Beta-lactamase (Class B1)
Beta-lactamase is a key enzyme in antibiotic resistance, catalysing the cleavage of the essential beta-lactam ring structure in penicillin and cephalosporinase type antibiotics. Substrate specificity varies considerably within the beta-lactamases, with some enzymes preferring penicillins and some cephalosporins.
Alongside the class B beta-lactamases, described here, there also exist three other classes of beta-lactam cleaving enzymes (A,C and D). These groups of enzymes use a serine nucleophilic mechanism, while class B uses a mono/dimetallic zinc mechanism. This entry describes the dimetallic mechanism. There is considerable variety in substrate specificity between the classes, although class C enzymes tend to have a high cephalosporinase activity
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P25910
 (3.5.2.6)
(3.5.2.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacteroides fragilis (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1znb
- METALLO-BETA-LACTAMASE
(1.85 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.15.10
 (see all for 1znb)
(see all for 1znb)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (2), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.2.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A mechanism has been proposed by Fabiane et al (PMID:9730812). The beta-lactam carbonyl interacts with zinc1 polarising the bond and enhancing its susceptibility to nucleophilic attack. A zinc1 associated water/hydroxide is the nucleophile which attacks the beta-lactam carbonyl carbon. The substrate carboxylate moiety interacts with zinc2 and lysine 184. Asparagine 193 and zinc1 stabilise the oxyanion. An incoming water molecule is activated by the zinc ions and deprontonated by the intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1znb) | ||
| Asn193 | Asn193(176)A | Stabilises the anionic tetrahedral intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp103, Cys181, His99, His101, His223, His162 | Asp103(86)A, Cys181(164)A, His99(82)A, His101(84)A, His223(206)A, His162(145)A | Binds one of the Zn(II) ions. | metal ligand |
| Lys184 | Lys184(167)A | Binds the carboxylate group of the substrate, helping to stabilise the intermediate and correctly position the substrate. | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, decyclisation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, rate-determining stepReferences
- Fabiane SM et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 12404-12411. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent β-Lactamase fromBacillus cereusat 1.9 Å Resolution: Binuclear Active Site with Features of a Mononuclear Enzyme†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi980506i. PMID:9730812.
- Spencer J et al. (2005), J Am Chem Soc, 127, 14439-14444. Antibiotic Recognition by Binuclear Metallo-β-Lactamases Revealed by X-ray Crystallography#. DOI:10.1021/ja0536062. PMID:16218639.
- Wang Z et al. (1999), Curr Opin Chem Biol, 3, 614-622. Metallo-β-lactamase: structure and mechanism. DOI:10.1016/s1367-5931(99)00017-4. PMID:10508665.
- Li Z et al. (1999), Protein Sci, 8, 249-252. For the record: Structural consequences of the active site substitution Cys181 → Ser in metallo-β-lactamase from bacteroides fragilis. DOI:10.1110/ps.8.1.249. PMID:10210203.
- Wang Z et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 10013-10023. On the Mechanism of the Metallo-β-lactamase fromBacteroides fragilis†. DOI:10.1021/bi990356r. PMID:10433708.
- Fitzgerald PM et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 6791-6800. Unanticipated Inhibition of the Metallo-β-lactamase fromBacteroidesfragilisby 4-Morpholineethanesulfonic Acid (MES): A Crystallographic Study at 1.85-Å Resolution‡. DOI:10.1021/bi9730339. PMID:9578564.
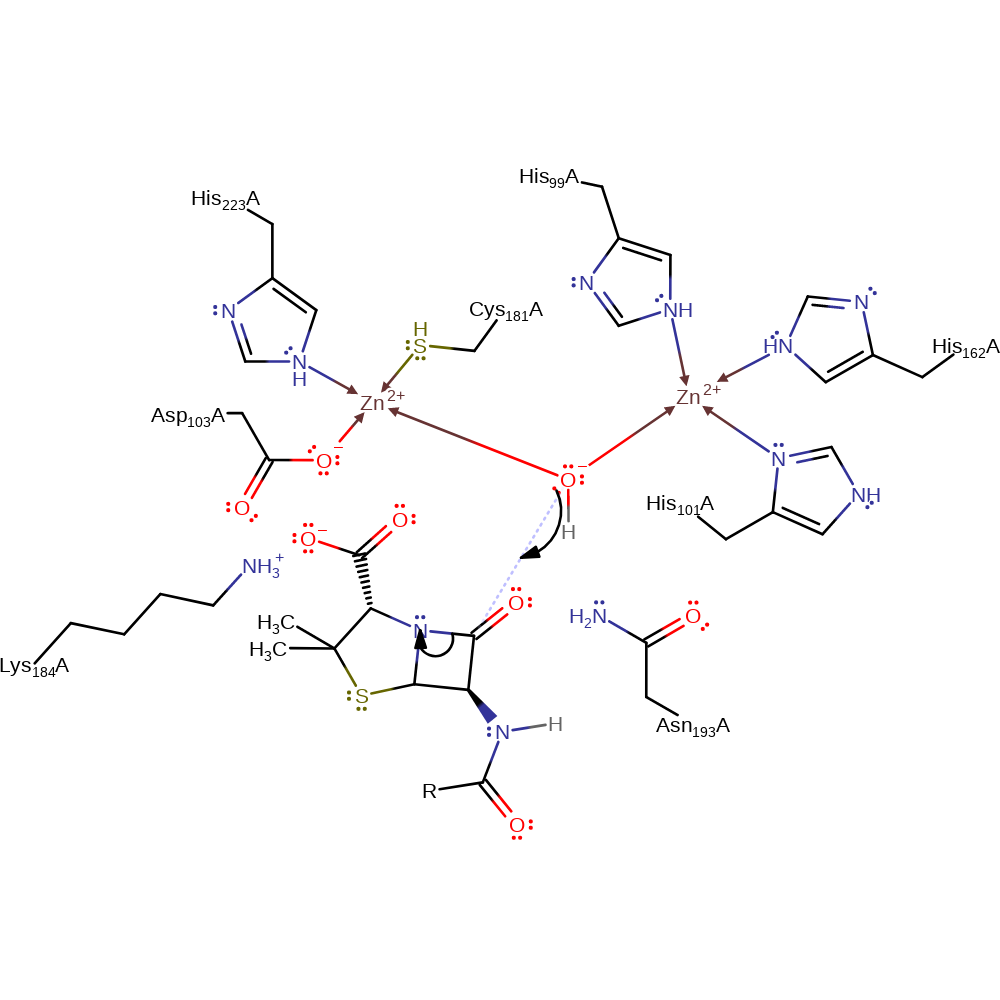
Step 1. Zinc activated water initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl of the beta-lactam ring, breaking the C-N bond in a substitution reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn193(176)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys181(164)A | metal ligand |
| His223(206)A | metal ligand |
| Asp103(86)A | metal ligand |
| His99(82)A | metal ligand |
| His162(145)A | metal ligand |
| His101(84)A | metal ligand |
| Lys184(167)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, decyclisation, intermediate formation
Step 2. The negatively charged nitrogen group then deprotonates an incoming, zinc-activated water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn193(176)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys181(164)A | metal ligand |
| His223(206)A | metal ligand |
| Asp103(86)A | metal ligand |
| His162(145)A | metal ligand |
| His101(84)A | metal ligand |
| His99(82)A | metal ligand |
| Lys184(167)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |



 Download:
Download: