Beta-phosphoglucomutase
This enzyme catalyses the interconversion of D-glucose 1-phosphate (G1P) and D-glucose 6-phosphate (G6P), forming beta-D-glucose 1,6-(bis)phosphate (beta-G16P) as an intermediate. It requires Mg(II) and phosphorylation of an aspartate residue at the active site. The enzyme is able to autophosphorylate itself with its substrate beta-D-glucose 1-phosphate. Although this is a slow reaction, only a single turnover is required for activation. Once the phosphorylated enzyme is formed, it generates the reaction intermediate beta-D-glucose 1,6-bisphosphate, which can be used to phosphorylate the enzyme in subsequent cycles [PMID:16784233].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P71447
 (5.4.2.6)
(5.4.2.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Il1403 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1o08
- Structure of Pentavalent Phosphorous Intermediate of an Enzyme Catalyzed Phosphoryl transfer Reaction observed on cocrystallization with Glucose 1-phosphate
(1.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1000
 1.10.150.240
1.10.150.240  (see all for 1o08)
(see all for 1o08)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Asp10 initiates the reaction by abstracting a proton from the -CH2-OH group of the substrate sugar, which attacks the phosphate of the phosphorylated Asp8 in a nucleophilic addition. This produces a pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate. The pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate collapses, eliminating Asp8 in an un-phosphorylated state. The bisphosphate intermediate rotates in the active site. Asp8 attacks the C1 phosphate of the intermediate in a nucleophilic addition. This produces a pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate. The intermediate collapses, eliminating the final product and Asp8 in its phosphorylated state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1o08) | ||
| Asp10 (main-N) | Asp1010(10)A (main-N) | Stabilises the Asp10 side chain. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp8 | Asp1008(8)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. This residue is phosphorylated in the enzyme's ground state. | nucleophile, nucleofuge, metal ligand |
| Asp10 | Asp1010(10)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. Acts as a general acid/base. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Leu9 (main-N), Ala115 (main-N), Lys145, Ser114, Thr16, Lys45 | Leu1009(9)A (main-N), Ala1115(115)A (main-N), Lys1145(145)A, Ser1114(114)A, Thr1016(16)A, Lys1045(45)A | Stabilises the phosphate intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu169, Asp170 | Glu1169(169)A, Asp1170(170)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Lahiri SD et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 8351-8359. Caught in the Act: The Structure of Phosphorylatedβ-Phosphoglucomutase fromLactococcus lactis†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0202373.
- Barrozo A et al. (2018), Org Biomol Chem, 16, 2060-2073. Computer simulations of the catalytic mechanism of wild-type and mutant β-phosphoglucomutase. DOI:10.1039/c8ob00312b. PMID:29508879.
- Marcos E et al. (2010), Proteins, 78, 2405-2411. Pentacoordinated phosphorus revisited by high-level QM/MM calculations. DOI:10.1002/prot.22758. PMID:20602355.
- Dai J et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 7818-7824. Conformational cycling in beta-phosphoglucomutase catalysis: reorientation of the beta-D-glucose 1,6-(Bis)phosphate intermediate. DOI:10.1021/bi060136v. PMID:16784233.
- Zhang G et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 9404-9416. Catalytic Cycling in β-Phosphoglucomutase: A Kinetic and Structural Analysis†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi050558p. PMID:15996095.
- Tremblay LW et al. (2005), J Am Chem Soc, 127, 5298-5299. Chemical Confirmation of a Pentavalent Phosphorane in Complex with β-Phosphoglucomutase. DOI:10.1021/ja0509073. PMID:15826149.
- Allen KN et al. (2004), Trends Biochem Sci, 29, 495-503. Phosphoryl group transfer: evolution of a catalytic scaffold. DOI:10.1016/j.tibs.2004.07.008. PMID:15337123.
- Lahiri SD et al. (2003), Science, 299, 2067-2071. The Pentacovalent Phosphorus Intermediate of a Phosphoryl Transfer Reaction. DOI:10.1126/science.1082710. PMID:12637673.

Step 1. Asp1010 deprotonates the -CH2-OH group of the substrate sugar, which attacks the phosphate of the phosphorylated Asp1008 in a nucleophilic addition. This produces a pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu1009(9)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1114(114)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala1115(115)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp1010(10)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1145(145)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp1010(10)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp1008(8)A | metal ligand |
| Glu1169(169)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1170(170)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1010(10)A | metal ligand |
| Thr1016(16)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1045(45)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp1010(10)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate collapses, eliminating Asp1008 in an un-phosphorylated state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr1016(16)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1045(45)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu1009(9)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1114(114)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala1115(115)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp1010(10)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1145(145)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp1008(8)A | metal ligand |
| Glu1169(169)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1170(170)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1010(10)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1008(8)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation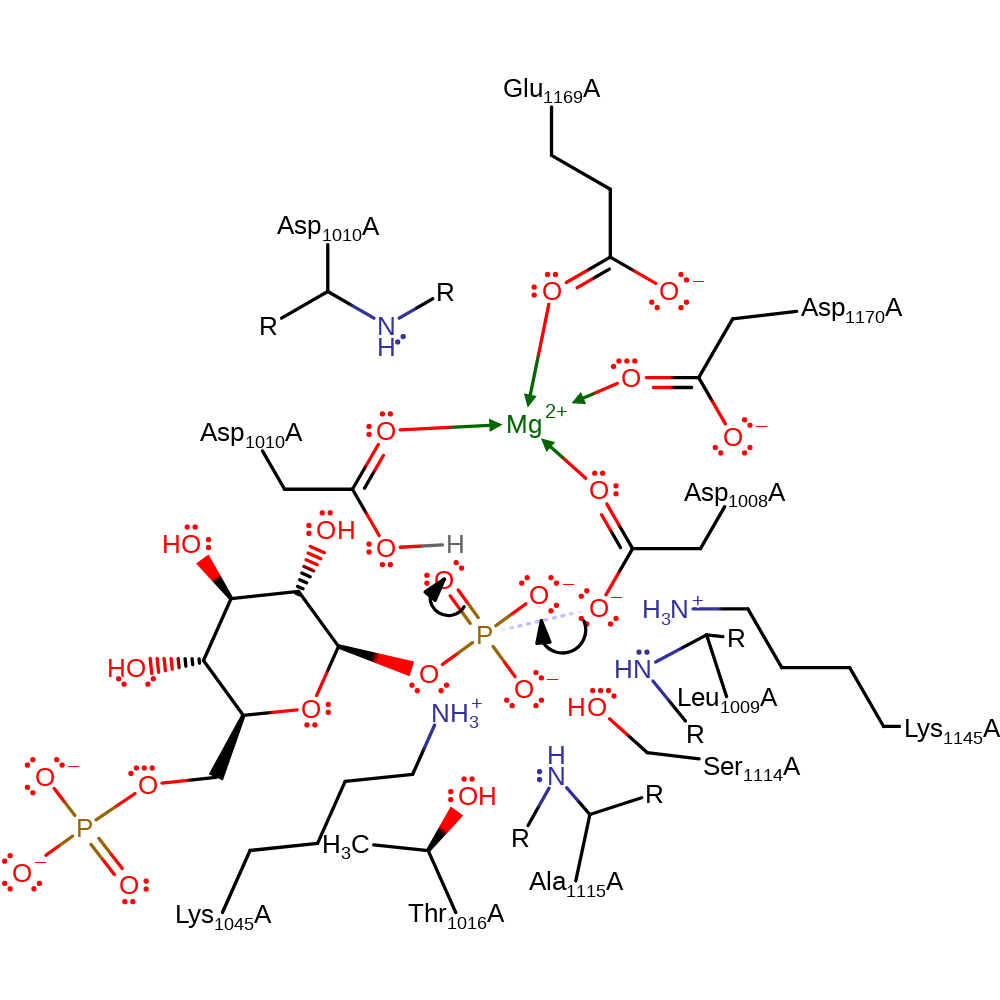
Step 3. The bisphosphate intermediate rotates in the active site. Asp1008 attacks the C1 phosphate of the intermediate in a nucleophilic addition. This produces a pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp1008(8)A | metal ligand |
| Glu1169(169)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1170(170)A | metal ligand |
| Thr1016(16)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1045(45)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser1114(114)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ala1115(115)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu1009(9)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys1145(145)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp1010(10)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp1010(10)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1008(8)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation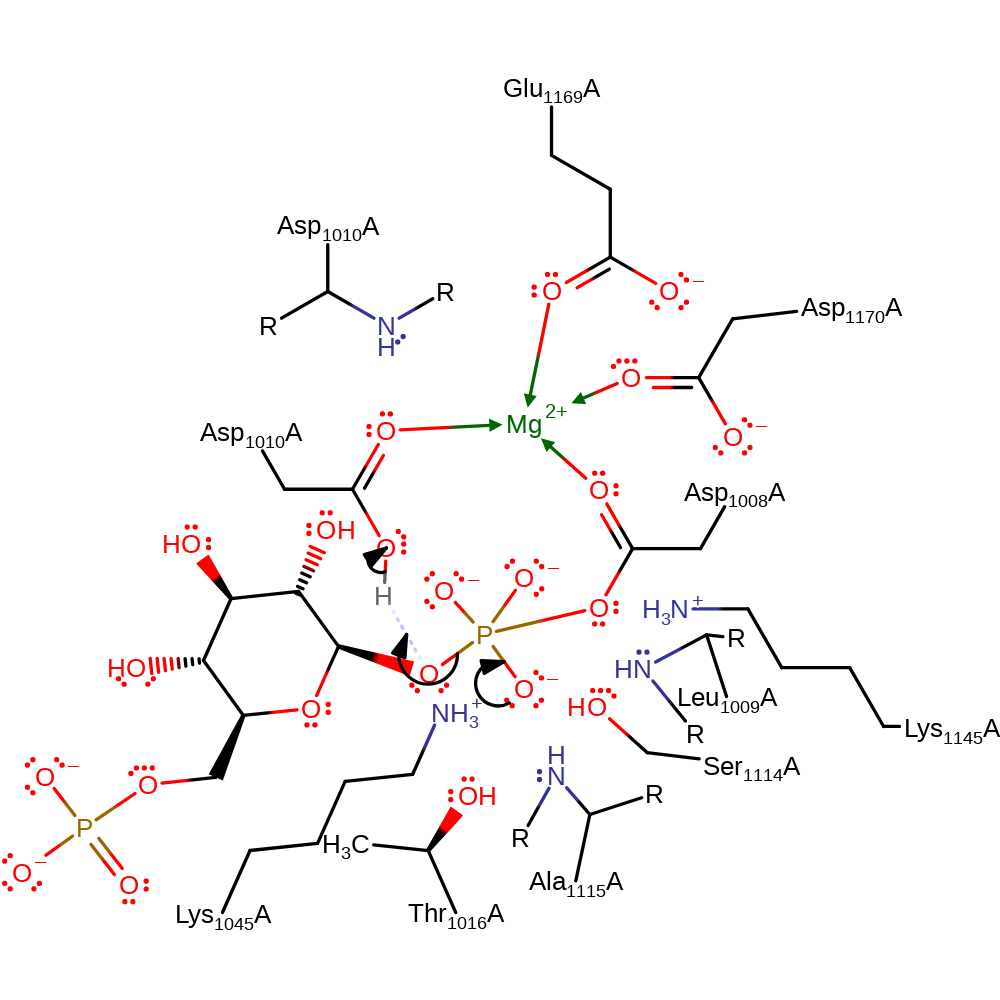
Step 4. The pentavalent, covalently attached intermediate collapses, eliminating the final product and Asp1008 in its phosphorylated state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu1009(9)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser1114(114)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ala1115(115)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp1010(10)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys1145(145)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp1008(8)A | metal ligand |
| Glu1169(169)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1170(170)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1010(10)A | metal ligand |
| Thr1016(16)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1045(45)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp1010(10)A | proton donor |


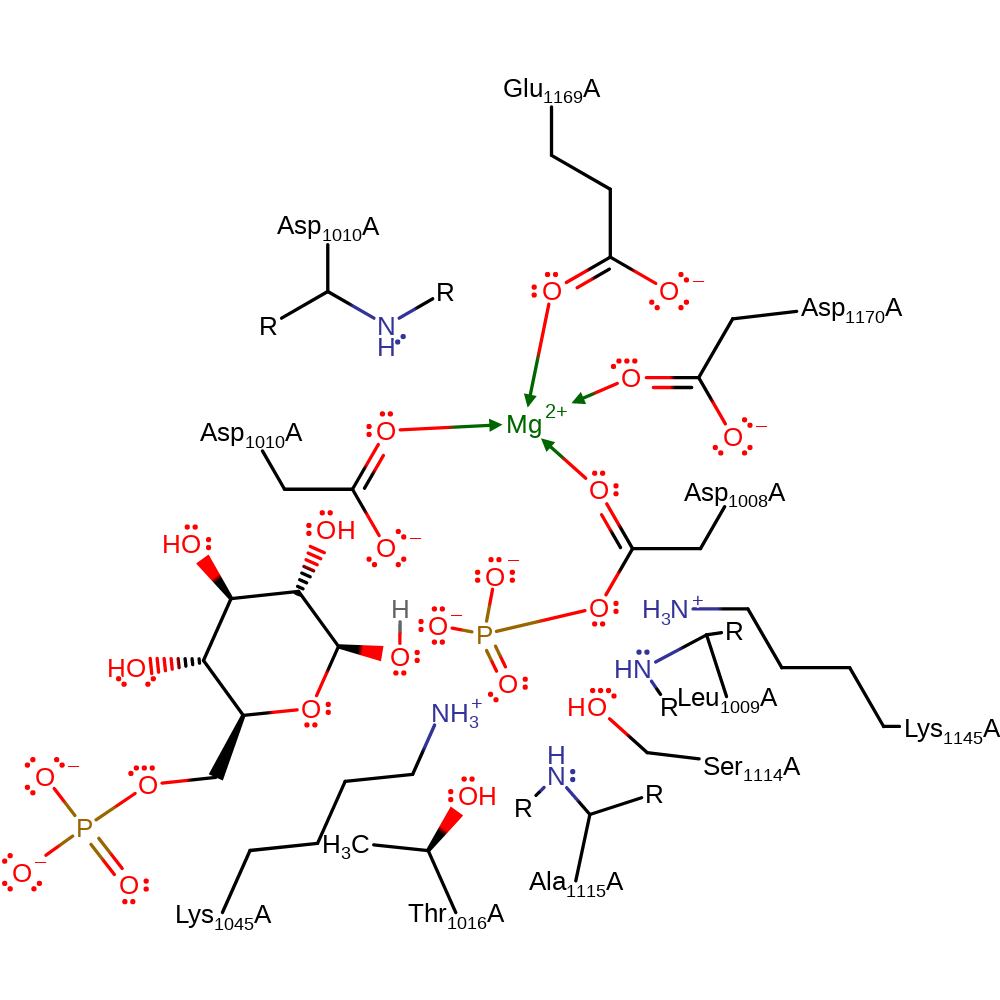 Download:
Download: