Pyruvate, phosphate dikinase
Pyruvate phosphate dikinase (PPDK) catalyses the interconversion of ATP, Pi , and pyruvate with AMP, PPi , and PEP. The enzyme has a three-domain structure consisting of consecutive N-terminal, central His455, and C-terminal domains. The nucleotide binding site is located within the N-terminal part of the polypeptide chain, whereas the pyruvate/PEP binding site is located within the C-terminal part of the chain. The first and second partial reactions take place in the active site formed at the interface of the N-terminal domain (which binds Mg(II), ATP, and Ppi) and the central domain (which contributes the catalytic His455) in PPDK conformer 1. The third partial reaction takes place in the active site formed at the interface of the C-terminal domain (which binds Mg(II) and pyruvate) and the central domain (which contributes the phosphorylated His455) in PPDK conformer 2.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P22983
 (2.7.9.1)
(2.7.9.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
[Clostridium] symbiosum (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1kc7
- Pyruvate Phosphate Dikinase with Bound Mg-phosphonopyruvate
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.1490.20
 3.20.20.60
3.20.20.60  3.50.30.10
3.50.30.10  3.30.470.20
3.30.470.20  (see all for 1kc7)
(see all for 1kc7)
- Cofactors
- Water (1), Magnesium(2+) (3) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.9.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Phosphoryl transfer is mediated by a carrier histidine, this His455 attacks the beta phosphate of the ATP in a nucleophilic substitution that results in His455 carrying a pyrophosphate moiety and the AMP product. Free phosphate attacks the terminal phosphate of the His455 pyrophosphate moiety in a nucleophilic substitution, resulting in free pyrophosphate and phosphorylated His455. In a proton relay chain involving bulk solvent, Tyr851, water, Ser764 and Cys831 the CH3 group of the pyruvate substrate is deprotonated. This initiates a double bond rearrangement that causes the ketone carbonyl group to attack the phosphorylated His455 in a nucleophilic substitution generating free His455 and the final product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1kc7) | ||
| His455 | His455(454)A | His455 is the phosphate carrier and initiates nucleophilic substitution on the beta phosphate of ATP leading to His455 carrying a pyrophosphate moiety. In the final step the ketone carbonyl group attacks phosphorylated His455 to generate His455 and phosphoenolpyruvate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, polar interaction |
| Ser764 | Ser764(763)A | Receives proton from Cys831 and transports to Tyr851. Proton shuttle. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Cys831 | Cys831(830)A | Acts as a general base to deprotonate methyl group of pyruvate substrate- then forms part of proton shuttle. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Tyr851 | Tyr851(850)A | End of proton shuttle, transfers proton to solvent. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Arg337, Arg92, Lys22 | Arg337(336)A, Arg92(91)A, Lys22(21)A | Electrostatically stabilises the transition state in the formation of pyrophosphorylated His residue. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met103 (main-N), Gly101 (main-N) | Met103(102)A (main-N), Gly101(100)A (main-N) | Forms oxyanion hole in the initial attack of His455 on beta-phosphate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, dephosphorylation, intermediate collapse, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, proton relay, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Ye D et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 37630-37639. Investigation of the Catalytic Site within the ATP-Grasp Domain of Clostridium symbiosum Pyruvate Phosphate Dikinase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m105631200. PMID:11468288.
- Herzberg O et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 780-787. Pyruvate site of pyruvate phosphate dikinase: crystal structure of the enzyme-phosphonopyruvate complex, and mutant analysis. DOI:10.1021/bi011799+. PMID:11790099.
- McGuire M et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 13463-13474. Location of the Phosphate Binding Site withinClostridium symbiosumPyruvate Phosphate Dikinase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi980920i. PMID:9753432.

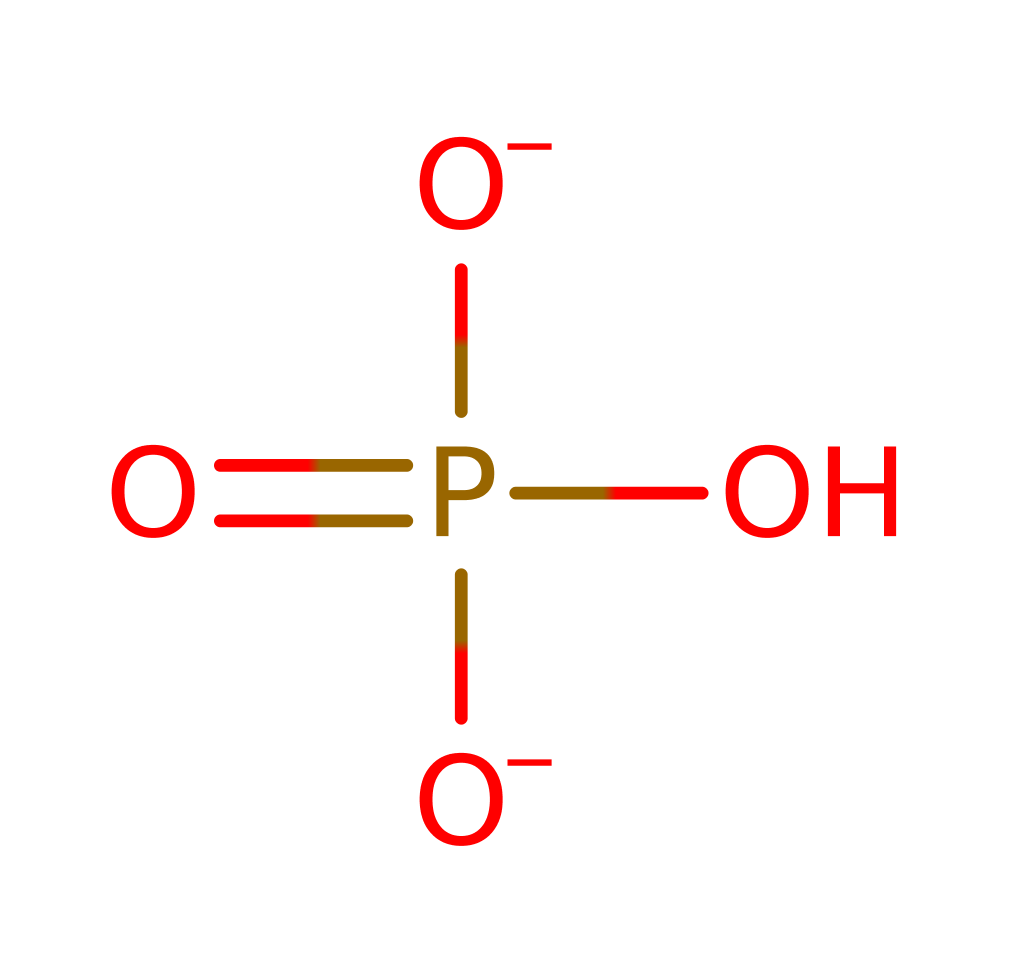
Step 1. His455 attacks the beta phosphate of the ATP in a nucleophilic substitution that results in His455 carrying a pyrophosphate moiety and the AMP product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg337(336)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His455(454)A | polar interaction |
| Lys22(21)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly101(100)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg92(91)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Met103(102)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His455(454)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed
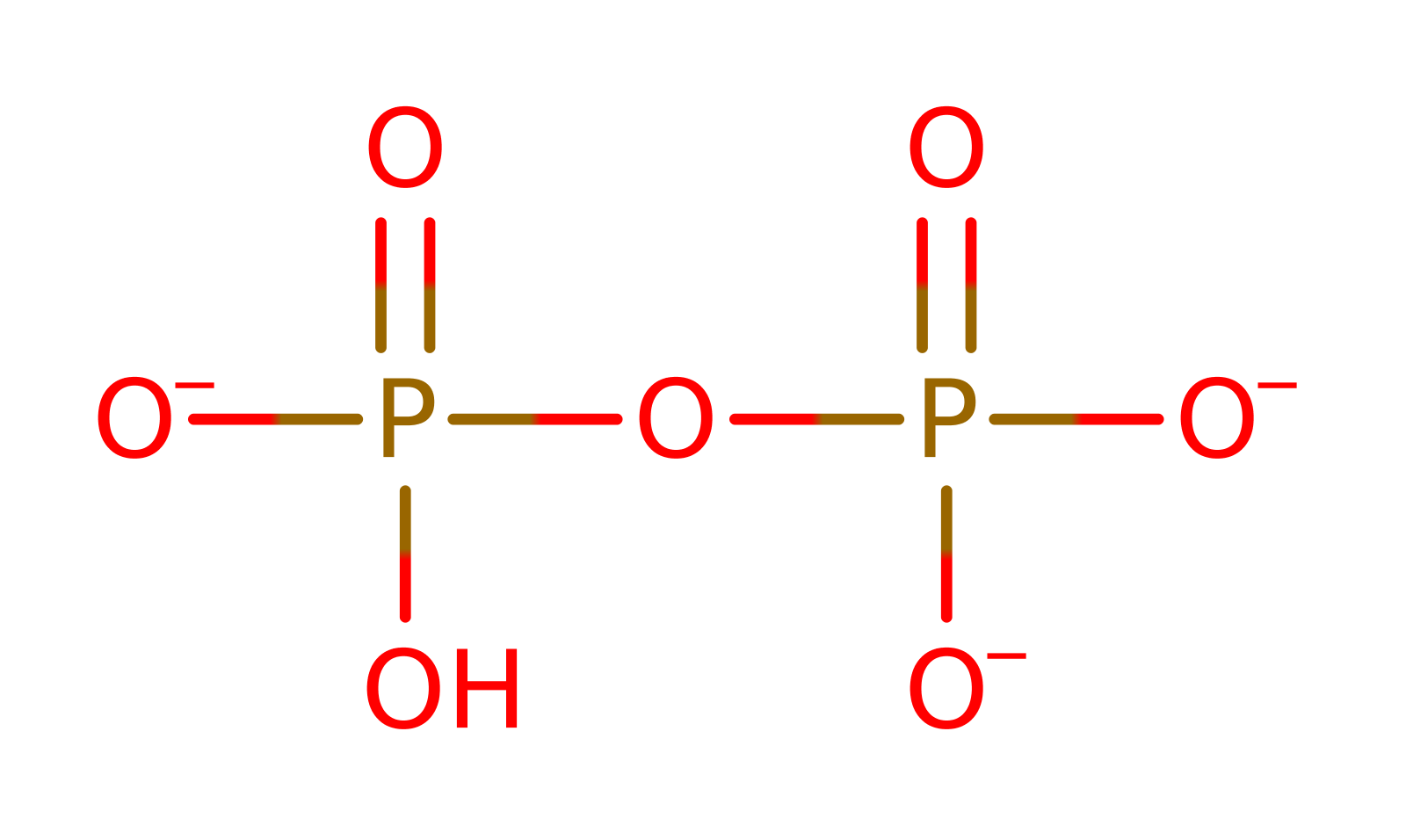
Step 2. Free phosphate attacks the terminal phosphate of the His455 pyrophosphate moiety in a nuclephilic substitution, resulting in free pyrophosphate and phosphorylated His455.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg337(336)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His455(454)A | covalently attached |
| Lys22(21)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly101(100)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Met103(102)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, dephosphorylation, overall reactant used, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed
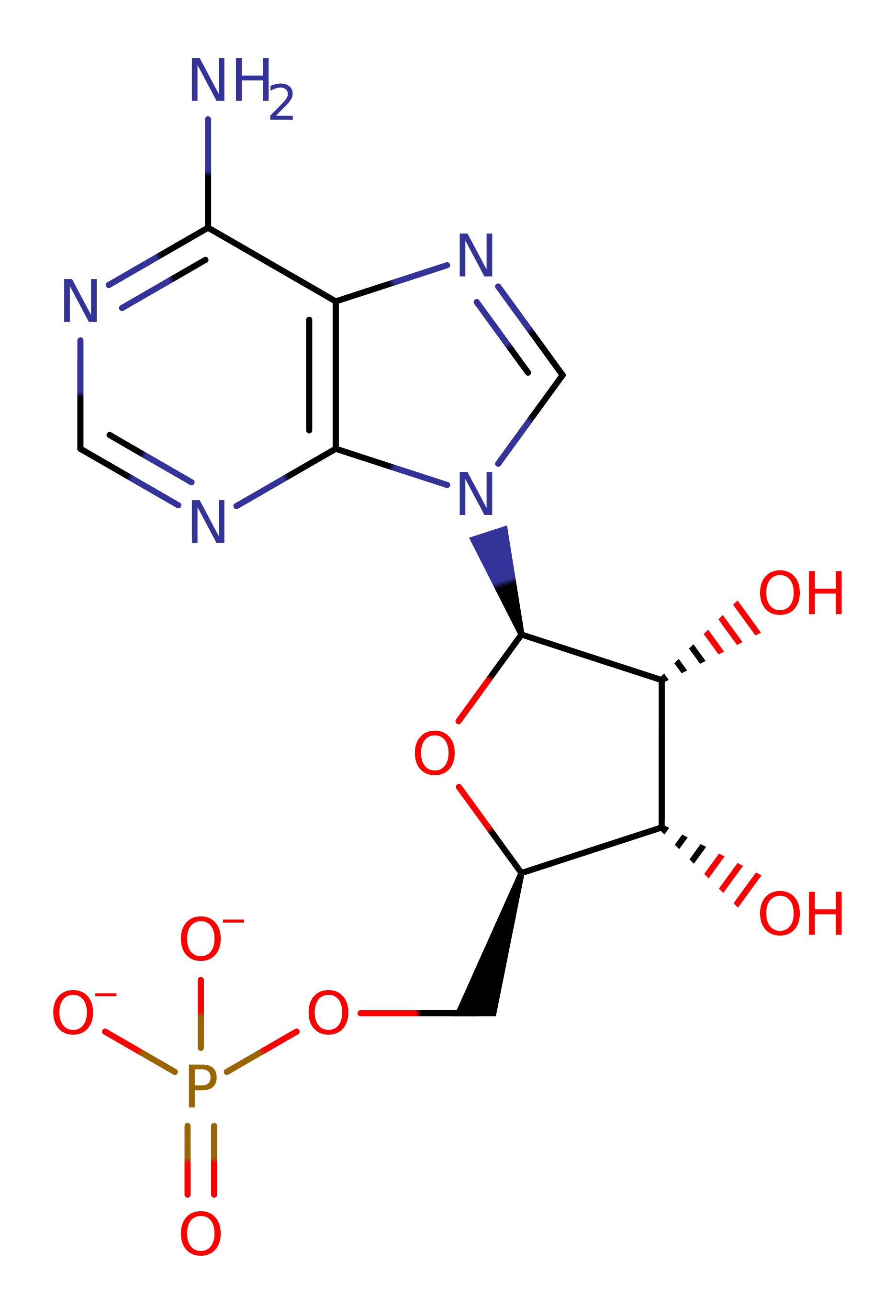
Step 3. In a proton relay chain involving bulk solvent, Tyr851, water, Ser764 and Cys831 the CH3 group of the pyruvate substrate is deprotonated. This initiates a double bond rearrangement that causes the ketone carbonyl group to attack the phosphorylated His455 in a nuclephilic substitution generating free His455 and the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His455(454)A | covalently attached |
| Cys831(830)A | proton relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser764(763)A | proton relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr851(850)A | proton relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr851(850)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser764(763)A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Cys831(830)A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr851(850)A | proton donor |
| His455(454)A | nucleofuge |
| Cys831(830)A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: