Isoaspartyl dipeptidase
Isoaspartyl dipeptidase (IAD) from Escherichia coli is a member of the amidohydrolase superfamily. It catalyses the hydrolysis of dipeptides containing a peptide bond to the beta-carboxylate group of aspartic acid. The apparent physiological role of IAD is to prevent the accumulation of beta-aspartyl dipeptides after proteolysis of these proteins. IAD shows little activity towards the hydrolysis of tripeptides or gamma-glutamyl dipeptides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P39377
 (3.4.19.-)
(3.4.19.-)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1onw
- Crystal structure of Isoaspartyl Dipeptidase from E. coli
(1.65 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.140
 (see all for 1onw)
(see all for 1onw)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.19.5)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The presence of the two Zn(II) ions lowers the pKa of a water molecule to such an extent that it exists as a hydroxide ion. The interaction between the carbonyl oxygen and Zn2 increases the electrophilic character of the carbonyl carbon atom. Asp 285 acts as a general base by abstracting the proton from the hydroxide ion, causing the oxygen atom to nucleophilically attack the substrate carbonyl carbon atom. This forms a negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate. As the carbonyl is reformed, the scissile C-N bond is broken, facilitated by Asp 285 acting as a general acid by donating a proton to the leaving group N atom.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1onw) | ||
| Lys162 | Kcx162A | Post-translationally carbamalated. Acts as a bridging ligand for both zinc ions through the carbamate group. | metal ligand |
| His201, His230 | His201A, His230A | Forms part of the zinc 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp285 | Asp285A | Part of the Zinc 1 binding site. Acts as a general base by abstracting a proton from the hydroxide ion, activating it further for nucleophilic attack. Acts as a general acid by donating that proton to the leaving group N atom. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His68, His70 | His68A, His70A | Forms part of the zinc 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Martí-Arbona R et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 7115-7124. Mechanism of the Reaction Catalyzed by Isoaspartyl Dipeptidase fromEscherichia coli†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi050008r. PMID:15882050.
- Zhang HM et al. (2015), J Chem Theory Comput, 11, 2525-2535. Include dispersion in quantum chemical modeling of enzymatic reactions: the case of isoaspartyl dipeptidase. DOI:10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00246. PMID:26575552.
- Thoden JB et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 4874-4882. High-resolution X-ray structure of isoaspartyl dipeptidase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1021/bi034233p. PMID:12718528.

Step 1. Asp285 deprotonates the zinc activated hydroxide group. This then attacks the carbonyl carbon of the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp285A | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand |
| Kcx162A | metal ligand |
| His70A | metal ligand |
| His68A | metal ligand |
| His230A | metal ligand |
| His201A | metal ligand |
| Asp285A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
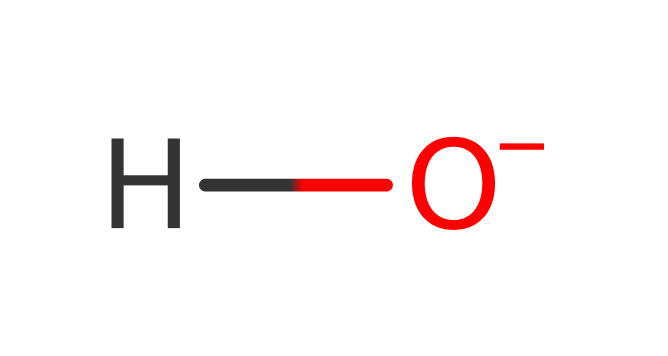
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the peptide bond. The amine side of the bond then deprotonates Asp285.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp285A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp285A | metal ligand |
| Kcx162A | metal ligand |
| His70A | metal ligand |
| His68A | metal ligand |
| His230A | metal ligand |
| His201A | metal ligand |
| Asp285A | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: