Chaperonin ATPase
Chaperonins are essential multisubunit assemblies that promote facilitated protein folding in concert with ATP hydrolysis - forming a 'cage' around the protein as it folds, with the 'timer' for protein release provided by ATP hydrolysis. Group II chaperonins are found in archaea and the eukaryotic cytosol. The mechanism for ATP hydrolysis of all chaperonins is the same, but the way this is linked to opening and closing of the cavity is different.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P61112

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermococcus sp. JCM 11816 (Archaea)

- PDB
-
1q3s
- Crystal structure of the chaperonin from Thermococcus strain KS-1 (FormIII crystal complexed with ADP)
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.260.10
 1.10.560.10
1.10.560.10  (see all for 1q3s)
(see all for 1q3s)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Asp 64 and Asp 393 bind and polarise a water molecule, which becomes nucleophilic enough to perform inline displacement on the gamma-phosphate of ATP. A pentacovalent intermediate is formed. The negative charges on the gamma-phosphate group are stabilised by contacts with Thr 97, Thr 98 and an Mg(II) ion, lowering the free energies of transition states and the intermediate. The intermediate collapses to yield the products of ATP hydrolysis: ADP and free orthophosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1q3s) | ||
| Asp393 | Asp393A | Asp 393 holds and polarises a water molecule for inline attack on the gamma-phosphate of ATP. Upon the loss of water the Asp 393 interaction after ATP hydrolysis may be the trigger for conformational change and chaperonin opening, | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp64 | Asp64A | Asp 64 holds and polarises a water molecule for inline attack on the gamma-phosphate of ATP. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr97 | Thr97A | Thr 97 hydrogen bonds to the gamma phosphate of ATP during the transition states and intermediate, stabilising charge build-up. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr98 | Thr98A | Thr 98 hydrogen bonds to the gamma phosphate of ATP during the transition states and intermediate, stabilising charge build-up. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Ditzel L et al. (1998), Cell, 93, 125-138. Crystal Structure of the Thermosome, the Archaeal Chaperonin and Homolog of CCT. DOI:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81152-6. PMID:9546398.
- An YJ et al. (2017), Nat Commun, 8, 827-. Structural and mechanistic characterization of an archaeal-like chaperonin from a thermophilic bacterium. DOI:10.1038/s41467-017-00980-z. PMID:29018216.
- Shomura Y et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 335, 1265-1278. Crystal Structures of the Group II Chaperonin from Thermococcus strain KS-1: Steric Hindrance by the Substituted Amino Acid, and Inter-subunit Rearrangement between Two Crystal Forms. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.11.028. PMID:14729342.

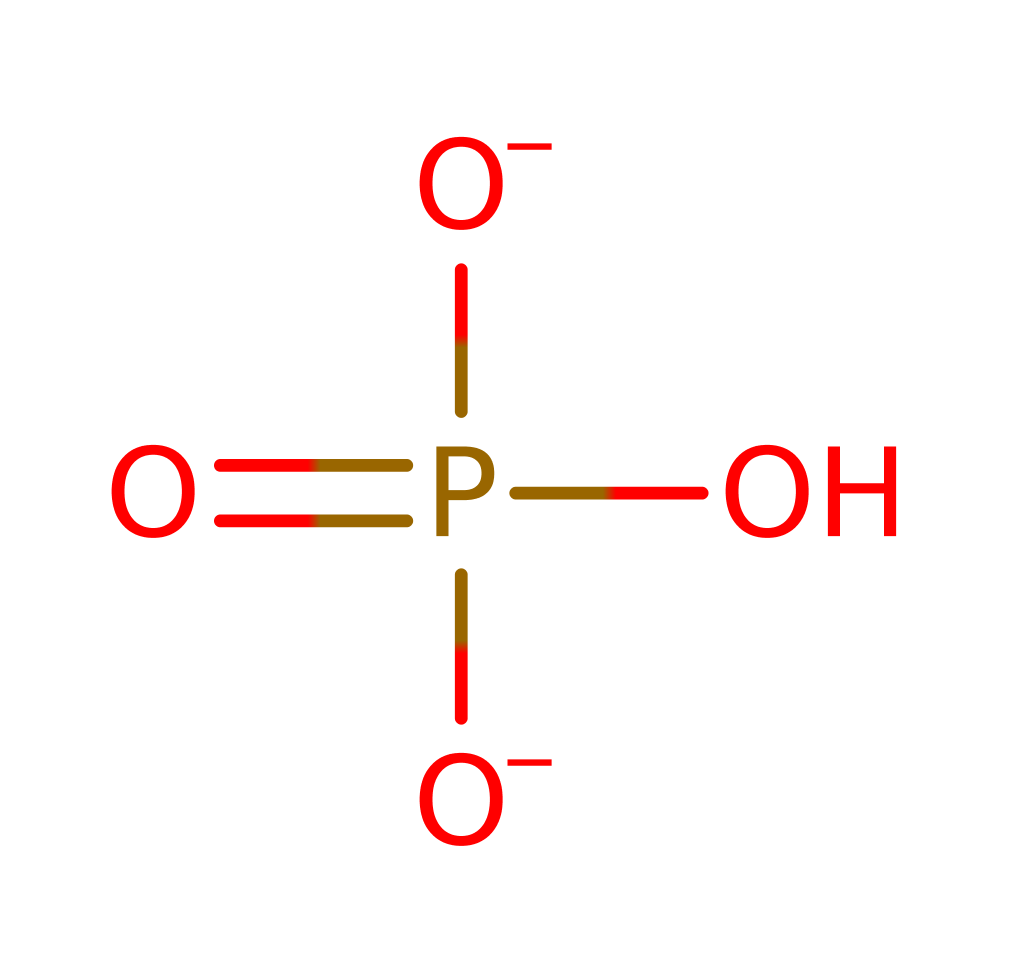
Step 1. Asp393 deprotonates water, which attacks the gamma phosphate of ATP in a nucleophilic addition, resulting in a pentavalent phosphate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr97A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr98A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp64A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp393A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp393A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The pentavalent intermediate collapses, releasing orthophosphate and ADP, which deprotonates Asp393.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr97A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr98A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp64A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp393A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp393A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: