Glycogen phosphorylase
Phophorylases are important allosteric enzymes in the carbohydrate metabolism. Enzymes from different sources differ in their regulatory mechanisms and in their natural substrates. However all known phosphorylases share catalytic and structural properties. For example glycogen phosphorylase catalyses the intracellular degradation of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate, the first step of glycolysis. It was the first enzyme to be discovered that was controlled by phosphorylation. Other phosphorylases include maltodextrin phosphorylase and starch phosphorylase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00489
 (2.4.1.1)
(2.4.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)

- PDB
-
1gpb
- GLYCOGEN PHOSPHORYLASE B: DESCRIPTION OF THE PROTEIN STRUCTURE
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.2000
 (see all for 1gpb)
(see all for 1gpb)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is covalently bound to Lys568 as a Schiff Base. Glycogen substrate binding (shown here as maltose) is followed by a conformational change which brings the substrate close to the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) resulting in the distortion and enhanced electrophilicity of the latter thus labelling the glucosyl phosphate linkage. Bond cleavage then ensues with the coenzyme PLP and its neighbouring basic groups, Gly674, Thr675 and Lys573, essentially sequestering the released inorganic phosphate. The glucosyl carbanion generated may be stabilised as an intermediate by a negatively charged enzymic group, attacked directly in a concerted reaction by the oligosaccharide or trapped by an enzymic group as a glucosyl enzyme intermediate. The latter is the most likely option, the glyucosyl bound via a carboxylate group, Glu671. The glucosyl unit now reacts with the nonreducing end of the oligosaccharide substrate and the reaction proceeds with retention of configuration at the glucose moiety. As a result from this Sn1 reaction, the products glucose-1-phosphate and a n-1 glycogen chain are formed.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1gpb) | ||
| Lys681 | Lys680A | Covalently attached to the PLP cofactor. | covalently attached |
| His378 (main-C), His378 | His377A (main-C), His377A | Activate and stabilises the sugar ring and oxycarbenium cation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys569, Arg570, Lys575, Thr677 (main-N) | Lys568A, Arg569A, Lys574A, Thr676A (main-N) | Stabilise and hold the inorganic phosphate in the correct position | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, cofactor used, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Schwarz A et al. (2005), Biochem J, 387, 437-445. Catalytic mechanism of α-retaining glucosyl transfer byCorynebacterium callunaestarch phosphorylase: the role of histidine-334 examined through kinetic characterization of site-directed mutants. DOI:10.1042/bj20041593. PMID:15535798.
- Brás NF et al. (2018), ChemMedChem, 13, 1608-1616. Understanding the Rate-Limiting Step of Glycogenolysis by Using QM/MM Calculations on Human Glycogen Phosphorylase. DOI:10.1002/cmdc.201800218. PMID:29905983.
- Buschiazzo A et al. (2004), EMBO J, 23, 3196-3205. Crystal structure of glycogen synthase: homologous enzymes catalyze glycogen synthesis and degradation. DOI:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600324. PMID:15272305.
- Geremia S et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 322, 413-423. Enzymatic Catalysis in Crystals of Escherichia coli Maltodextrin Phosphorylase. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00771-4. PMID:12217700.
- Oikonomakos NG et al. (2002), Bioorg Med Chem, 10, 1313-1319. The 1.76 A resolution crystal structure of glycogen phosphorylase B complexed with glucose, and CP320626, a potential antidiabetic drug. DOI:10.2210/pdb1h5u/pdb. PMID:11886794.
- Livanova NB et al. (2002), Biochemistry (Mosc), 67, 1089-1098. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a catalytic and conformational cofactor of muscle glycogen phosphorylase B. DOI:10.1023/a:1020978825802. PMID:12460107.
- Leonidas DD et al. (1992), Protein Sci, 1, 1112-1122. Control of phosphorylasebconformation by a modified cofactor: Crystallographic studies on R-state glycogen phosphorylase reconstituted with pyridoxal 5′-diphosphate. DOI:10.1002/pro.5560010905. PMID:1304390.
- Barford D et al. (1991), J Mol Biol, 218, 233-260. Structural mechanism for glycogen phosphorylase control by phosphorylation and AMP. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(91)90887-c. PMID:1900534.
- Tagaya M et al. (1984), J Biol Chem, 259, 4860-4865. Catalytic reaction of glycogen phosphorylase reconstituted with a coenzyme-substrate conjugate. PMID:6425278.

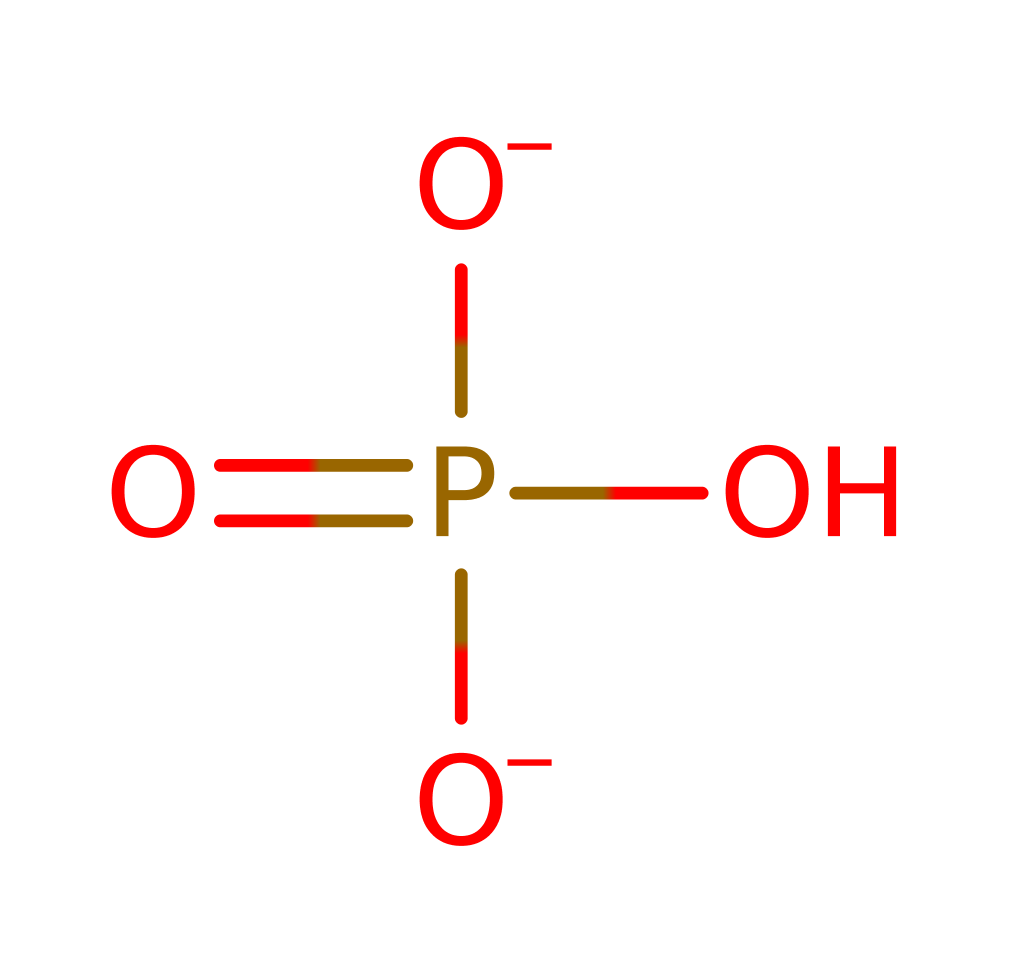
Step 1. The ring oxygen of the substrate initiates an elimination of the alcohol product, which deprotonates a non-covalently bound phosphate, which in turn deprotonates the phosphate of the covalently attached PLP cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys680A | covalently attached |
| His377A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His377A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg569A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys574A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr676A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys568A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, cofactor used, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay
Step 2. The phosphate of the covalently attached PLP cofactor deprotonates the non-covalently bound phosphate, which in turn attacks the intermediate in a nucleophilic addition that produces the second product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys680A | covalently attached |
| His377A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His377A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys568A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg569A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys574A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr676A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |



 Download:
Download: