Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase
Glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterases display broad specificity for glycerophosphodiesters; glycerophosphocholine, glycerophosphoethanolamine, glycerophosphoglycerol, and bis(glycerophosphoglycerol) all of which are are hydrolysed by this enzyme. Although this enzyme will function with Ca(II) ions, it more active with Mg(II) ions.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q8RB32

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Caldanaerobacter subterraneus subsp. tengcongensis MB4 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2pz0
- Crystal structure of Glycerophosphodiester Phosphodiesterase (GDPD) from T. tengcongensis
(1.91 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.190
 (see all for 2pz0)
(see all for 2pz0)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1), Water (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.4.46)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His17 deprotonates the substrate alcohol, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group, eliminating the product alcohol with concomitant deprotonation of His59. His59 then deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group, destroying the cyclic intermediate with concomitant deprotonation of His17.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2pz0) | ||
| Glu35, Asp37, Glu110 | Glu44A, Asp46A, Glu119A | Involved in coordinating the magnesium ion. | metal ligand |
| Asp230 | Asp239A | Increases the basicity of the general acid/base His17. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| His8, His50 | His17A, His59A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg9, Lys112 | Arg18A, Lys121A | Acts to stabilise the transition states and reactive intermediates formed. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
Chemical Components
intramolecular elimination, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionReferences
- Shi L et al. (2008), Proteins, 72, 280-288. Crystal structure of glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (GDPD) from Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis , a metal ion-dependent enzyme: Insight into the catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1002/prot.21921. PMID:18214974.

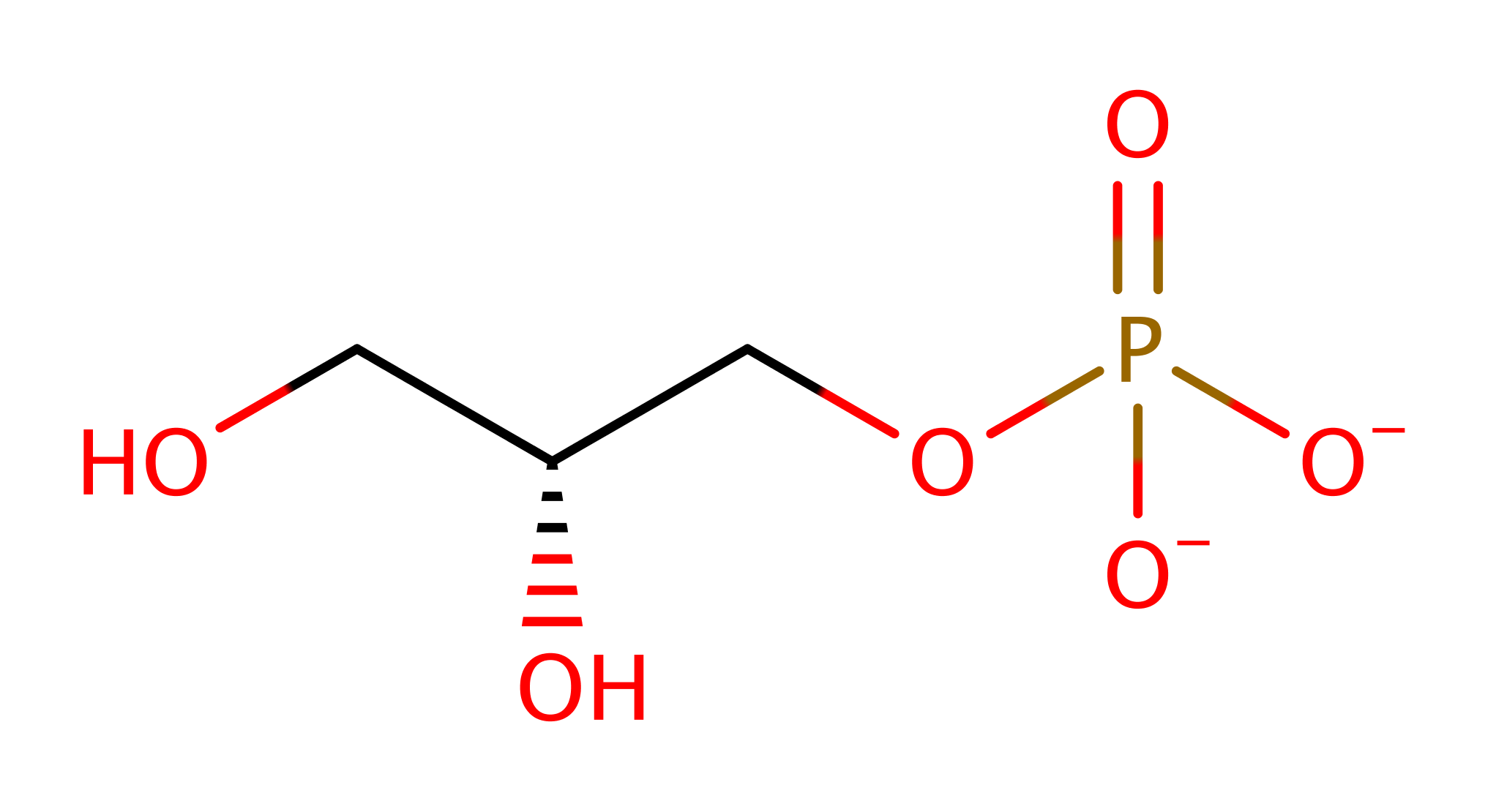
Step 1. His17 deprotonates the substrate alcohol, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group, eliminating the product alcohol with concomitant deprotonation of His59
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His17A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp239A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| His59A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys121A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg18A | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu44A | metal ligand |
| Asp46A | metal ligand |
| Glu119A | metal ligand |
| His59A | proton donor |
| His17A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular elimination, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed
Step 2. His59 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphate group, destroying the cyclic intermediate with concomitant deprotonation of His17
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His17A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp239A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| His59A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys121A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg18A | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu44A | metal ligand |
| Asp46A | metal ligand |
| Glu119A | metal ligand |
| His17A | proton donor |
| His59A | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: