Benzoylformate decarboxylase
Benzoylformate decarboxylase is a thiamine diphosphate dependent enzyme. It catalyses the formation of carbon dioxide from bezoylformate and is part of the pathway that synthesises benzoate from (R)-mandelate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P20906
 (4.1.1.7)
(4.1.1.7)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas putida (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1mcz
- BENZOYLFORMATE DECARBOXYLASE FROM PSEUDOMONAS PUTIDA COMPLEXED WITH AN INHIBITOR, R-MANDELATE
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1220
 3.40.50.970
3.40.50.970  (see all for 1mcz)
(see all for 1mcz)
- Cofactors
- Thiamine(1+) diphosphate(3-) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.1.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This alternative mechanism is based off more up to date computational experiments (26/06/2018), which used density functional theory calculations. The mechanism begins with intramolecular proton transfer within the cofactor which activates it for nucleophilic attack on phenylglyoxylate. This results in an oxyanion being formed which can accept a proton from the His70/Glu28 proton relay system. Carbon dioxide is then eliminated with TDP acting as an electron sink. TDP then tautomerizes, this is facilitated by another intramolecular proton transfer. The oxyanion is regenerated by the proton relay system, and its collapse leads to TDP being cleaved and the product being formed. TDP then undergoes a final intramolecular proton transfer which results in the cofactor being regenerated in its native state. See other mechanism for further references.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mcz) | ||
| His70, Glu28 | His70E, Glu28E | Part of a proton relay system throughout the mechanism. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25 (main-N), Ser26 | Gly25E (main-N), Ser26E | Stabilizes the reactant via hydrogen bonding. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, proton relay, decarboxylation, intramolecular elimination, tautomerisation (not keto-enol), overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Planas F et al. (2018), Front Chem, 6, 205-. A Theoretical Study of the Benzoylformate Decarboxylase Reaction Mechanism. DOI:10.3389/fchem.2018.00205. PMID:29998094.

Step 1. There is intramolecular proton transfer within the cofactor, resulting in an ylide being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used
Step 2. The carboanion of the ylide performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon resulting in an oxyanion intermediate being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation
Step 3. The oxyanion accepts a proton from His70, which accepts a proton from Glu28 in a proton relay.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | proton relay |
| His70E | proton acceptor |
| Glu28E | proton donor |
| His70E | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay
Step 4. Carbon dioxide is eliminated from the intermediate, with TDP acting as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, ingold: intramolecular elimination
Step 5. TDP initiates a double bond rearrangement which results in an intramolecular proton transfer within the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
tautomerisation (not keto-enol), proton relay
Step 6. The hydroxyl oxygen is deprotonated by the Glu28/His70 proton relay system, resulting in the formation of another oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His70E | proton relay |
| Glu28E | proton acceptor |
| His70E | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay
Step 7. The imine nitrogen of the cofactor then accepts a proton from the relay system.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His70E | proton relay |
| Glu28E | proton donor |
| His70E | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, proton transfer
Step 8. The collapse of the oxyanion leads to the elimination of TDP and the formation of the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, ingold: intramolecular elimination, intermediate terminated
Step 9. The cofactor is regenerated in its native state via an intramolecular proton transfer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
proton relay, native state of cofactor regeneratedIntroduction
In this 3rd proposed mechanism, based off the same 2018 computational study, decarboxylation occurs immediately after the formation of the substrate-cofactor intermediate. The difference barrier energies between these two mechanisms is not sufficiently high to conclude which is the more accurate. See the other mechanisms for the references.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mcz) |
Chemical Components
cofactor used, proton transfer, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, decarboxylation, intramolecular elimination, proton relay, tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences

Step 1. There is intramolecular proton transfer within the cofactor, resulting in an ylide being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
cofactor used, proton transfer
Step 2. The carboanion of the ylide performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon resulting in an oxyanion intermediate being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 3. Carbon dioxide is eliminated from the intermediate, with TDP acting as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, ingold: intramolecular elimination
Step 4. The enolate oxygen accepts a proton from the His70/Glu28 proton relay system.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His70E | proton relay |
| Glu28E | proton donor |
| His70E | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, proton transfer
Step 5. TDP initiates a double bond rearrangement which results in an intramolecular proton transfer within the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, tautomerisation (not keto-enol)
Step 6. The hydroxyl oxygen is deprotonated by the Glu28/His70 proton relay system, resulting in the formation of another oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His70E | proton relay |
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | proton donor |
| Glu28E | proton acceptor |
| His70E | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton relay, proton transfer
Step 7. The imine nitrogen of the cofactor then accepts a proton from the relay system.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His70E | proton relay |
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | proton acceptor |
| Glu28E | proton donor |
| His70E | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay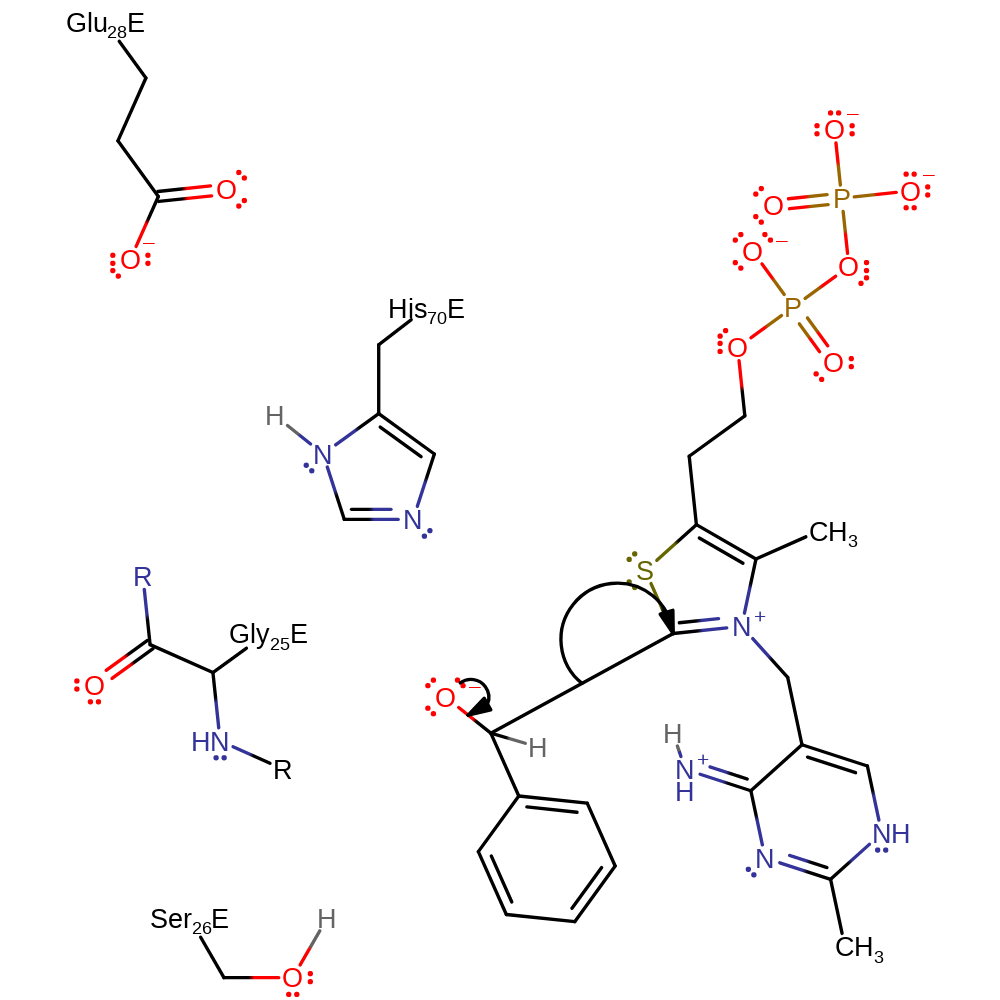
Step 8. The collapse of the oxyanion leads to the elimination of TDP and the formation of the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu28E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly25E (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly25E (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
intermediate terminated, ingold: intramolecular elimination, overall product formed
Step 9. The cofactor is regenerated in its native state via an intramolecular proton transfer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
native state of cofactor regenerated, proton relayIntroduction
Glu47E deprotonates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of the N=CH-S group, activating the thiamine diphosphate cofactor. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate attacks the carbonyl carbon of alpha-oxo-benzeneacetic acid in a nucleophilic addition. The formed oxyanion deprotonates His70E. Carbon dioxide eliminates from the covalently attached aromatic intermediate. Thiamine diphosphate acts as an electron sink. Thiamine diphosphate initiates a double bond rearrangement, which results in the intermediate being protonated by His281A. His70E deprotonates the hydroxide of the intermediate, which initiates an elimination which results in a reformation of the carbanionic activated cofactor and the benzaldehyde product. The carbanion of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor deprotonates the adjacent amine, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of Glu47E. His281A deprotonates water.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mcz) | ||
| Glu47 | Glu47E | Acts as a general acid/base, important for activating the thiamine diphosphate cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu28 | Glu28E | Activates His70B. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26 | Ser26E | Activates His281A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70, His281 | His70E, His281F | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gly401 (main-C) | Gly401F (main-C) | Stabilises the reactive intermediates of the thiamine-diphosphate cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, inferred reaction step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, aldol addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, bimolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Polovnikova ES et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 1820-1830. Structural and Kinetic Analysis of Catalysis by a Thiamin Diphosphate-Dependent Enzyme, Benzoylformate Decarboxylase†. DOI:10.1021/bi026490k. PMID:12590569.
- Hasson MS et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 9918-9930. The Crystal Structure of Benzoylformate Decarboxylase at 1.6 Å Resolution: Diversity of Catalytic Residues in Thiamin Diphosphate-Dependent Enzymes†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi973047e. PMID:9665697.

Step 1. Glu47E deprotonates the thiamine diphosphate cofactor, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of the N=CH-S group, activating the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu47E | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly401F (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu47E | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), cofactor used, inferred reaction step
Step 2. The carbanion of thiamine diphosphate attacks the carbonyl carbon of alpha-oxo-benzeneacetic acid in a nucleophilic addition. The formed oxyanion deprotonates His70E
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu47E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly401F (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, aldol addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 3. Carbon dioxide eliminates from the covalently attached aromatic intermediate. Thiamine diphosphate acts as an electron sink.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu47E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly401F (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), overall product formed, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse
Step 4. Thiamine diphosphate initiates a double bond rearrangement, which results in the intermediate being protonated by His281A.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu47E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly401F (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), intermediate formation
Step 5. His70E deprotonates the hydroxide of the intermediate, which initiates an elimination which results in a reformation of the carbanionic activated cofactor and the benzaldehyde product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu47E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly401F (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | hydrogen bond donor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His70E | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 6. The carbanion of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor deprotonates the adjacent amine, which initiates double bond rearrangement that results in the deprotonation of Glu47E. His281A deprotonates water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu47E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly401F (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser26E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His70E | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu28E | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His281F | proton acceptor |
| Glu47E | proton donor |




 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: 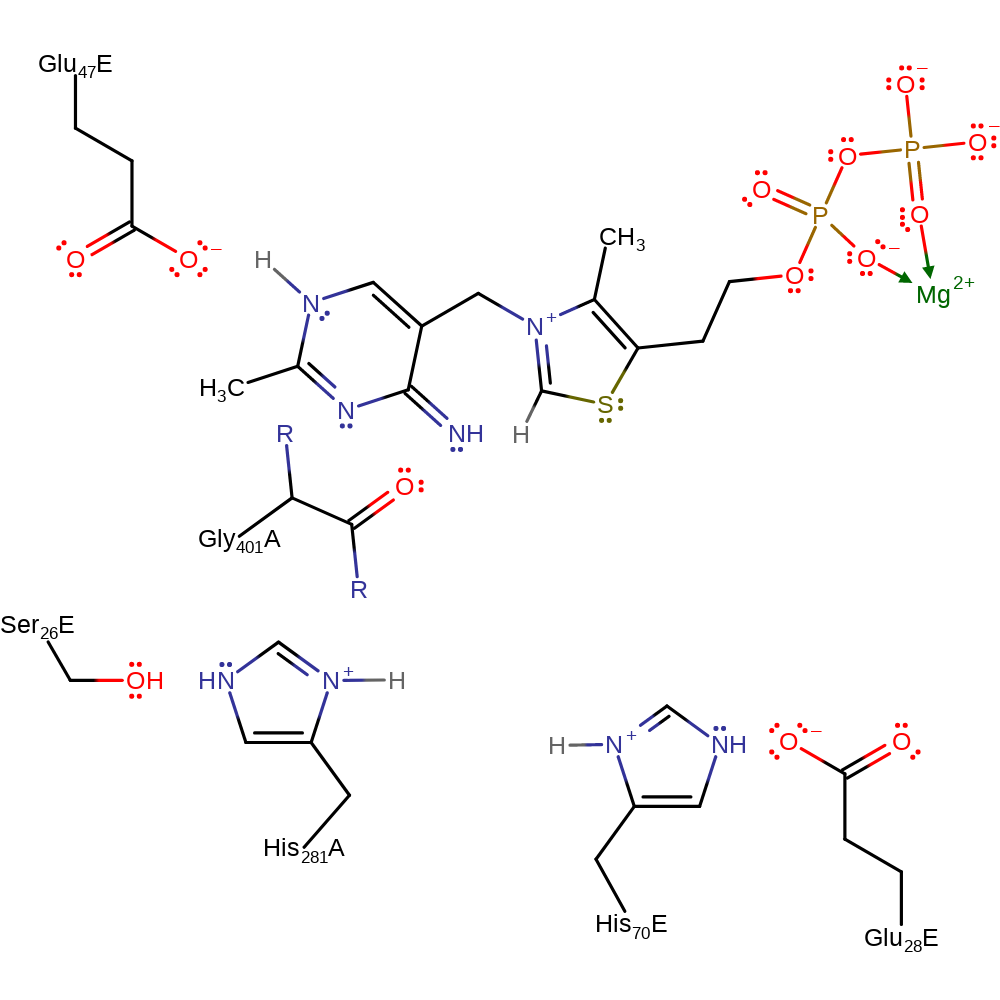 Download:
Download: