O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNASec:L-selenocysteinyl-tRNA synthase
A pyridoxal-phosphate dependent protein. Catalyses the conversion of O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) to selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec), part of the selenoprotein biosynthesis pathway. In archaea and eukarya, selenocysteine formation is achieved in a two-step process where O-phosphoseryl-tRNASec kinase phosphorylates the endogenous L-seryl-tRNASec to O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNASec, followed by the conversion of the mis-acylated amino acid-tRNA species to L-selenocysteinyl-tRNASec by Sep-tRNA:Sec-tRNA synthase. The active site is formed at the dimer interface of the tetrameric units, with residues necessary for catalysis originating from both chains.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q6LZM9
 (2.9.1.2)
(2.9.1.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Methanococcus maripaludis S2 (Archaea)

- PDB
-
2z67
- Crystal structure of archaeal O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) selenium transferase (SepSecS)
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.640.10
 (see all for 2z67)
(see all for 2z67)
- Cofactors
- Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.9.1.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The amino group of tRNA-SEC attacks the Schiff base immine, forming a substrate-cofactor-enzyme intermediate. A proton is transferred from the tRNA-SEC nitrogen to that of the Lys278. An external aldamine adduct is formed between the tRNA-SEC substrate and PLP cofactor on elimination of Lys278. Lys278 abstracts a proton from the C(a) of the external aldimine. Electron delocalisation across the aromatic ring facilitates rapid beta-elimination of phosphate, forming dehydroalanyl-tRNASec as the product. An activated water molecule attacks the selenophosphate phosphate substrate, resulting in displacement if selenium which attacks the dehydroalanyl intermediate. A proton is donated to the intermediate from Lys278. Lys278 attacks the external aldimine. An internal proton rearrangement occurs. The side chain nitrogen of Lys278 displaces the anionic form of L-Selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec), reforming the internal aldimine.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2z67) | ||
| Lys278 | Lys278(298)A | Covalently attached to the PLP cofactor in the ground state of the enzyme. Acts as a general acid/base as well as a catalytic nucleophile during the course of the reaction. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleofuge, polar interaction, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleophile, activator, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| His166, Arg72, Ser95, Gln102, Ala249, Arg307, Arg94 | His166(186)A, Arg72(92)B, Ser95(115)B, Gln102(122)B, Ala249(269)A, Arg307(327)B, Arg94(114)B | These residues form part of the PLP-binding pocket and help to stabilise the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton transfer, intramolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, schiff base formed, charge delocalisation, overall product formed, cofactor used, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, hydrolysis, intermediate terminated, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate collapseReferences
- Palioura S et al. (2009), Science, 325, 321-325. The Human SepSecS-tRNASec Complex Reveals the Mechanism of Selenocysteine Formation. DOI:10.1126/science.1173755. PMID:19608919.
- Itoh Y et al. (2014), J Mol Biol, 426, 1723-1735. Dimer-dimer interaction of the bacterial selenocysteine synthase SelA promotes functional active-site formation and catalytic specificity. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2014.01.003. PMID:24456689.
- Araiso Y et al. (2008), Nucleic Acids Res, 36, 1187-1199. Structural insights into RNA-dependent eukaryal and archaeal selenocysteine formation. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkm1122. PMID:18158303.
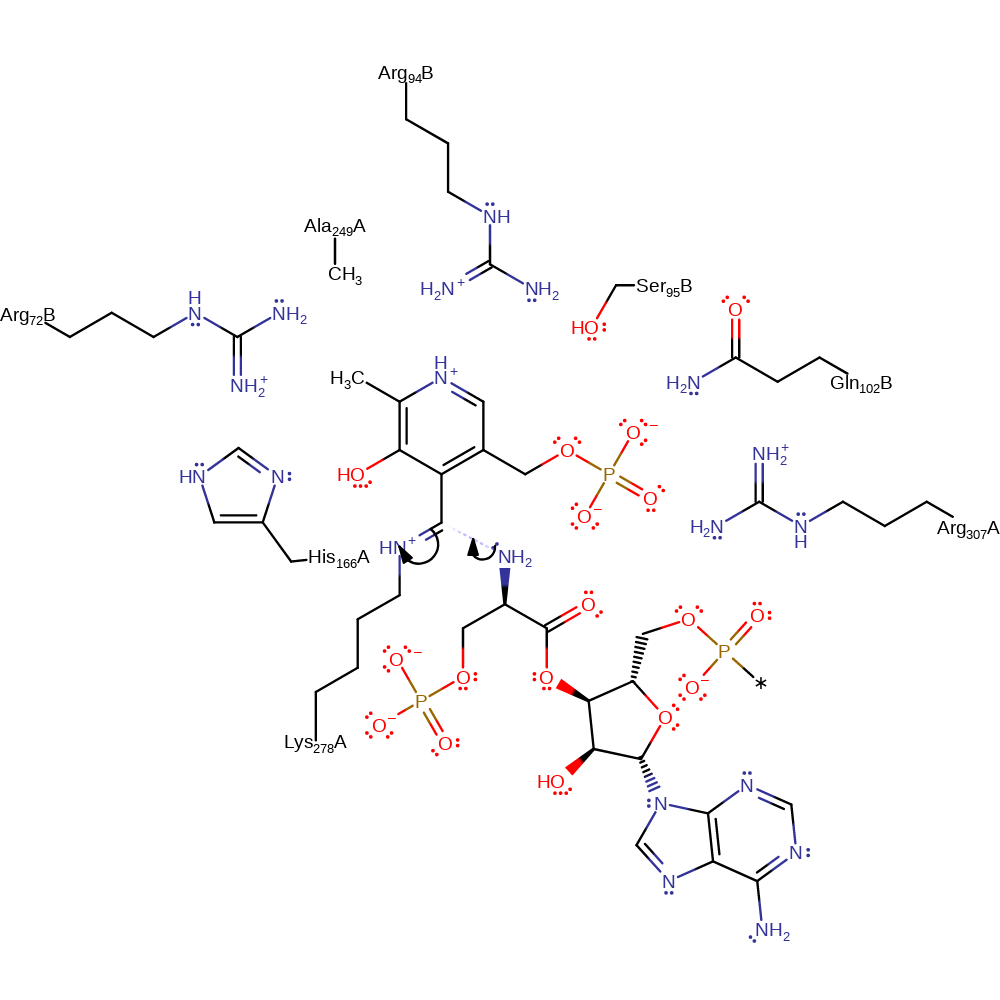
Step 1. The amino group of tRNA-SEC attacks the Schiff base immine, forming a substrate-cofactor-enzyme intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Arg72(92)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys278(298)A | activator, covalently attached |
| Lys278(298)A | electron pair acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 2. A proton is transferred from the tRNA-SEC nitrogen to that of the Lys278.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Arg72(92)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys278(298)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys278(298)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 3. An external aldamine adduct is formed between the tRNA-SEC substrate and PLP cofactor on elimination of Lys278.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | van der waals interaction, steric role |
| Arg72(92)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys278(298)A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, schiff base formed
Step 4. Lys278 abstracts a proton from the C(a) of the external aldimine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | van der waals interaction, steric role |
| Arg72(92)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys278(298)A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys278(298)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, charge delocalisation, intermediate formation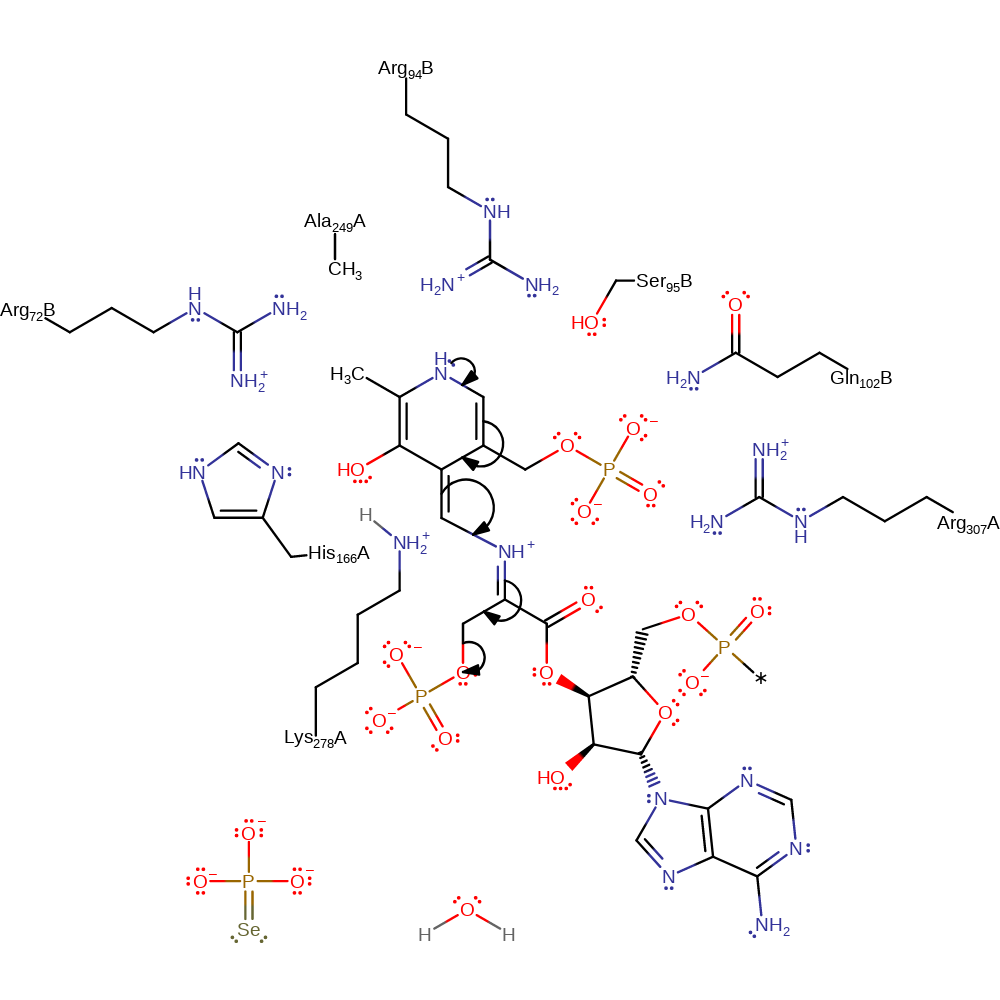
Step 5. Electron delocalization across the aromatic ring facilitates rapid beta-elimination of phosphate, forming dehydroalanyl-tRNASec as the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Arg72(92)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys278(298)A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, overall product formed, intermediate formation, cofactor used
Step 6. An activated water molecule attacks the selenophosphate phosphate substrate, resulting in displacement if selenium which attacks the dehydroalanyl intermediate. A proton is donated to the intermediate from Lys278.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | van der waals interaction, steric role |
| Arg72(92)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys278(298)A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys278(298)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, hydrolysisCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | van der waals interaction, steric role |
| Arg72(92)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys278(298)A | polar interaction, activator |
| Lys278(298)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Arg72(92)B | electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg307(327)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Lys278(298)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys278(298)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate terminated, inferred reaction step
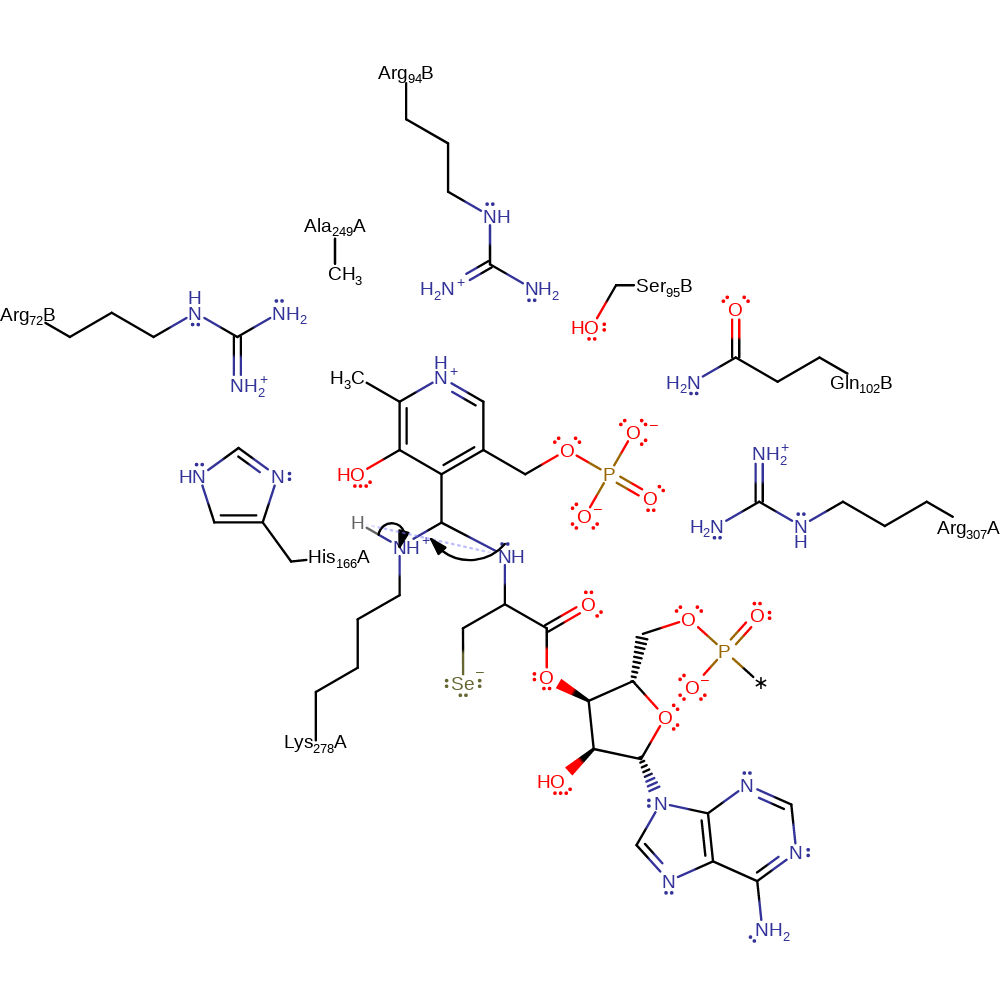
Step 9. The side chain nitrogen of Lys278 displaces the anionic form of L-Selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec), reforming the internal aldimine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Arg72(92)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg307(327)B | electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys278(298)A | covalently attached |
| Lys278(298)A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formed, intermediate collapse
Step 10. The terminal amine group deprotonates the unidentified base. The unidentified base is thought to correspond to an active site arginine residue, as seen in related mechanisms [PMID:18158303].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala249(269)A | van der waals interaction, steric role |
| Arg72(92)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser95(115)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His166(186)A | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg94(114)B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln102(122)B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg307(327)B | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys278(298)A | covalently attached |




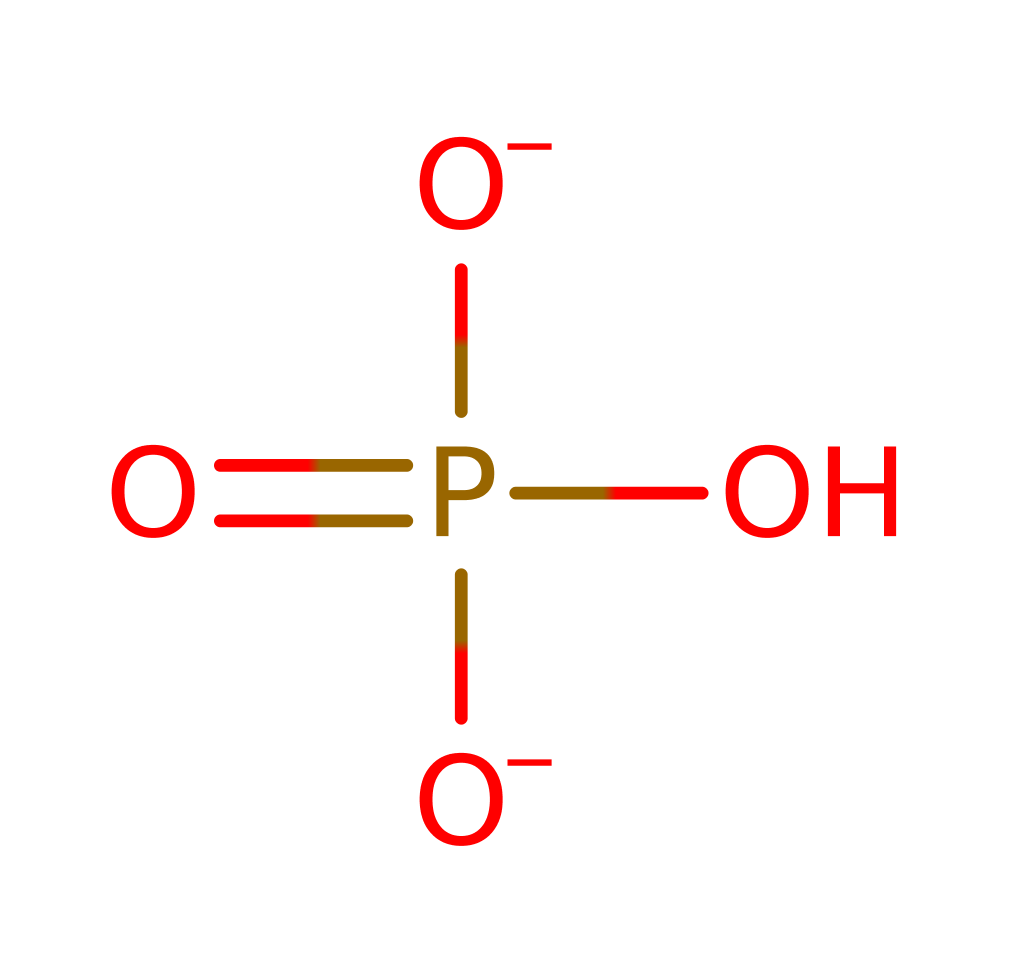

 Download:
Download: