin then donates a second electron to the bound peroxo moiety, which initiates a proton transfer relay through Thr252, water, Asp251, Arg186 to bulk solvent. Both Heme and Iron donate single electrons to the bound peroxo moiety, which eliminates water and initiates a proton transfer relay through the same chain as used previously. The iron-bound oxy group abstracts a hydrogen from the camphor substrate. In the final step, the camphor radical initiates a homolytic substitution, hydroxylating the intermediate to form 5-hydroxycamphor. The iron centre accepts a single electron and water displaces the product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1yrc) | ||
| Cys358 | Cys357A | One of the axial ligands of the heme iron. Antibonding interactions of the iron with the axial ligands (Cys357 and a water molecule) stabilise the doublet with respect to the quartet and sextet states. | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu359 (main-N), Gly360 (main-N) | Leu358A (main-N), Gly359A (main-N) | The stabilisation of the high-spin state could be explained by electrostatic interactions of the protein with the cysteine sulfur decreasing the spin density in the sulfur atom for all the spin states. Such effect is caused by hydrogen bonds from Gly359 and Leu358 to the sulfur. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp252, Thr253, Arg187 | Asp251A, Thr252A, Arg186A | Form a proton relay chain from the active site to bulk solvent. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall reactant used, cofactor used, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation, bimolecular homolytic addition, redox reaction, radical formation, coordination to a metal ion, radical termination, proton transfer, proton relay, electron relay, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, hydrogen transfer, bimolecular homolytic substitution, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Schlichting I et al. (2000), Science, 287, 1615-1622. The Catalytic Pathway of Cytochrome P450cam at Atomic Resolution. DOI:10.1126/science.287.5458.1615. PMID:10698731.
- Poulos TL (2014), Chem Rev, 114, 3919-3962. Heme enzyme structure and function. DOI:10.1021/cr400415k. PMID:24400737.
- Hiruma Y et al. (2013), J Mol Biol, 425, 4353-4365. The structure of the cytochrome p450cam-putidaredoxin complex determined by paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy and crystallography. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2013.07.006. PMID:23856620.
- Stoll S et al. (2012), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 109, 12888-12893. Double electron-electron resonance shows cytochrome P450cam undergoes a conformational change in solution upon binding substrate. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1207123109. PMID:22826259.
- Galinato MG et al. (2011), Biochemistry, 50, 1053-1069. Elucidating the role of the proximal cysteine hydrogen-bonding network in ferric cytochrome P450cam and corresponding mutants using magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy. DOI:10.1021/bi101911y. PMID:21158478.
- Hayashi T et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 1398-1400. A role of the heme-7-propionate side chain in cytochrome P450cam as a gate for regulating the access of water molecules to the substrate-binding site. DOI:10.1021/ja807420k. PMID:19133773.
- Sakurai K et al. (2009), Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun, 65, 80-83. Substrate binding induces structural changes in cytochrome P450cam. DOI:10.1107/S1744309108044114. PMID:19193991.
- Aldag C et al. (2009), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 106, 5481-5486. Probing the role of the proximal heme ligand in cytochrome P450cam by recombinant incorporation of selenocysteine. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0810503106. PMID:19293375.
- Harada K et al. (2008), J Am Chem Soc, 130, 432-433. Evaluation of the functional role of the heme-6-propionate side chain in cytochrome P450cam. DOI:10.1021/ja077902l. PMID:18088124.
- Zheng J et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 13204-13215. QM/MM Study of Mechanisms for Compound I Formation in the Catalytic Cycle of Cytochrome P450cam. DOI:10.1021/ja063439l. PMID:17017800.
- Spolitak T et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 20300-20309. Reaction of ferric cytochrome P450cam with peracids: kinetic characterization of intermediates on the reaction pathway. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M501761200. PMID:15781454.
- Davydov R et al. (2005), J Am Chem Soc, 127, 1403-1413. Substrate modulation of the properties and reactivity of the oxy-ferrous and hydroperoxo-ferric intermediates of cytochrome P450cam as shown by cryoreduction-EPR/ENDOR spectroscopy. DOI:10.1021/ja045351i. PMID:15686372.
- Nagano S et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 31659-31663. Crystallographic study on the dioxygen complex of wild-type and mutant cytochrome P450cam. Implications for the dioxygen activation mechanism. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M505261200. PMID:15994329.
- Guallar V et al. (2004), J Am Chem Soc, 126, 8501-8508. Cytochrome P450CAM Enzymatic Catalysis Cycle: A Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Study. DOI:10.1021/ja036123b. PMID:15238007.
- Pylypenko O et al. (2004), Annu Rev Biochem, 73, 991-1018. Structural aspects of ligand binding to and electron transfer in bacterial and fungal P450s. DOI:10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073711. PMID:15189165.
- Hays AM et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 344, 455-469. Conformational states of cytochrome P450cam revealed by trapping of synthetic molecular wires. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.046. PMID:15522298.
- Hishiki T et al. (2000), J Biochem, 128, 965-974. X-ray crystal structure and catalytic properties of Thr252Ile mutant of cytochrome P450cam: roles of Thr252 and water in the active center. PMID:11098139.
- Vidakovic M et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 9211-9219. Understanding the role of the essential Asp251 in cytochrome p450cam using site-directed mutagenesis, crystallography, and kinetic solvent isotope effect. DOI:10.1021/bi980189f. PMID:9649301.
- Schlichting I et al. (1997), FEBS Lett, 415, 253-257. Crystal structure of cytochrome P-450cam complexed with the (1S)-camphor enantiomer. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01135-6. PMID:9357977.

Step 1. When camphor binds, it displaces the axial water ligand and an inversion of the spin state is observed. Putidaredoxin donates a single electron to the Fe(III) centre of the heme cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys357A | metal ligand |
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp251A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr252A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys357A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu358A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly359A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), overall reactant used, cofactor used, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation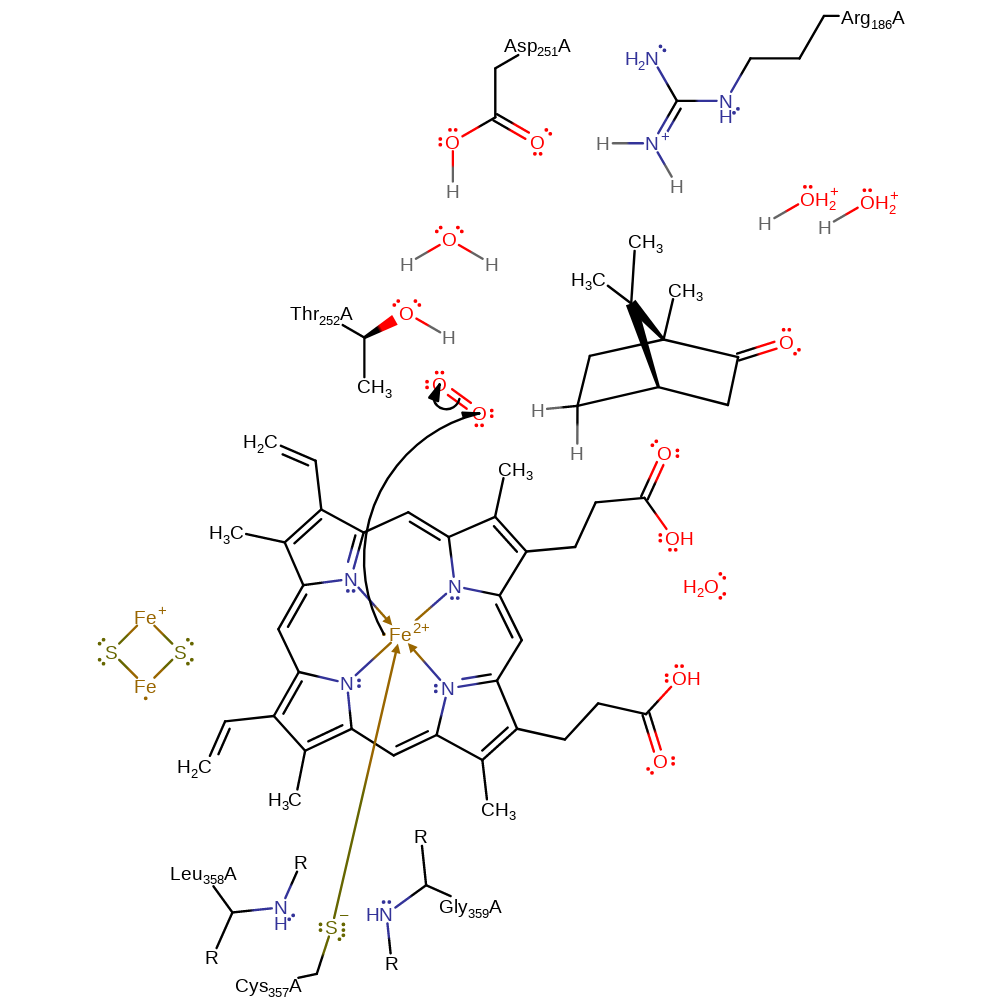
Step 2. In a homolytic addition, Fe(II) donates a single electron to the dioxygen substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys357A | metal ligand |
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp251A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr252A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys357A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu358A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly359A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular homolytic addition, redox reaction, radical formation, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation
Step 3. Putidaredoxin donates a second electron to the bound peroxo moiety, which initiates a proton transfer relay through Thr252, water, Asp251, Arg186 to bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys357A | metal ligand |
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Asp251A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Thr252A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Cys357A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu358A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly359A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp251A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Arg186A | proton acceptor |
| Thr252A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Arg186A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, radical termination, proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay, electron relay
Step 4. Iron donates a single electron to the bound peroxo moiety, which eliminates water and initiates a proton transfer relay through Thr252, water, Asp251, Arg186 to bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Asp251A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Thr252A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Cys357A | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu358A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly359A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp251A | proton donor |
| Arg186A | proton acceptor |
| Thr252A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Asp251A | proton acceptor |
| Arg186A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, electron transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay
Step 5. The oxyferryl intermediate (starting state) can be envisioned as the product of an intramolecular single-electron transfer reaction from the porphyrin ligand to a putative Fe(V) centre, to give Fe(IV) moiety and a radicaloid porphyrin ligand [PMID:10698731]. The iron-bound oxy group abstracts a hydrogen from the camphor substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys357A | metal ligand |
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp251A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr252A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys357A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu358A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly359A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
radical formation, hydrogen transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation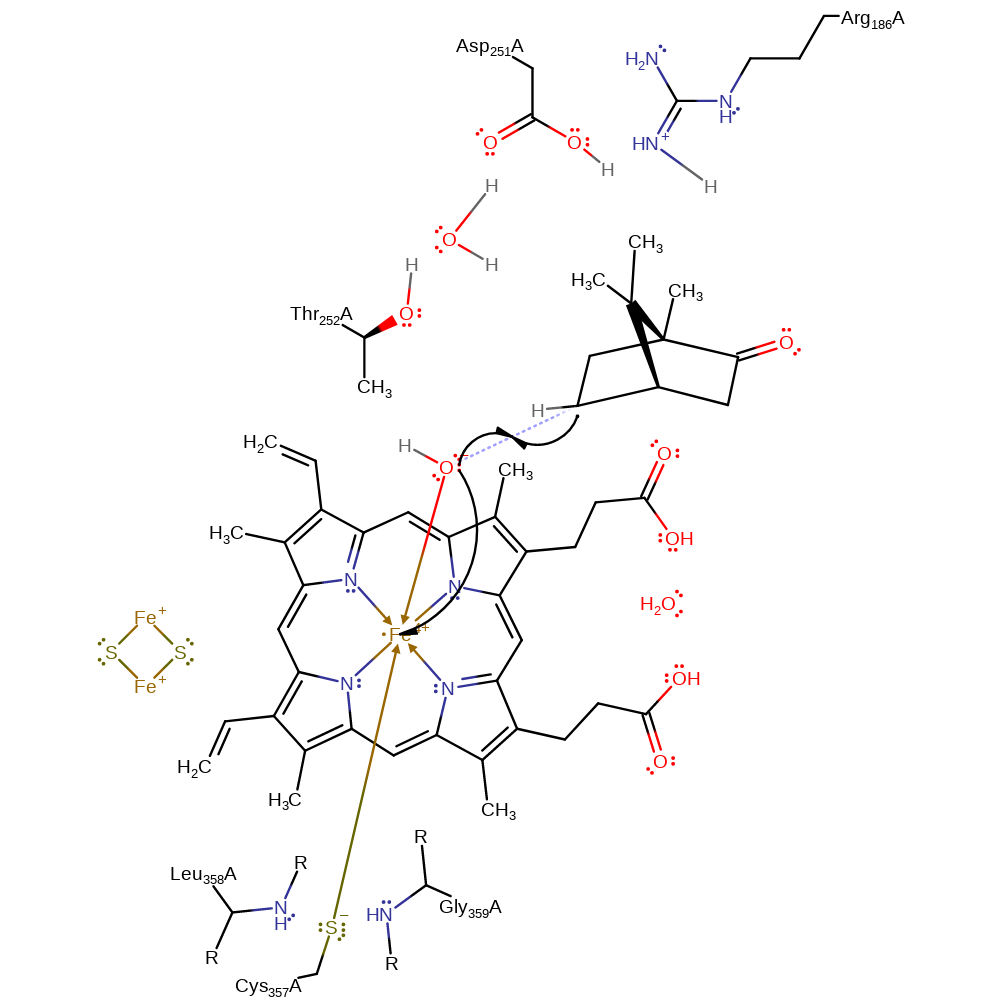
Step 6. The camphor radical initiates a homolytic substitution, hydroxylating the intermediate to form 5-hydroxycamphor. The iron centre accepts a single electron and water displaces the product
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys357A | metal ligand |
| Arg186A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp251A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr252A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys357A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu358A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly359A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |






 Download:
Download: