Malonyl-CoA-acyl carrier protein transacylase
In Escherichia coli Fatty acid synthesis, FAS II includes a specific malonyl-CoA:ACP transacylase (MCAT), which catalyses specifically the elongation step. The initiation of each elongation step in the fatty acid synthesis cycle requires the transfer of a malonyl moiety from the respective CoA thioester to the -SH group of the phosphopantetheine arm of the acyl carrier protein (ACP), the central component of any FAS. MCAT, along with Acyl-carrier-protein S-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.38), is essential for the initiation of fatty-acid biosynthesis in bacteria. This enzyme also provides the malonyl groups for polyketide biosynthesis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0AAI9
 (2.3.1.39)
(2.3.1.39)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1mla
- THE ESCHERICHIA COLI MALONYL-COA:ACYL CARRIER PROTEIN TRANSACYLASE AT 1.5-ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION. CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A FATTY ACID SYNTHASE COMPONENT
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.366.10
 (see all for 1mla)
(see all for 1mla)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.39)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic residues consist of a conventional Ser-His dyad, which is unusually hydrogen to the main chain carbonyl of a glutamine residue. The reactions consists of an acylation step and the subsequent transfer of the acyl moiety proceed via tetrahedral intermediates, analogously to serine proteases. His201 deprotonates Ser92 to form a nucleophile. This subsequently attacks the carbonyl group-subsequent break down of this tetrahedral intermediate eliminates CoA forming a thioester with the enzyme. His201 then deprotonates a water molecule, which nucleophilically attacks the carbonyl group a second time break down results in elimination of the enzyme.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1mla) | ||
| Ser92 | Ser92A | Deprotonated by His201, performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group of the substrate to form a tetrahedral intermediate. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge, activator |
| His201 | His201A | Deprotonates Ser92 to activate it for nucleophilic attack. Similarly deprotonates a water molecule. Acts as a general acid to leaving groups of both tetrahedral intermediates. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, increase nucleophilicity |
| Leu93 (main-N), Arg117, Gln11 | Leu93A (main-N), Arg117A, Gln11A | Act to stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln250 (main-C) | Gln250A (main-C) | Forms a hydrogen bond to His201 to aid it in its role as general acid/base. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Serre L et al. (1995), J Biol Chem, 270, 12961-12964. The Escherichia coli malonyl-CoA:acyl carrier protein transacylase at 1.5-A resolution. Crystal structure of a fatty acid synthase component. DOI:10.2210/pdb1mla/pdb. PMID:7768883.
- Paiva P et al. (2018), ACS Catal, 8, 4860-4872. Understanding the Catalytic Machinery and the Reaction Pathway of the Malonyl-Acetyl Transferase Domain of Human Fatty Acid Synthase. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.8b00577.
- Serre L et al. (1994), J Mol Biol, 242, 99-102. Crystallization of the Malonyl Coenzyme A-Acyl Carrier Protein Transacylase from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1994.1559. PMID:8078074.
- Joshi VC (1972), Biochem J, 128, 43P.2-44P. Mechanism of malonyl-coenzyme A-acyl-carrier protein transacylase. DOI:10.1042/bj1280043pb. PMID:4563767.
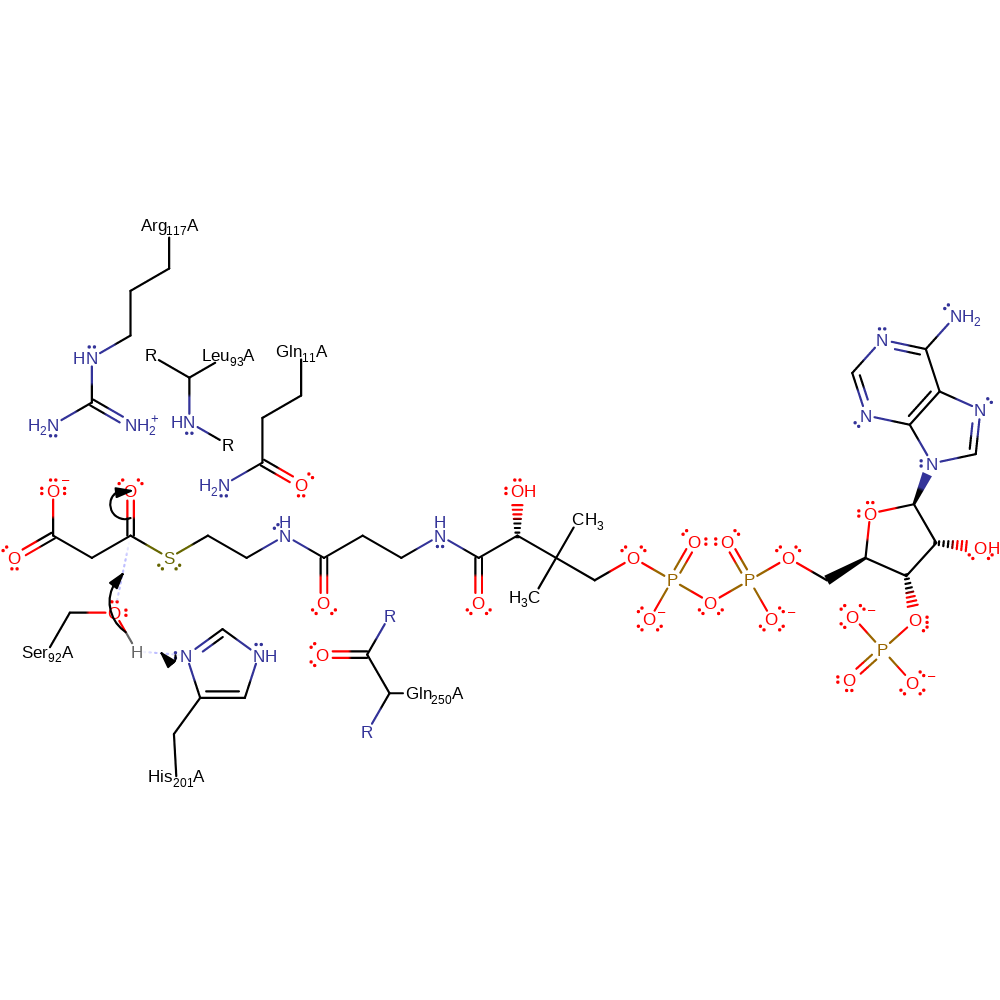
Step 1. Ser92 is activated towards nucleophilic attack at the thio-carbonyl of malonyl-CoA by the general base His201. A catalytic dyad is present between Ser92A and His201A, with the protonated form of His201A being stabilised through a hydrogen bond with the main chain carbonyl of Gln250A [PMID:7768883].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser92A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His201A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase nucleophilicity |
| Gln250A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| Gln11A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg117A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Ser92A | proton donor |
| His201A | proton acceptor |
| Ser92A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The tetrahedral enzyme-substrate intermediate collapses, eliminating the coenzyme A component.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser92A | covalently attached, activator |
| His201A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln250A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln11A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg117A | hydrogen bond donor, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu93A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 3. The terminal thiolate of the previously eliminated CoA acts as a general base towards His201.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser92A | covalently attached |
| His201A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln250A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln11A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg117A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu93A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His201A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed
Step 4. The enzyme-malonyl carbonyl linkage acts as an electrophile towards the terminal thiol of the acyl carrier protein which is deprotonated by the general acid His201.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His201A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 5. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses eliminating the malonyl acyl-carrier protein adduct and free serine side chain, which is reprotonated by the general acid His201A.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser92A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His201A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gln11A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg117A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His201A | proton donor |
| Ser92A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |


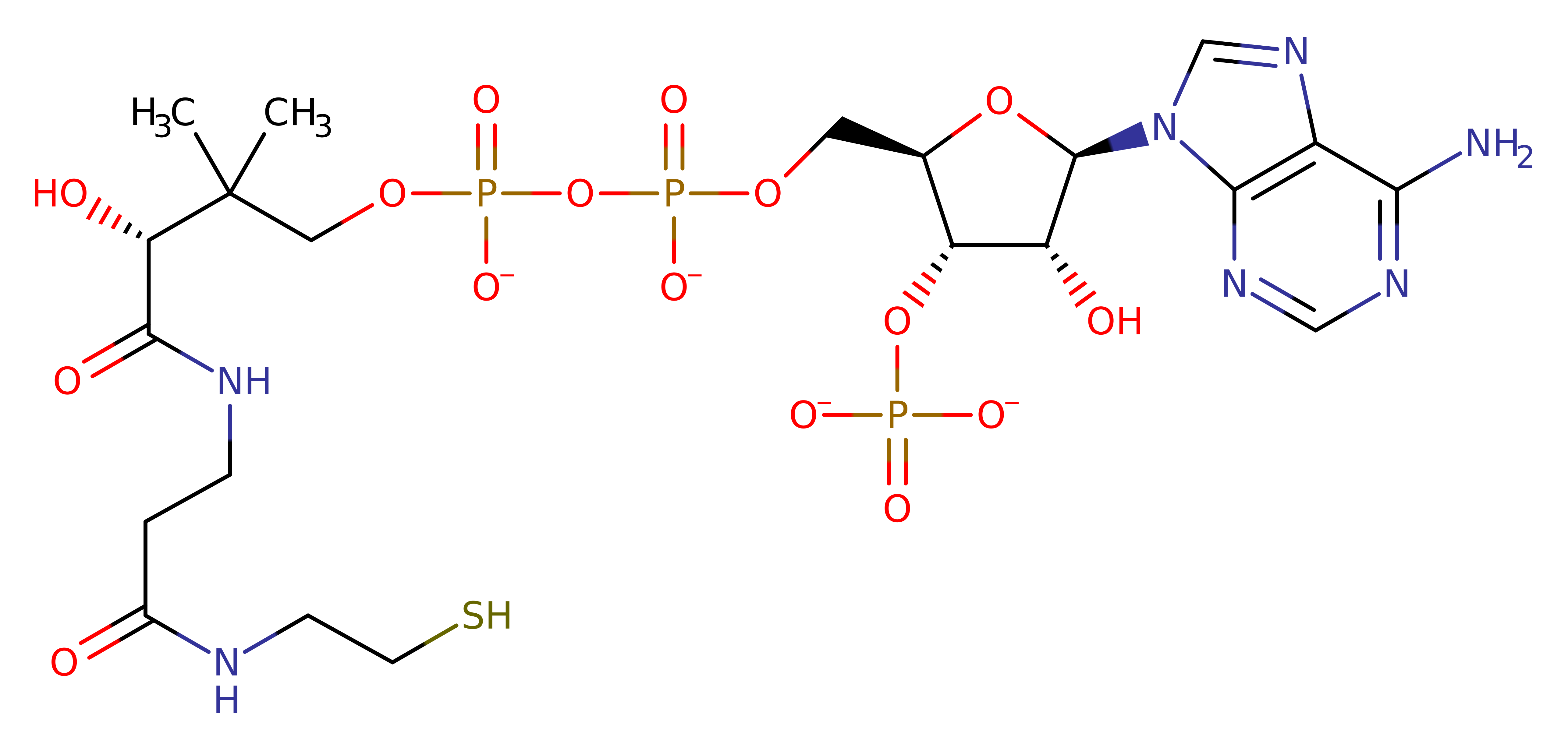

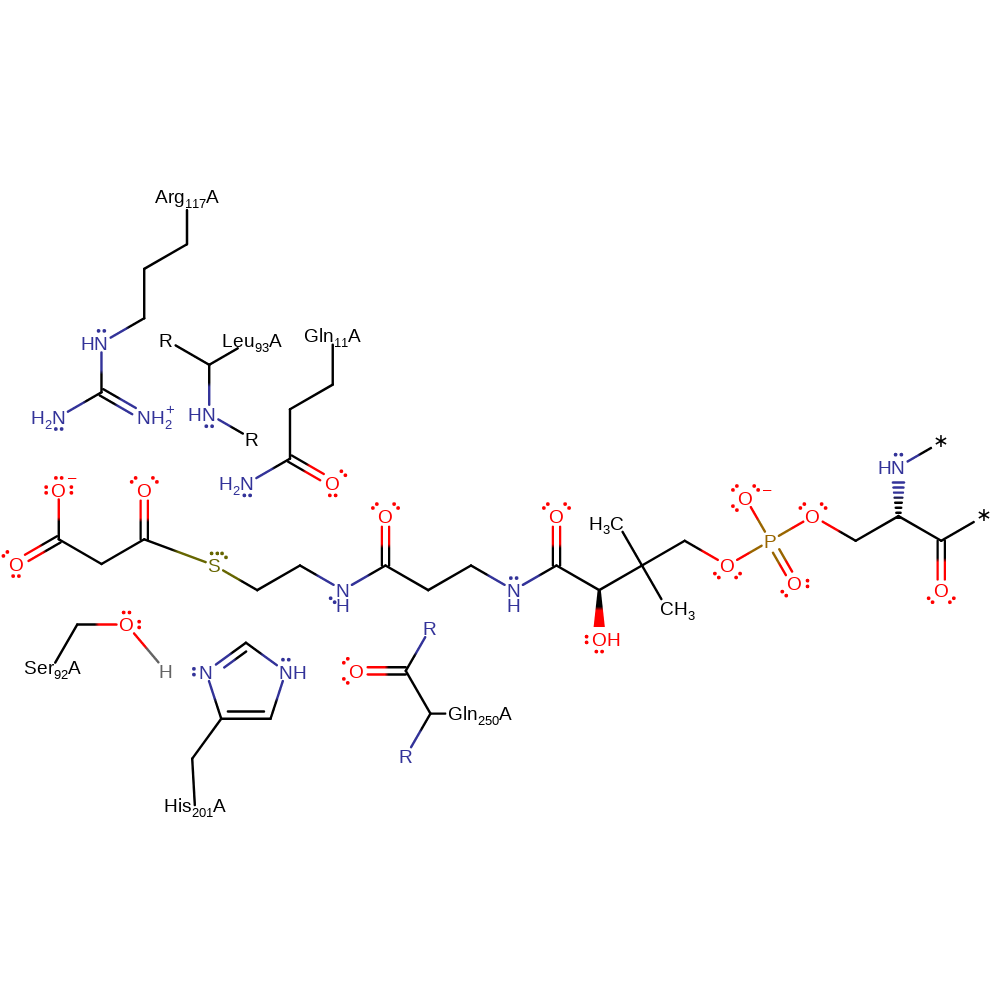 Download:
Download: