Methylisocitrate lyase
Involved in the catabolism of short chain fatty acids (SCFA) via the 2-methylcitrate cycle I (propionate degradation route). Catalyses the thermodynamically favored C-C bond cleavage of (2R,3S)-2-methylisocitrate to yield pyruvate and succinate via an alpha-carboxy-carbanion intermediate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P77541
 (4.1.3.30)
(4.1.3.30)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1mum
- Structure of the 2-Methylisocitrate Lyase (PrpB) from Escherichia coli
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.60
 (see all for 1mum)
(see all for 1mum)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Water (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.3.30)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Asp58 deprotonates water which depotonates the alcohol group of the (2S,3R)-3-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate substrate. This initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate. Then the oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123 and formation of the final product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mum) | ||
| Glu115, Tyr43, His113 | Glu115(114)A, Tyr43(42)A, His113(112)A | These residues are not thought to be active in this proposal. | |
| Cys123, Asp58 | Cys123(122)A, Asp58(57)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg158, Glu188, Asn210 | Arg158(157)A, Glu188(187)A, Asn210(209)A | Help to stabilise the negatively charge intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85, Asp87 | Asp85(84)A, Asp87(86)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Liu S et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 2949-2962. Crystal Structures of 2-Methylisocitrate Lyase in Complex with Product and with Isocitrate Inhibitor Provide Insight into Lyase Substrate Specificity, Catalysis and Evolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0479712. PMID:15723538.
- Grimek TL et al. (2003), J Bacteriol, 185, 4837-4843. Residues C123 and D58 of the 2-methylisocitrate lyase (PrpB) enzyme of Salmonella enterica are essential for catalysis. PMID:12897003.
- Grimm C et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 328, 609-621. Crystal structure of 2-methylisocitrate lyase (PrpB) from Escherichia coli and modelling of its ligand bound active centre. PMID:12706720.

Step 1. Asp58 deprotonates water which depotonates the alcohol group of the (2S,3R)-3-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate substrate. This initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Asp58(57)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed
Step 2. The oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123. The position of the observed succinate product suggests that upon cleavage of the C2-C3 bond the aci-carboxylate intermediate must move away from the pyruvate bringing the hydrogen accepting carbon atom within range of the thiol group [PMID:15723538].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Cys123(122)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed
Step 3. Cys123 deprotonates water and water deprotonates Asp58 to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Cys123(122)A | proton acceptor |
| Asp58(57)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
Glu115 deprotonates water which depotonates the alcohol group of the (2S,3R)-3-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate substrate. This initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate. Then the oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123 and formation of the final product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mum) | ||
| Glu115, Cys123 | Glu115(114)A, Cys123(122)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr43, His113, Asp58 | Tyr43(42)A, His113(112)A, Asp58(57)A | These residues are not thought to be active in this proposal. | |
| Arg158, Glu188, Asn210 | Arg158(157)A, Glu188(187)A, Asn210(209)A | Help to stabilise the negatively charge intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85, Asp87 | Asp85(84)A, Asp87(86)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Liu S et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 2949-2962. Crystal Structures of 2-Methylisocitrate Lyase in Complex with Product and with Isocitrate Inhibitor Provide Insight into Lyase Substrate Specificity, Catalysis and Evolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0479712. PMID:15723538.

Step 1. Glu115 deprotonates water which depotonates the alcohol group of the (2S,3R)-3-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate substrate. This initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Glu115(114)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed
Step 2. The oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123. The position of the observed succinate product suggests that upon cleavage of the C2-C3 bond the aci-carboxylate intermediate must move away from the pyruvate bringing the hydrogen accepting carbon atom within range of the thiol group [PMID:15723538].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed
Step 3. Cys123 deprotonates water and water deprotonates Asp58 to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Cys123(122)A | proton acceptor |
| Glu115(114)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
Arg158 guanidium group serves as the initial base, thereby offsetting the negative charge that forms at C(3) as the cleavage step proceed. The resulting intermediate initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate. Then the oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123 and formation of the final product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mum) | ||
| Arg158 | Arg158(157)A | Acts as a general acid/base, also helps to stabilise the negatively charge intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Cys123 | Cys123(122)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu115, Tyr43, His113, Asp58 | Glu115(114)A, Tyr43(42)A, His113(112)A, Asp58(57)A | These residues are not thought to be active in this proposal. | |
| Glu188, Asn210 | Glu188(187)A, Asn210(209)A | Help to stabilise the negatively charge intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85, Asp87 | Asp85(84)A, Asp87(86)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Liu S et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 2949-2962. Crystal Structures of 2-Methylisocitrate Lyase in Complex with Product and with Isocitrate Inhibitor Provide Insight into Lyase Substrate Specificity, Catalysis and Evolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0479712. PMID:15723538.
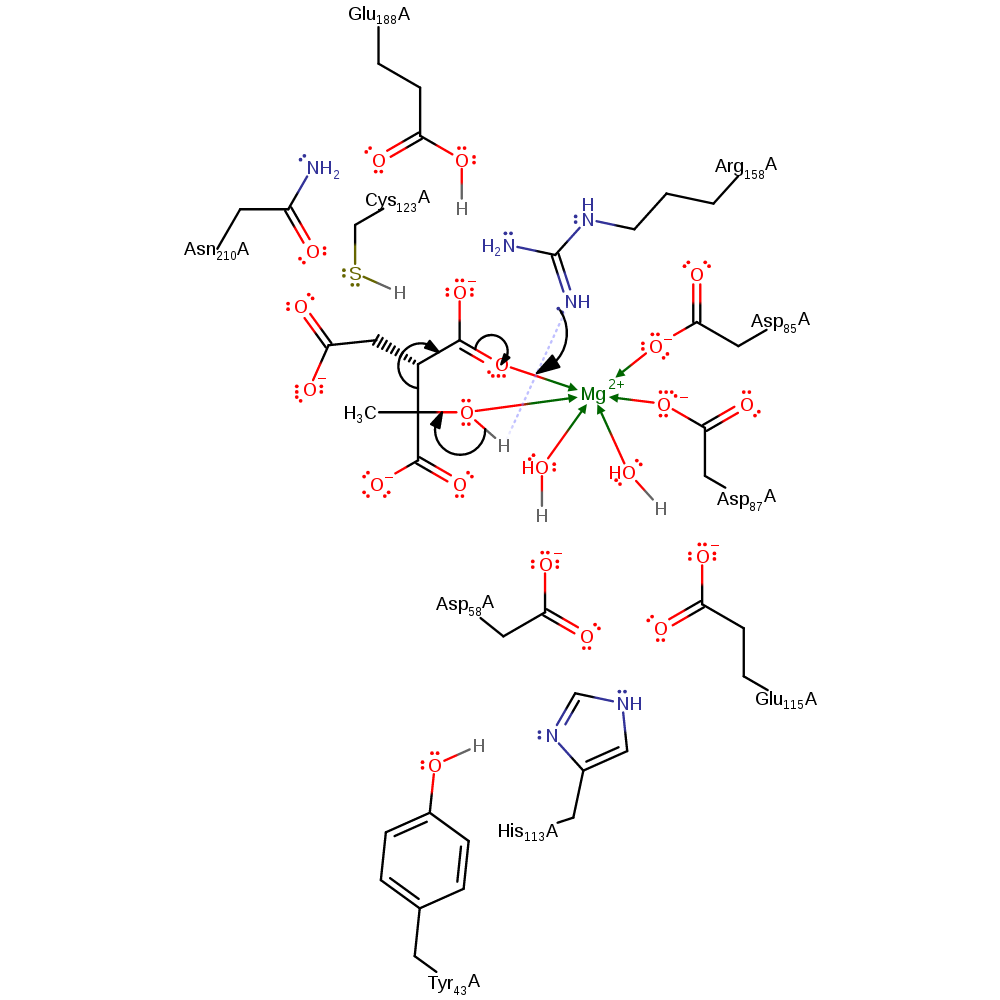
Step 1. Arg158 depotonates the alcohol group of the (2S,3R)-3-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate substrate. This initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Arg158(157)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed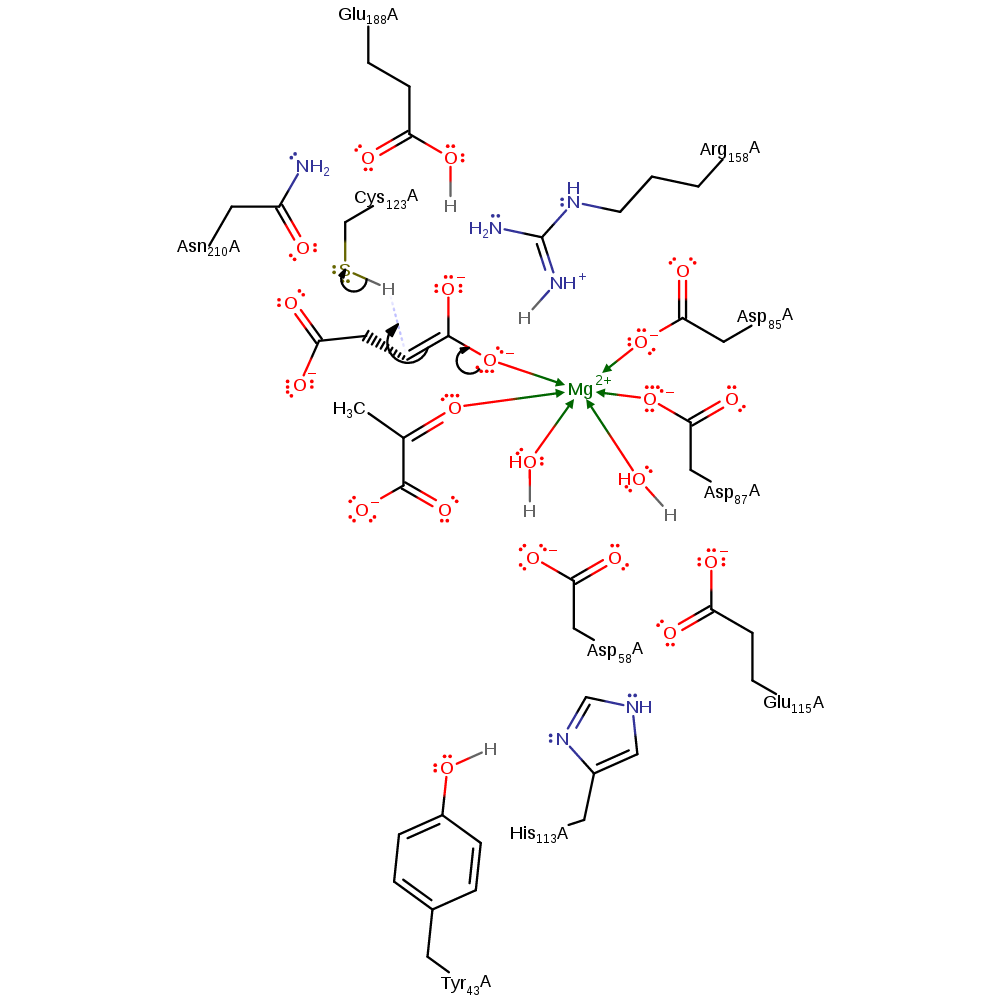
Step 2. The oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123. The position of the observed succinate product suggests that upon cleavage of the C2-C3 bond the aci-carboxylate intermediate must move away from the pyruvate bringing the hydrogen accepting carbon atom within range of the thiol group [PMID:15723538].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed
Step 3. Inferred step in which Cys123 deprotonates water and water deprotonates Arg158 to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Cys123(122)A | proton acceptor |
| Arg158(157)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
This alternative has the Tyr43 hydroxyl group serving as the general acid/base. In the X-ray structures, Tyr43 hydroxyl forms a hydrogen bond with His113 Nε atom. The Nδ atom of His113 is hydrogen bonded to an internal water molecule, which in turn forms hydrogen bonds with Glu115 carboxylate group. The network of interactions provides a second route for shuttling a proton from C(2)OH to Glu115, this time via Tyr43 hydroxyl. The resulting intermediate initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate. Then the oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123 and formation of the final product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mum) | ||
| Glu115, Tyr43, His113 | Glu115(114)A, Tyr43(42)A, His113(112)A | Form a proton relay chain that is responsible for the initial proton abstraction. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys123 | Cys123(122)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp58 | Asp58(57)A | Not thought to be active in this proposal. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg158, Glu188, Asn210 | Arg158(157)A, Glu188(187)A, Asn210(209)A | Help to stabilise the negatively charge intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85, Asp87 | Asp85(84)A, Asp87(86)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Liu S et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 2949-2962. Crystal Structures of 2-Methylisocitrate Lyase in Complex with Product and with Isocitrate Inhibitor Provide Insight into Lyase Substrate Specificity, Catalysis and Evolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0479712. PMID:15723538.

Step 1. Tyr43 initiates a proton relay chain involving His113, Glu115 and the magnesium bound water, which depotonates the alcohol group of the (2S,3R)-3-hydroxybutane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate substrate. This initiates an elimination that produces the pyruvate poduct and an intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Glu115(114)A | proton donor |
| His113(112)A | proton acceptor |
| Glu115(114)A | proton relay |
| His113(112)A | proton donor |
| Glu115(114)A | proton acceptor |
| His113(112)A | proton relay |
| Tyr43(42)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, overall product formed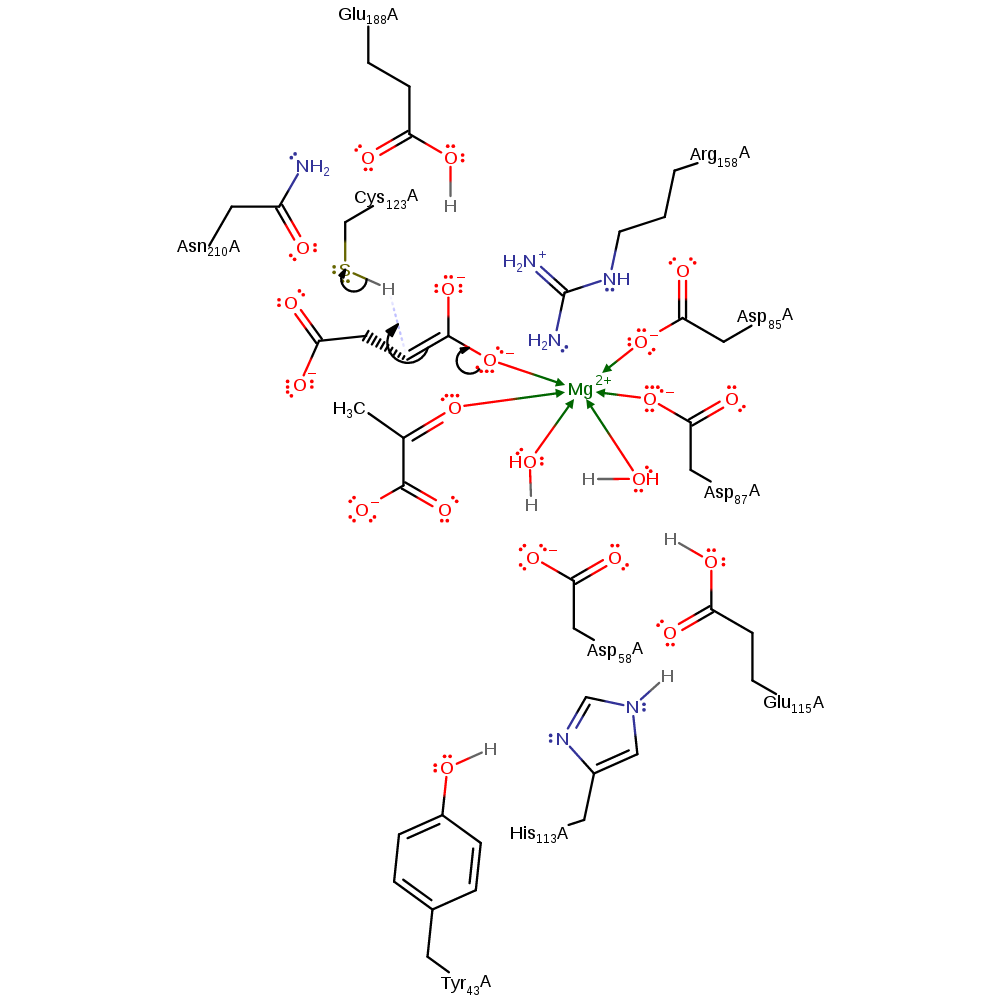
Step 2. The oxyanion of the intermediate initiates a double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonatation of Cys123. The position of the observed succinate product suggests that upon cleavage of the C2-C3 bond the aci-carboxylate intermediate must move away from the pyruvate bringing the hydrogen accepting carbon atom within range of the thiol group [PMID:15723538].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg158(157)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys123(122)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed
Step 3. Cys123 deprotonates water and water deprotonates Tyr43 via the proton relay chain to regenerate the active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn210(209)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu188(187)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys123(122)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp58(57)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp85(84)A | metal ligand |
| Asp87(86)A | metal ligand |
| Cys123(122)A | proton acceptor |
| Glu115(114)A | proton donor |
| His113(112)A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Tyr43(42)A | proton donor |
| Glu115(114)A | proton acceptor, proton relay |
| His113(112)A | proton relay |

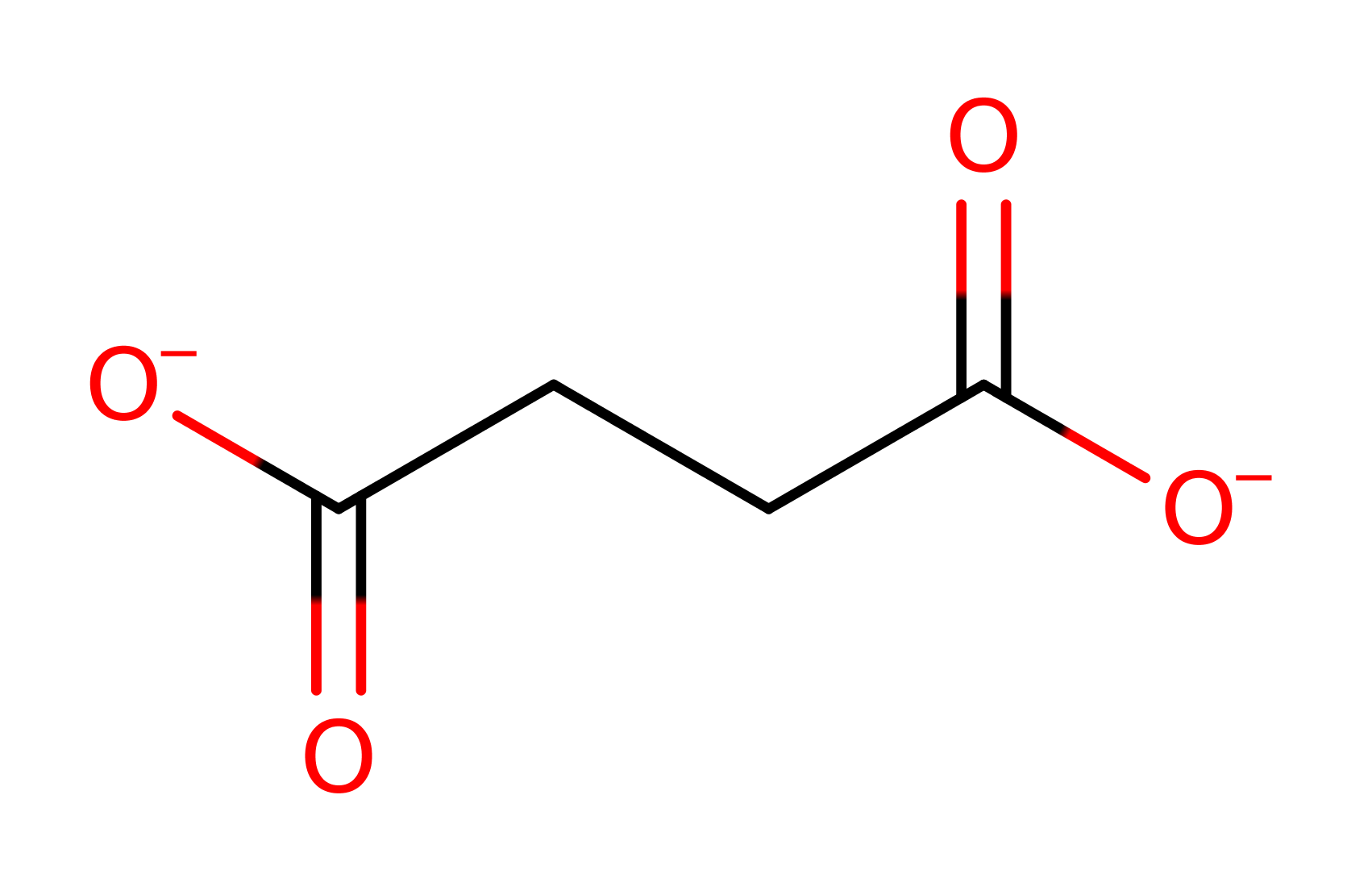

 Download:
Download: 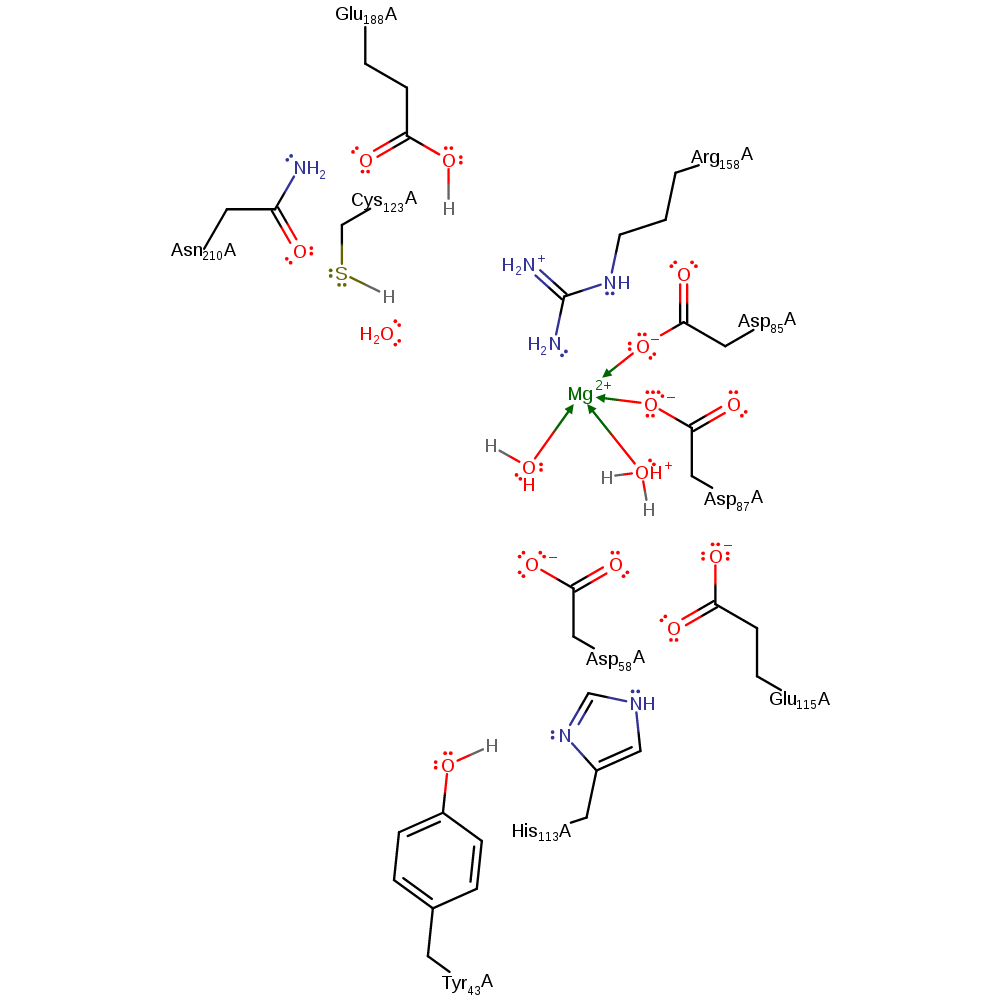 Download:
Download: 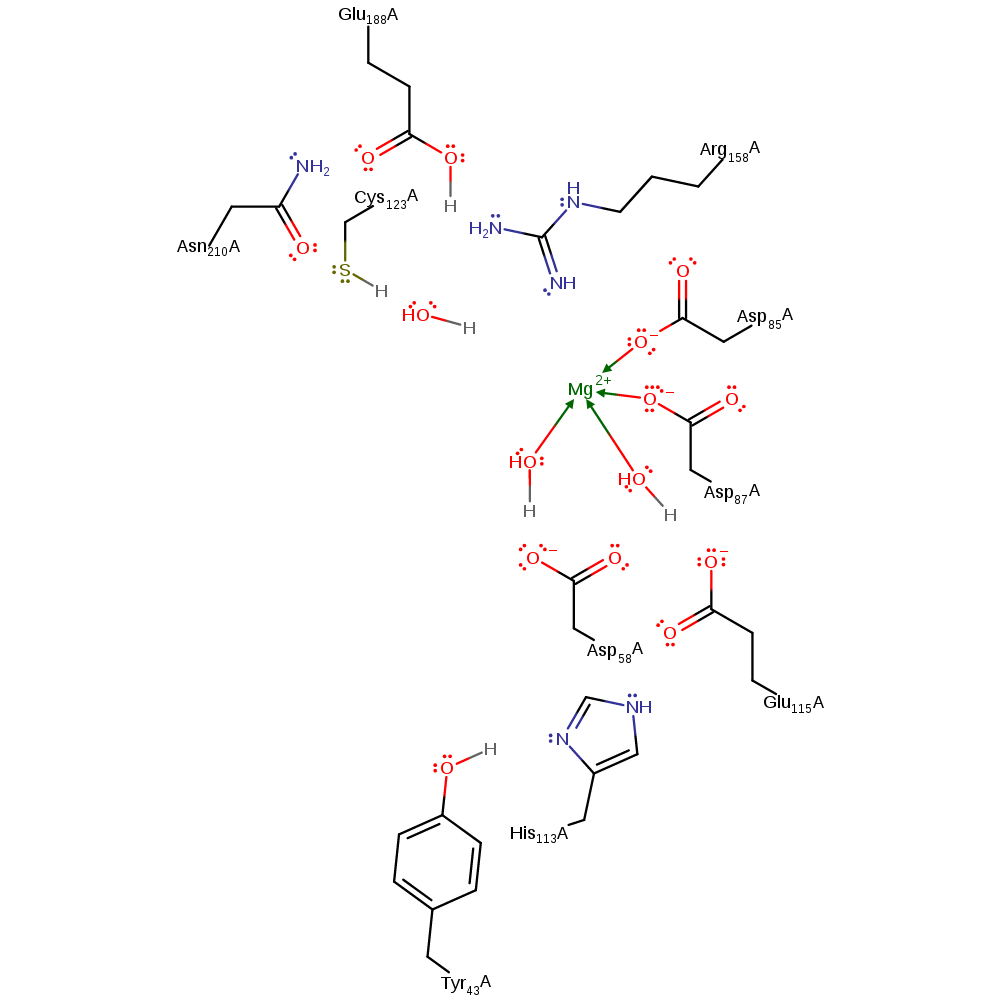 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: