NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone)
Quinone reductase exists as a dimer of identical subunits, each comprising of 273 amino acids with two identical catalytic sites at equivalent positions. The enzyme catalyses the FAD dependent reduction of quinones. The dimer binds two FAD cofactors which remain non-covalently bound during catalysis. NAD(P)H and NAD(P)+ cycle in and out of the catalytic site. The catalytic domain has the characteristic twisted central parallel beta sheet surrounded on both sides by connecting helices, as found in other flavoproteins.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P15559
 (1.6.5.2)
(1.6.5.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1d4a
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN NAD[P]H-QUINONE OXIDOREDUCTASE AT 1.7 A RESOLUTION
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.360
 (see all for 1d4a)
(see all for 1d4a)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), 1,4-benzoquinone (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.6.5.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The obligatory two-electron reduction is shown here to proceed via two direct hydride transfers.
The mechanism has two distinct steps. Firstly, hydride transfer occurs from NAD(P)H to the enzyme-bound flavin followed by the release of NAD(P)+. Secondly, a hydride transfer takes place from the flavin to the quionone followed by the releases of hydroquinone. The mechanism follows a 'ping-pong' kinetic scheme. The binding of the quinone substrate cannot occur until NAD(P)+ is released because the nictotinamide and quninone share the same binding site.
This enzyme features two independent, equivalent active sites which are located at opposite ends of the dimer interface. Residues from both monomers line the large active sites which extend from the protein surface to the isoalloxazine rings of the FAD cofactors [PMID:11035252].
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1d4a) | ||
| Gly150 (main-N) | Gly149A (main-N) | The residue hydrogen bonds to the N1 of the flavin cofactor, stabilising the enolate anion through charge delocalisation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr156 | Tyr155A | The residue hydrogen bonds to the flavin enolate oxygen. It acts as a proton donor to the anion, with concurrent abstraction of a proton from the close proximity His161. This acquired proton is then removed by His161 in the second reaction step, leading to a hydride transfer from the flavin cofactor to the quinone substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His162 | His161A | The residue acts as a general acid towards Tyr155 in the first reaction step, and then as a general base towards the same Tyr155 in the second reaction step. This initiates the hydride transfer from the flavin cofactor to the quinone substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, proton transfer, proton relay, aromatic bimolecular elimination, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, native state of cofactor is not regeneratedReferences
- Foster CE et al. (2000), Free Radic Biol Med, 29, 241-245. Structures of mammalian cytosolic quinone reductases. DOI:10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00299-9. PMID:11035252.
- Cavelier G et al. (2001), Proteins, 43, 420-432. Mechanism of NAD(P)H:Quinone reductase: Ab initio studies of reduced flavin. DOI:10.1002/prot.1055.abs. PMID:11340659.
- Li R et al. (1995), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 92, 8846-8850. The three-dimensional structure of NAD(P)H:quinone reductase, a flavoprotein involved in cancer chemoprotection and chemotherapy: mechanism of the two-electron reduction. DOI:10.1073/pnas.92.19.8846. PMID:7568029.
Step 1. A hydride ion is transferred from NADH to the FAD cofactor, with concomitant double bond rearrangement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly149A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr155A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His161A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, overall product formed, intermediate formation
Step 2. The FADH deprotonates Tyr155, which in turn deprotonates His161.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His161A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly149A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr155A | proton relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr155A | proton acceptor |
| His161A | proton donor |
| Tyr155A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay, intermediate formation
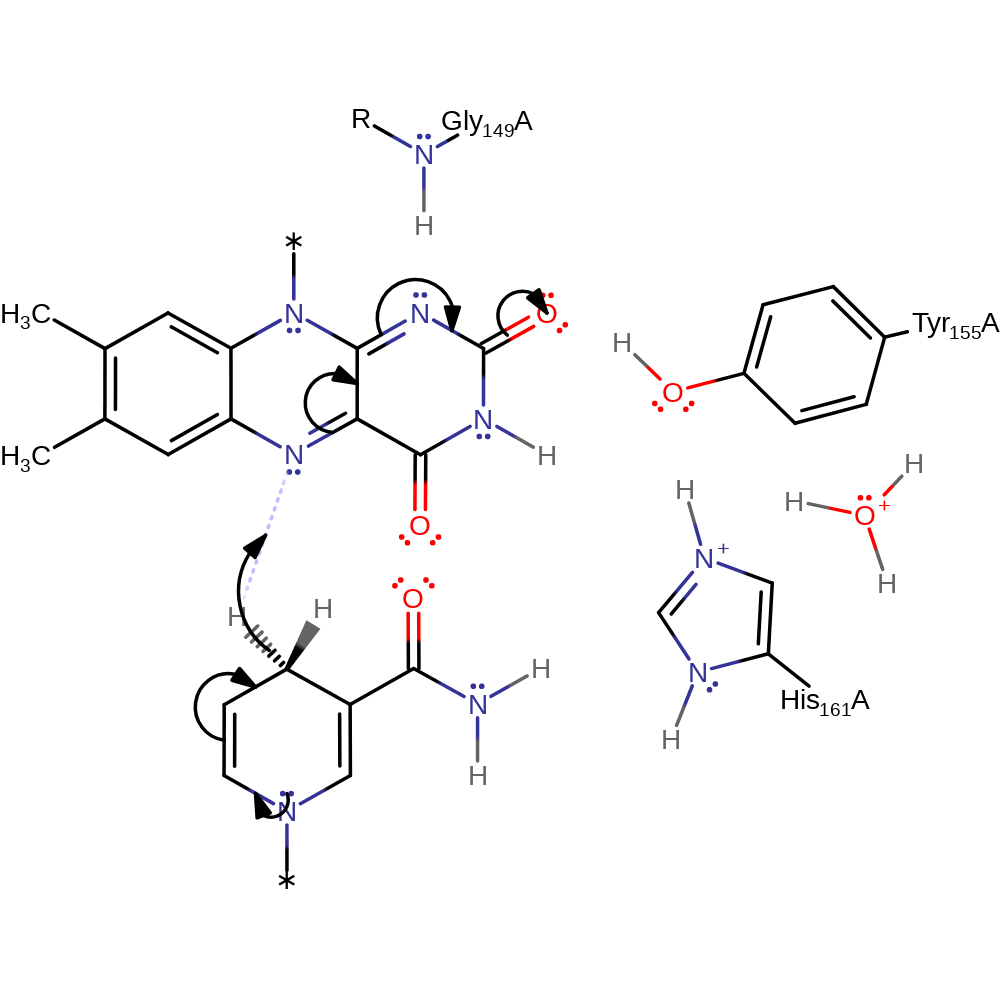
Step 3. NAD+ is released, followed by binding of the quinine. His161 deprotonates Tyr155, which in turn deprotonates the FADH, resulting in double bond rearrangement and the elimination of a hydride to the quinone.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His161A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly149A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr155A | proton relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His161A | proton acceptor |
| Tyr155A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular elimination, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay, intermediate formation, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated
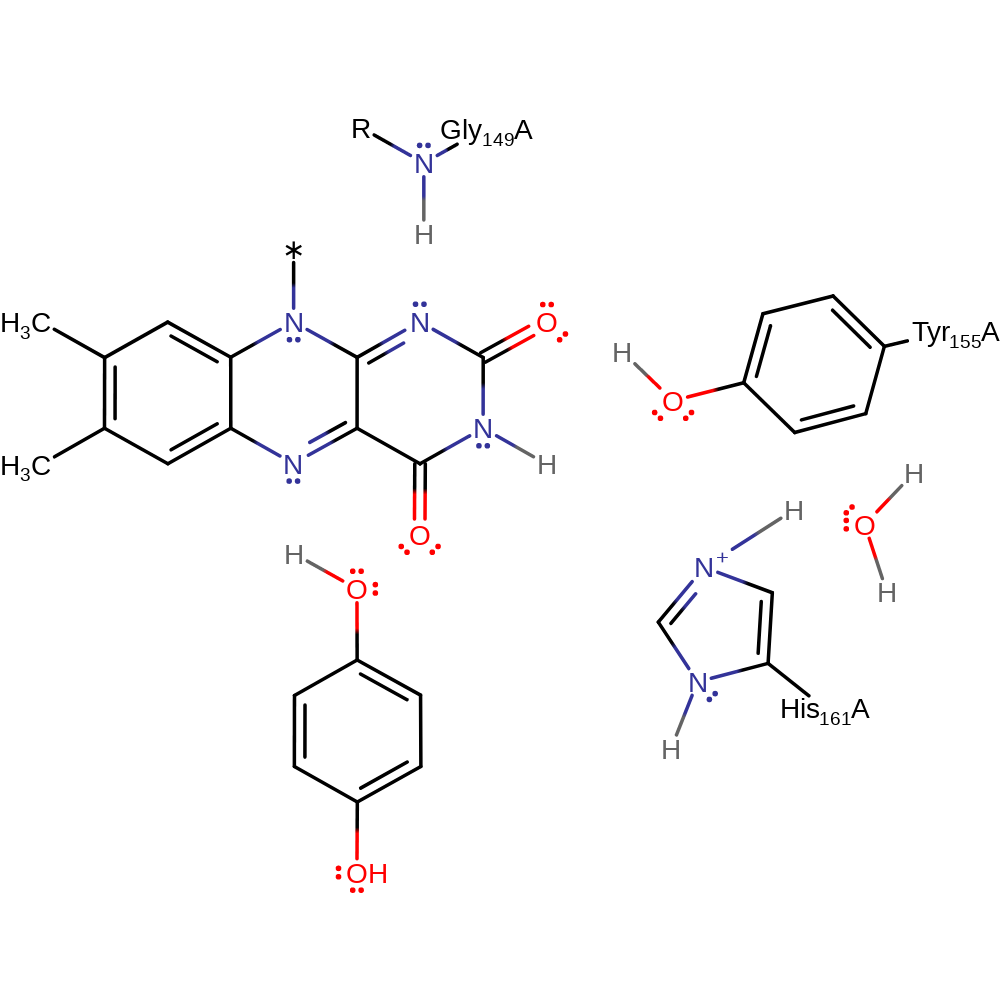
Step 4. The negatively charged substrate deprotonates His161, which is rapidly re-protonated from the solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His161A | hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Tyr155A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly149A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His161A | proton acceptor, proton donor |





 Download:
Download: