Receptor protein-tyrosine kinase
Phosphorylated insulin receptor tyrosine kinase from Homo sapiens catalyses the phosphorylation of Tyr on intracellular proteins that are related to the STATK pathway. The phosphoryl group is transferred from ATP to form ADP. On carrying out this function, the enzyme activates the signalling cascade inside the cell. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is thought to have a restricted range of protein substrates, with a consensus YMXM phosphorylation motif having been defined [PMID:17085043].
There are two alternative mechanisms suggested for this enzyme, and there is still some debate as to whether this enzyme works via the associative (SN2-type) mechanism or the dissociative (SN1-type) mechanism. However, experimental and QM/MM studies, as well as crystallographic evidence, seems to support the dissociative mechanism [PMID:17085043, PMID:16023488, PMID:19334696 and Pichierri et al.].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P06213
 (2.7.10.1)
(2.7.10.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1ir3
- PHOSPHORYLATED INSULIN RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASE IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE SUBSTRATE AND ATP ANALOG
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.510.10
 (see all for 1ir3)
(see all for 1ir3)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.10.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The entry represents the proposed dissociative (SN1-type) mechanism. Here a metaphosphate anion is eliminated from the ATP substrate in an intramolecular elimination. This extremely reactive intermediate then attacks the protein tyrosine substrate in an addition reaction with concomittant deprotonation of the hydroxyl by the metaphosphate anion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ir3) | ||
| Asp1177, Asn1164 | Asp1150(173)A, Asn1137(160)A | Form Mg binding site | metal ligand |
| Asp1159 | Asp1132(155)A | Activates the substrate tyrosine, increasing its nucleophilicty. | increase nucleophilicity, steric role |
| Arg1163 | Arg1136(159)A | Hydrogen bonds to the negatively charged oxygen of the gamma phosphate, stabilising the transition state. | increase electrophilicity, promote heterolysis, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, heterolysis, overall reactant used, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, rate-determining step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Pichierri F et al. (2003), Theochem, 622, 257-267. Mechanism of tyrosine phosphorylation catalyzed by the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase: a semiempirical PM3 study. DOI:10.1016/s0166-1280(02)00651-6.
- Zhou B et al. (2009), J Phys Chem A, 113, 5144-5150. A computational study of the phosphorylation mechanism of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. DOI:10.1021/jp810827w. PMID:19334696.
- Bose R et al. (2006), Curr Opin Struct Biol, 16, 668-675. Protein tyrosine kinase–substrate interactions. DOI:10.1016/j.sbi.2006.10.012. PMID:17085043.
- Hines AC et al. (2005), Bioorg Chem, 33, 285-297. Bisubstrate analog probes for the insulin receptor protein tyrosine kinase: Molecular yardsticks for analyzing catalytic mechanism and inhibitor design. DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2005.02.002. PMID:16023488.
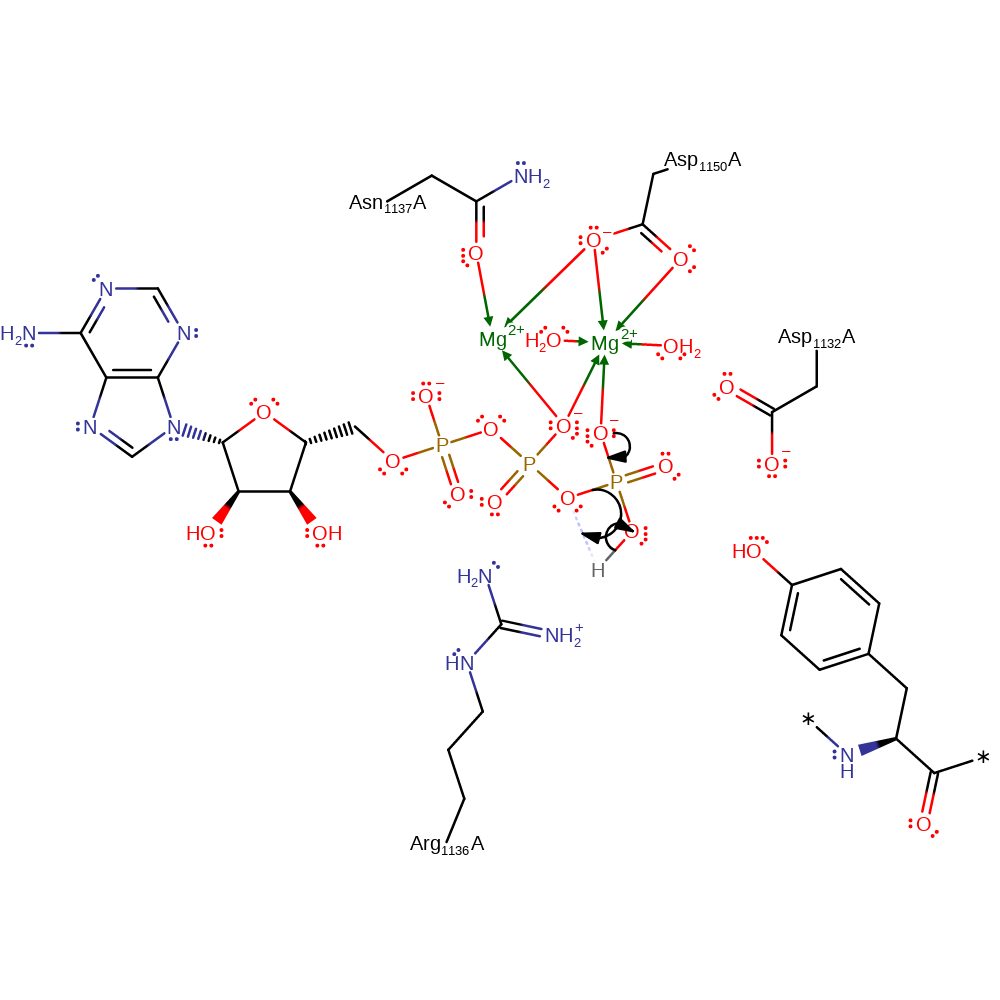
Step 1.
The gamma phosphate of the ATP substrate eliminates itself in a heterolysis, resulting in the transfer of a proton from the gamma phosphate to the beta phosphate and formation of ADP and the highly reactive metaphosphate anion.
It should be noted that whilst the metaphosphate (PO3-) ion is very reactive and not yet observed in enzymatic phosphoryl transfer reactions, there is indirect evidence of its existence through the use of AlF3 and BeF3 mimics, as well as computational studies [doi:10.1016/s0166-1280(02)00651-6].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp1132(155)A | steric role |
| Arg1136(159)A | electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Asn1137(160)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1150(173)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, heterolysis, overall reactant used, dephosphorylation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, rate-determining step
Step 2. The protein tyrosine initiated a nucleophilic attack on the metaphosphate intermediate in an addition reaction, the resulting species then deprotonates the tyrosine phenol group to form the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp1132(155)A | increase nucleophilicity, steric role |
| Arg1136(159)A | electrostatic stabiliser, increase electrophilicity |
| Asn1137(160)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1150(173)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, overall reactant used, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
This entry represents the associative (SN2-type) mechanism. Here Asp1132 deprotonates the substrate Tyr hydroxide, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the gamma phosphate of ATP, which forms a pentavalent transition state. The transition state is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to Arg 1136. The leaving group is protonated by the protonated Asp 1132, assisted by the interaction of Mg(II) which serves to make the oxygen lone pair more available for protonation.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ir3) | ||
| Asp1177, Asn1164 | Asp1150(173)A, Asn1137(160)A | Form Mg binding site | metal ligand |
| Asp1159 | Asp1132(155)A | Acts as a general base to deprotonate the Tyr residue hydroxide of the substrate, activating it for nucleophilic attack. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg1163 | Arg1136(159)A | Hydrogen bonds to the negatively charged oxygen of the gamma phosphate, stabilising the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Pichierri F et al. (2003), Theochem, 622, 257-267. Mechanism of tyrosine phosphorylation catalyzed by the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase: a semiempirical PM3 study. DOI:10.1016/s0166-1280(02)00651-6.

Step 1. Asp11592 deprotonates the substrate Tyr hydroxide, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the gamma phosphate of ATP, which forms a pentavalent transition state. The transition state is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to Arg 1163.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg1136(159)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn1137(160)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1150(173)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1132(155)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 2. The leaving group is protonated by the protonated Asp 1159, assisted by the interaction of Mg(II) which serves to make the oxygen lone pair more available for protonation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg1136(159)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn1137(160)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1150(173)A | metal ligand |
| Asp1132(155)A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: