Aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase
Aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) catalyses the conversion of serotonin to N-acetylserotonin, the precursor to the circadian neurohormone melatonin, important in coordinating daily and seasonal rhythms with light levels in the surrounding environment. Levels of AANAT (and levels of melatonin) are controlled by the proteolysis of AANAT.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q29495
 (2.3.1.87)
(2.3.1.87)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Ovis aries (sheep)

- PDB
-
1b6b
- MELATONIN BIOSYNTHESIS: THE STRUCTURE OF SEROTONIN N-ACETYLTRANSFERASE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION SUGGESTS A CATALYTIC MECHANISM
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.630.30
 (see all for 1b6b)
(see all for 1b6b)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.87)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His122 initiates the reaction by deprotonating the indol substrate, which adds to the carbonyl carbon of acyl-CoA. The CoA is eliminated and reprotonated from Tyr168, which returns to its native state by deprotonating the product secondary amine.
It remains uncertain whether Tyr168 or His120 acts as the proton donor to the coenzyme-A anion, although crystallographic data would suggest His120 to be situated too far from the acyl-CoA binding site to be directly involved. The structural element Loop1 appears to undergo significant changes in organisation during substrate binding. Pro64, which is positioned within this flexible region, has been shown to be crucial for efficient substrate recognition.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1b6b) | ||
| Tyr168, His122 | Tyr168(141)A, His122(95)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser97, Leu111 (main-C), Leu124 (main-N) | Ser97(70)A, Leu111(84)A (main-C), Leu124(97)A (main-N) | Activate the catalytic general acid/base residues. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Hickman AB et al. (1999), Mol Cell, 3, 23-32. Melatonin biosynthesis: the structure of serotonin N-acetyltransferase at 2.5 A resolution suggests a catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.2210/pdb1b6b/pdb. PMID:10024876.
- Klein DC (2007), J Biol Chem, 282, 4233-4237. Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase: "the Timezyme". DOI:10.1074/jbc.R600036200. PMID:17164235.
- Scheibner KA et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 18118-18126. Investigation of the Roles of Catalytic Residues in SerotoninN-Acetyltransferase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m200595200. PMID:11884405.
- Zheng W et al. (2001), Chem Biol, 8, 379-389. Mechanistic studies on the alkyltransferase activity of serotonin N-acetyltransferase. DOI:10.1016/s1074-5521(01)00020-5.

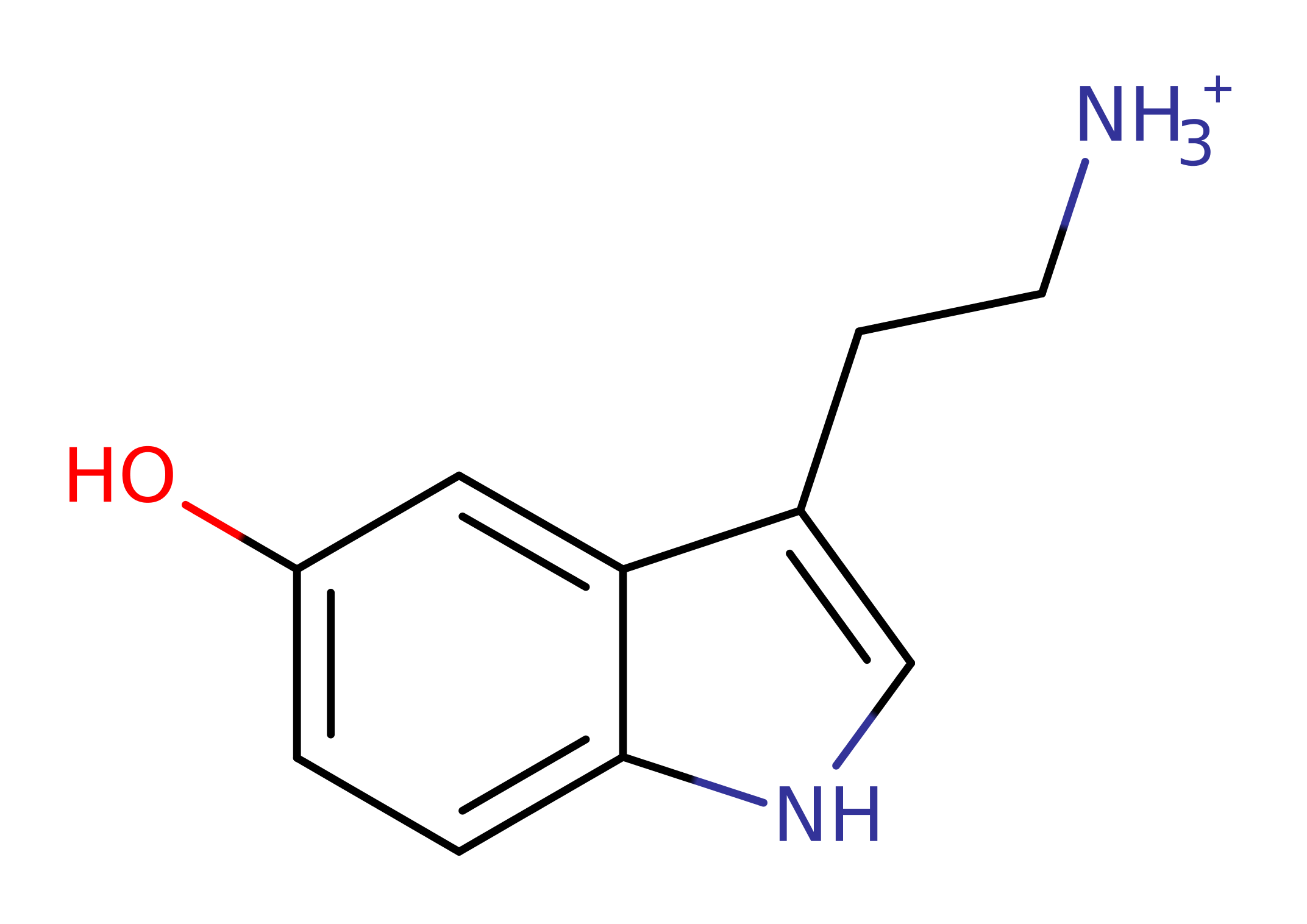
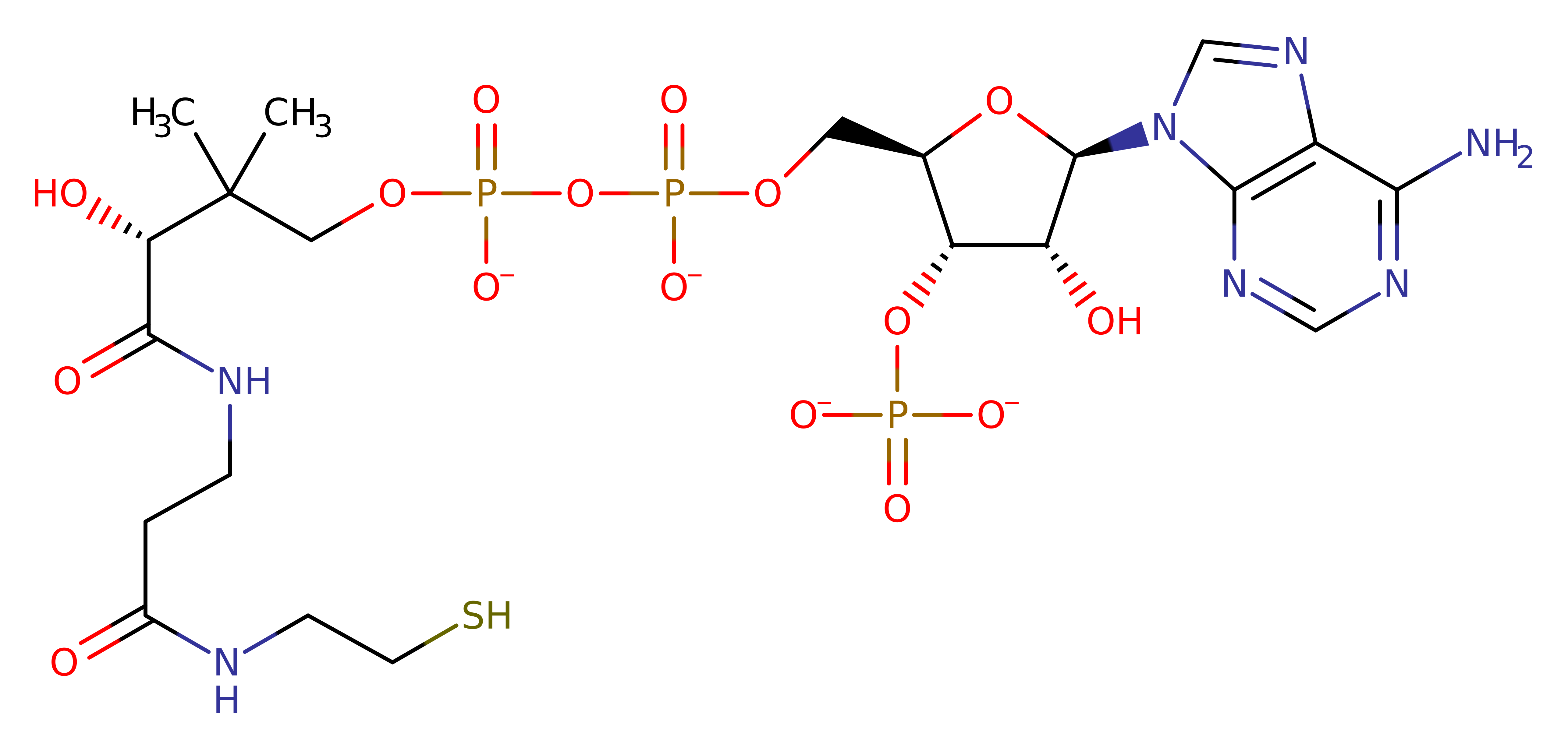
Step 1. His122 deprotonates the amine of 3-(2-aminoethyl)-indol-5-ol, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of acyl-CoA in an addition reaction
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu111(84)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Leu124(97)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser97(70)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His122(95)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr168(141)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His122(95)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating CoA, which deprotonated Tyr168
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr168(141)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu111(84)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser97(70)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His122(95)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu124(97)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr168(141)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr168(141)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Leu111(84)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser97(70)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His122(95)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu124(97)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr168(141)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, intermediate terminated, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His122(95)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser97(70)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu111(84)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His122(95)A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: