Isocitrate lyase
Isocitrate lyase catalyses the reversible lysis of a C-C bond of isocitrate to form glycoxylate and succinate. The enzyme directs acetyl-CoA away from beta-oxidation of fatty acids into the glyoxylate shunt pathway, giving a net carbon gain. It plays a key role in the persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within humans.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P9WKK7
 (4.1.3.1)
(4.1.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1f61
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ISOCITRATE LYASE FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.60
 (see all for 1f61)
(see all for 1f61)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.3.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This proposal suggests that there is no covalent intermediate, and that Cys191 simply abstracts the alpha-proton from the succinate substrate.
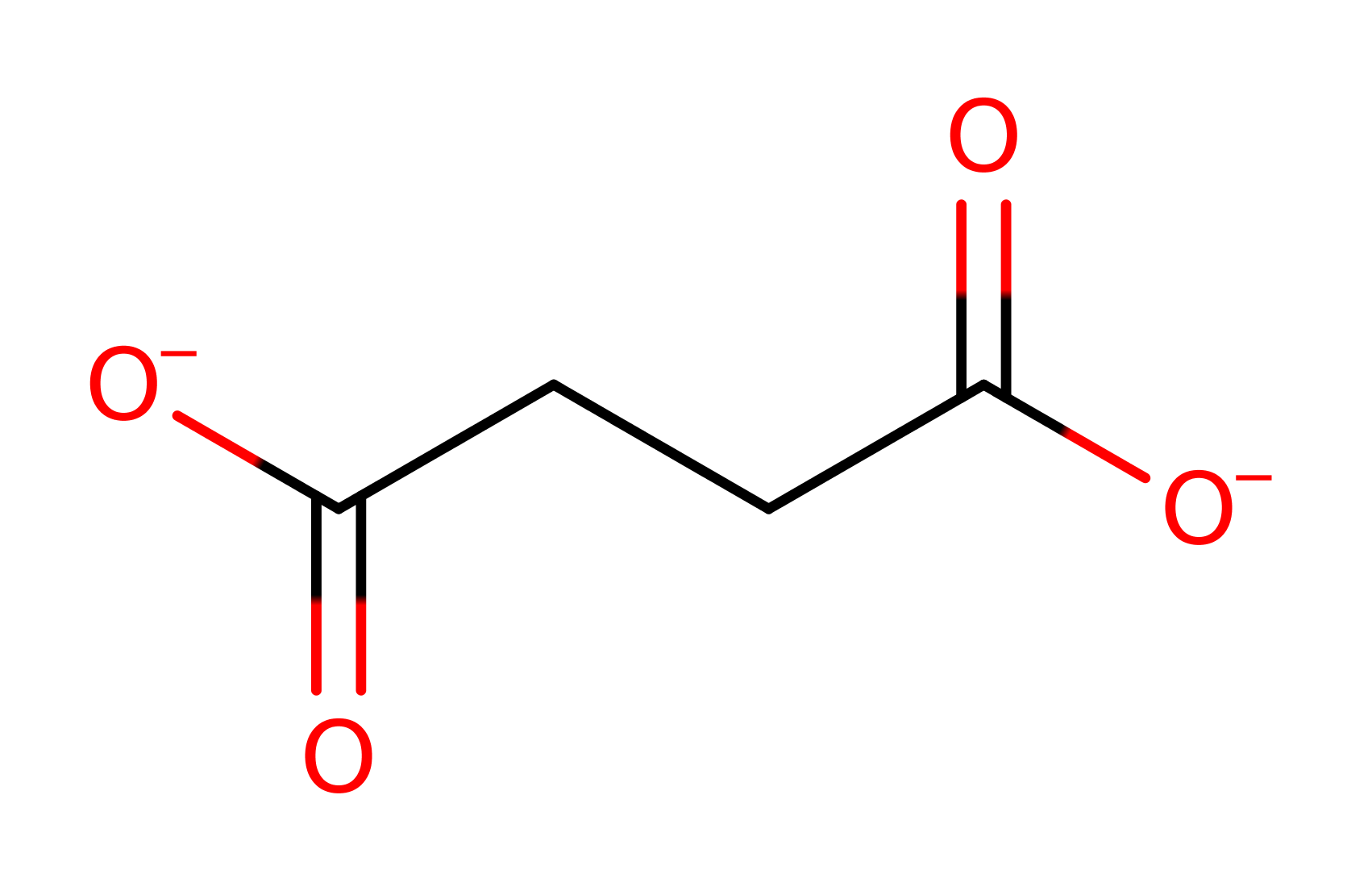
In the reverse mechanism glyoxylate binds first to the enzyme, followed by succinate to form a tertiary complex. A Claisen condensation occurs, via the formation of an enolic intermediate to form the isocitrate product. The key step in the reaction is the deprotonation of the alpha proton of the carboxylate of succinate by Cys191, forming 4,4-di-hydroxy-3-butenoate. This intermediate then attacks the glyoxylate substrate. An unidentified residue is thought to act as a the general acid to the 6 carbon intermediate, while an oxyanion hole stabilises the negative charge on the intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1f61) | ||
| Asp153 | Asp153(154)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Cys191 | Cys191(192)A | The residue acts as a base towards the succinate substrate, abstracting the alpha proton and leading to the formation of the 4,4-di-hydroxy-3-butenoate intermediate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| His180, Arg228 | His180(181)A, Arg228(229)A | Forms an oxyanion hole which stabilises the anionic intermediate. Both of these residues (along with Tyr89) have been postulated to act as the general acid required for protonation of the alkoxide to form isocitrate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser315, Ser317 | Ser315(316)A, Ser317(318)A | These residues are important in stabilising the dioxyanion of the aci-carboxylate of succinate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His193 | His193(194)A | The residue is thought to act as a general base towards the catalytic Cys191, although crystallographic data suggests that proton abstraction may not be direct over the 5A separation | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, proton relay, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Sharma V et al. (2000), Nat Struct Biol, 7, 663-668. Structure of isocitrate lyase, a persistence factor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1038/77964. PMID:10932251.
- Park Y et al. (2016), J Struct Biol, 194, 395-403. Crystal structure and functional analysis of isocitrate lyases from Magnaporthe oryzae and Fusarium graminearum. DOI:10.1016/j.jsb.2016.03.019. PMID:27016285.
- Moynihan MM et al. (2014), Biochemistry, 53, 178-187. Cysteine Is the General Base That Serves in Catalysis by Isocitrate Lyase and in Mechanism-Based Inhibition by 3-Nitropropionate. DOI:10.1021/bi401432t. PMID:24354272.
- Liu S et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 2949-2962. Crystal Structures of 2-Methylisocitrate Lyase in Complex with Product and with Isocitrate Inhibitor Provide Insight into Lyase Substrate Specificity, Catalysis and Evolution†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi0479712. PMID:15723538.
- Britton K et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 349-362. The crystal structure and active site location of isocitrate lyase from the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00117-9. PMID:10801489.
- Rehman A et al. (1997), Curr Microbiol, 35, 14-17. Lysine 194 Is Functional in Isocitrate Lyase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1007/s002849900203.
- Rehman A et al. (1997), Curr Microbiol, 35, 267-269. Cysteine 195 Has a Critical Functional Role in Catalysis by Isocitrate Lyase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1007/s002849900251.
- Rehman A et al. (1997), Curr Microbiol, 34, 205-211. Serine319 and 321 Are Functional in Isocitrate Lyase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1007/s002849900169.

Step 1. His193 deprotonates Cys191 which in turn deprotonates the alpha carbon of succinate to form the enolte.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His193(194)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys191(192)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Arg228(229)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His180(181)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser315(316)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser317(318)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp153(154)A | metal ligand |
| His193(194)A | proton acceptor |
| Cys191(192)A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, proton relay
Step 2. The intermedite reforms the keto form with concomitant addition to the glyoxylate substrate to form the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His193(194)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys191(192)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg228(229)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His180(181)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser315(316)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser317(318)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp153(154)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic additionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His193(194)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys191(192)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg228(229)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His180(181)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser315(316)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser317(318)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp153(154)A | metal ligand |
| His193(194)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepIntroduction
This alternative mechanism has been suggested in which Cys191 acts forms a covalent bond to the glyoxylate substrate. Here the Cys191 is activated by His193 and then acts as a nucleophile, forming a tetrahedral, covalently bound, intermediate of glyoxylate. The succinate anion then attacks the hemimercaptal carbon of glyoxylate, and the thiolate anion would act as an effective leaving group, especially when facilitated by reformation of the ion pair.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1f61) | ||
| Asp153 | Asp153(154)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Cys191 | Cys191(192)A | Acts as a general acid/base (the thiol proton is abstracted by His193 in an activation step) and then as a catalytic nucleophile. | covalent catalysis, proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| His180, Arg228 | His180(181)A, Arg228(229)A | Forms an oxyanion hole which stabilises the anionic intermediate | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser315, Ser317 | Ser315(316)A, Ser317(318)A | These residues are important in stabilising the dioxyanion of the aci-carboxylate of succinate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His193 | His193(194)A | Acts as a general acid/base, abstracting the thiol proton of Cys191. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
Chemical Components
References
- Diehl P et al. (1994), J Bacteriol, 176, 927-931. The importance of four histidine residues in isocitrate lyase from Escherichia coli. PMID:8300547.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys191(192)A | covalent catalysis, proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| His193(194)A | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| His180(181)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg228(229)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser315(316)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser317(318)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp153(154)A | metal ligand |



 Download:
Download: 