Pyruvate decarboxylase
pyruvate decarboxylase isoenzyme 1 (PDC1) is the major isoform of pyruvate decarboxylase and is implicated in the nonoxidative conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide during alcoholic fermentation. PDC1 is a thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzyme. It also requires Mg2+ for activity, however the magnesium is involved in anchoring the cofactor rather than directly involved in catalysis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P06169
 (4.1.1.-, 4.1.1.43, 4.1.1.72, 4.1.1.74)
(4.1.1.-, 4.1.1.43, 4.1.1.72, 4.1.1.74)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
1pvd
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE THIAMIN DIPHOSPHATE DEPENDENT ENZYME PYRUVATE DECARBOXYLASE FROM THE YEAST SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE AT 2.3 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.970
 (see all for 1pvd)
(see all for 1pvd)
- Cofactors
- Thiamine(1+) diphosphate(3-) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glu51B activates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor by abstracting a proton from the NH group of the 6-membered ring. This results in double bond rearrangement and the abstraction of a proton from the N=CH-S moiety. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate then attacks the carbonyl carbon of pyruvate in a nucleophilic addition that results in the cofactor undergoing another double bond rearrangement and abstracting the proton back from Glu51B. Carbon dioxide eliminates from the covalently attached pyruvate intermediate. Thiamine diphosphate acts as an electron sink. Thiamine diphosphate initiates a double bond rearrangement, which results in the intermediate deprotonating Asp28B, which in turn deprotonates His115B. Glu51B deprotonates thiamine diphosphate, which initiates a double bond rearrangement, that deprotonates the hydroxide of the intermediate, and results in a reformation of the carbanionic activated cofactor and the acetaldehyde product. Finally, His115B deprotonates water. The carbanion of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor deprotonates the adjacent amine, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of Glu51B.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1pvd) | ||
| Asp444, Asn471, Gly473 (main-C) | Asp444(443)A, Asn471(470)A, Gly473(472)A (main-C) | Coordinates the magnesium ion | metal ligand |
| Glu477 | Glu477(476)A | Perturbates the pKa of Asp28B. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Glu51 | Glu51(50)B | This is a key residue in cofactor activation. It acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His114 | His114(113)B | Perturbates the pKa of His115B. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Asp28, His115 | Asp28(27)B, His115(114)B | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Gly413 (main-C) | Gly413(412)A (main-C) | Helps stabilise the cofactor in its active conformation. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aldol addition, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decarboxylation, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, proton relay, intramolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Liu M et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 7355-7368. Catalytic Acid−Base Groups in Yeast Pyruvate Decarboxylase. 1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis and Steady-State Kinetic Studies on the Enzyme with the D28A, H114F, H115F, and E477Q Substitutions†. DOI:10.1021/bi002855u. PMID:11412090.
- Andrews FH et al. (2013), FEBS J, 280, 6395-6411. Using site-saturation mutagenesis to explore mechanism and substrate specificity in thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzymes. DOI:doi:10.1111/febs.12459.
- Hou Q et al. (2012), Theor Chem Acc, 131,A QM/MM study on the catalytic mechanism of pyruvate decarboxylase. DOI:10.1007/s00214-012-1280-1.
- Wang J et al. (2005), J Phys Chem B, 109, 18664-18672. Theoretical Study toward Understanding the Catalytic Mechanism of Pyruvate Decarboxylase. DOI:10.1021/jp052802s. PMID:16853401.
- Tittmann K et al. (1998), FEBS Lett, 441, 404-406. Activation of thiamine diphosphate in pyruvate decarboxylase fromZymomonas mobilis. DOI:10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01594-4. PMID:9891980.
- Arjunan P et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 256, 590-600. Crystal structure of the thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae at 2.3 A resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0111. PMID:8604141.

Step 1. Glu51B deprotonates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of the N=CH-S group, activating the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly413(412)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| His114(113)B | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| His115(114)B | polar interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp28(27)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu51(50)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp444(443)A | metal ligand |
| Asn471(470)A | metal ligand |
| Gly473(472)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu51(50)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate attacks the carbonyl carbon of pyruvate in a nucleophilic addition that results in the cofactor undergoing double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of Glu51B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly413(412)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His114(113)B | hydrogen bond donor, polar interaction |
| His115(114)B | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp28(27)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu477(476)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu51(50)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp444(443)A | metal ligand |
| Asn471(470)A | metal ligand |
| Gly473(472)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu51(50)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aldol addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 3. Carbon dioxide eliminates from the covalently attached pyruvate intermediate. Thiamine diphosphate acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly413(412)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His114(113)B | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115(114)B | polar interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp28(27)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu477(476)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Glu51(50)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp444(443)A | metal ligand |
| Asn471(470)A | metal ligand |
| Gly473(472)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, decarboxylation, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 4. Thiamine diphosphate initiates a double bond rearrangement, which results in the intermediate deprotonating Asp28B, which in turn deprotonates His115B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly413(412)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His114(113)B | polar interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His115(114)B | hydrogen bond donor, polar interaction |
| Asp28(27)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Glu51(50)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp444(443)A | metal ligand |
| Asn471(470)A | metal ligand |
| Gly473(472)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp28(27)B | proton donor |
| His115(114)B | proton donor |
| Asp28(27)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), proton relay
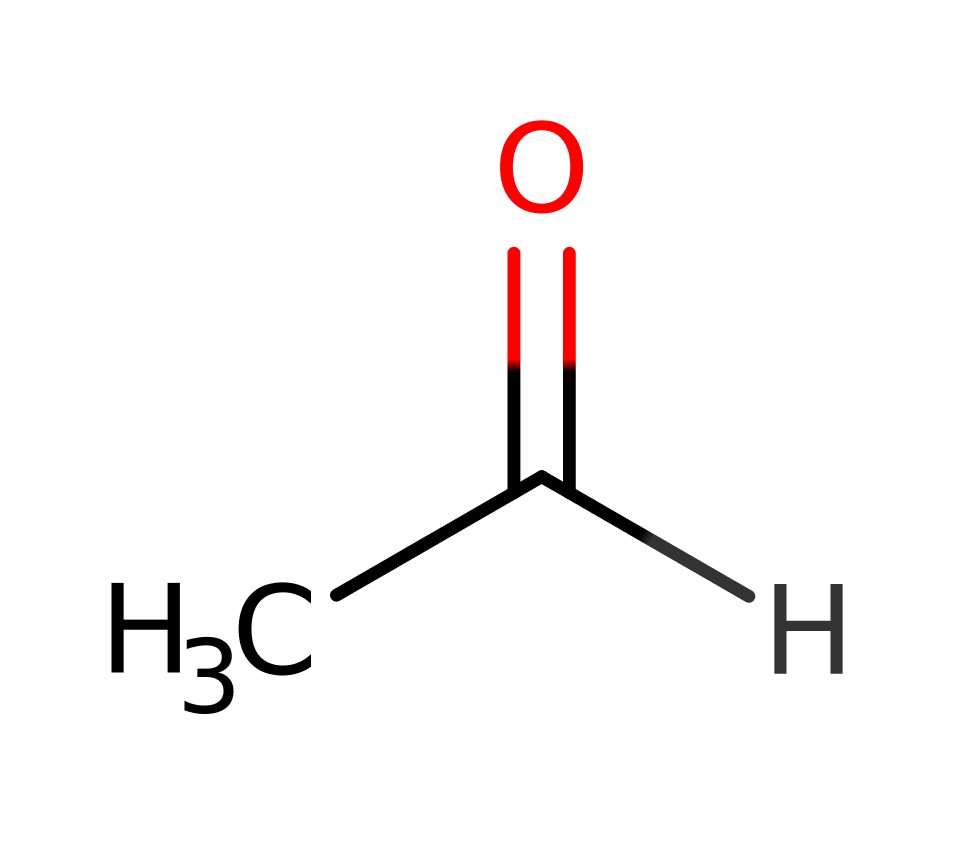
Step 5. Glu51B deprotonates thiamine diphosphate, which initiates a double bond rearrangement, that deprotonates the hydroxide of the intermediate, and results in a reformation of the carbanionic activated cofactor and the acetaldehyde product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly413(412)A (main-C) | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His114(113)B | polar interaction |
| His115(114)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp28(27)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu51(50)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp444(443)A | metal ligand |
| Asn471(470)A | metal ligand |
| Gly473(472)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu51(50)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), overall product formed, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 6. His115B deprotonates water. The carbanion of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor deprotonates the adjacent amine, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of Glu51B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly413(412)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| His114(113)B | polar interaction, activator |
| His115(114)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu51(50)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp444(443)A | metal ligand |
| Asn471(470)A | metal ligand |
| Gly473(472)A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| His115(114)B | proton acceptor |
| Glu51(50)B | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: