Isopenicillin-N synthase
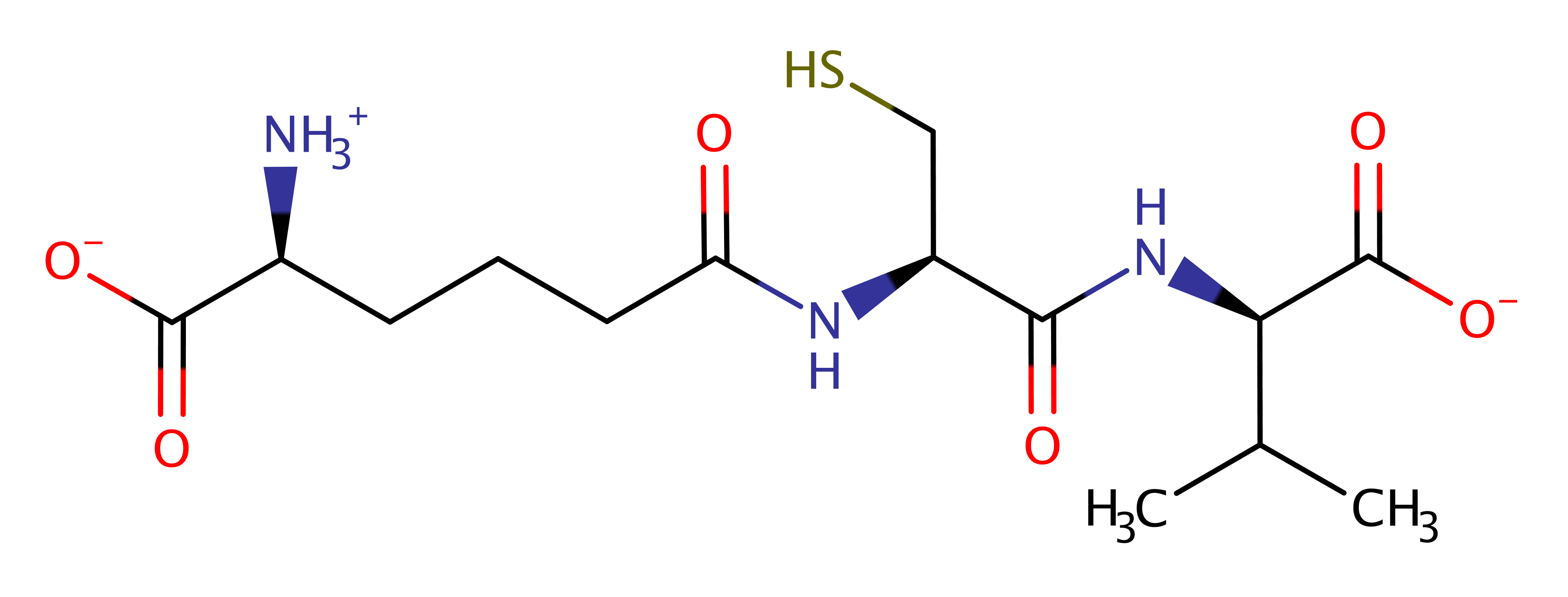
Isopenicillin N synthase(IPNS), a non-haem iron-dependent oxidase, catalyses the reaction of delta-(L-aminoadipoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (ACV) and dioxygen to form isopenicillin N (IPN) and 2 water molecules. IPN is the precursor of the antibiotics, penicillins and cephalosporins.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P05326
 (1.21.3.1)
(1.21.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Aspergillus nidulans FGSC A4 (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1odm
- ISOPENICILLIN N SYNTHASE FROM ASPERGILLUS NIDULANS (ANAEROBIC AC-VINYLGLYCINE FE COMPLEX)
(1.15 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.60.120.330
 (see all for 1odm)
(see all for 1odm)
- Cofactors
- Iron(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
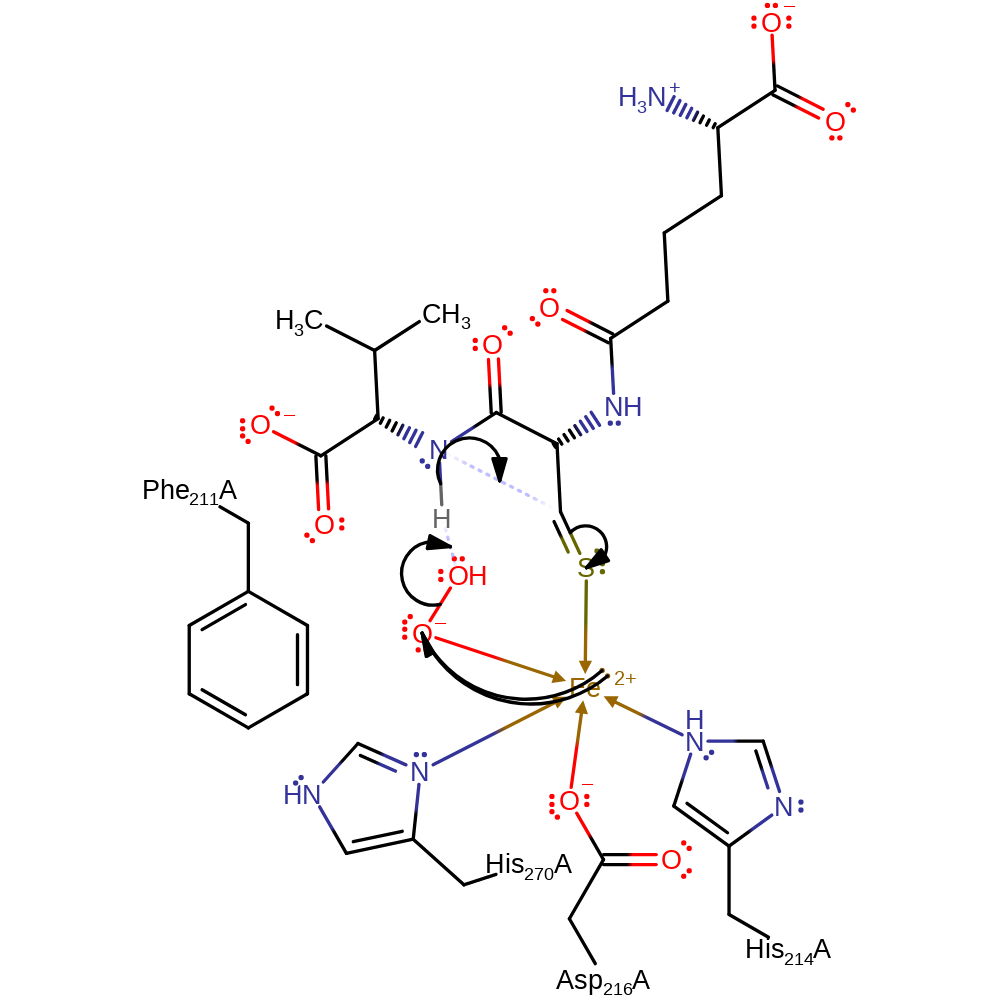
The thio group of ACV cysteinyl residue ligands to the iron and results in a reduction of the Fe(II)/Fe(III) redox potential, allowing dioxygen to bind at the site trans to Asp126, thereby initiating the reaction cycle. With a nonlinear, haemoglobin-like binding of dioxygen, a superoxide is formed, juxtaposed to the pro-3-S hydrogen of the ACV cysteinyl residue, and it abstracts this hydrogen atom to form the thioaldehyde intermediate. Subsequent cleavage of the hydroperoxide along with the deprotonation of the adjacent Fe coordinated water results in the release of a water molecule. This water molecule is then deprotonated by the hydroxide it just deprotonated which enables it to accept a proton from the amide of the intermediate which results in the closure of the beta-lactam ring. After that a homolytic addition occurs between the Fe coordinated oxygen and the tertiary carbon on the substrate which generates a radical intermediate. This radical intermediate can then initiate the thiazoladine closure after the homolysis of the S-Fe bond.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1odm) | ||
| His270, His214, Asp216 | His270A, His214A, Asp216A | Forms Fe binding site | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation, cofactor used, redox reaction, radical formation, bimolecular homolytic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, hydride transfer, coordination, electron transfer, radical termination, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, cyclisation, homolysis, unimolecular homolytic elimination, colligation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formedReferences
- McNeill LA et al. (2017), Chemistry, 23, 12815-12824. Terminally Truncated Isopenicillin N Synthase Generates a Dithioester Product: Evidence for a Thioaldehyde Intermediate during Catalysis and a New Mode of Reaction for Non-Heme Iron Oxidases. DOI:10.1002/chem.201701592. PMID:28703303.
- Lundberg M et al. (2007), J Phys Chem B, 111, 9380-9389. Protein environment facilitates O2 binding in non-heme iron enzyme. An insight from ONIOM calculations on isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS). DOI:10.1021/jp071878g. PMID:17637052.










 Download:
Download: 




 Download:
Download: