Ribonuclease D
Ribonuclease D is a divalent metal cation dependent exonuclease that acts on tRNA and is involved in the 3' processing of various precursor tRNAs. Initiates hydrolysis at the 3'-terminus of an RNA molecule and releases 5'-mononucleotides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P09155
 (3.1.13.5)
(3.1.13.5)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1yt3
- Crystal Structure of Escherichia coli RNase D, an exoribonuclease involved in structured RNA processing
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.420.10
 (see all for 1yt3)
(see all for 1yt3)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
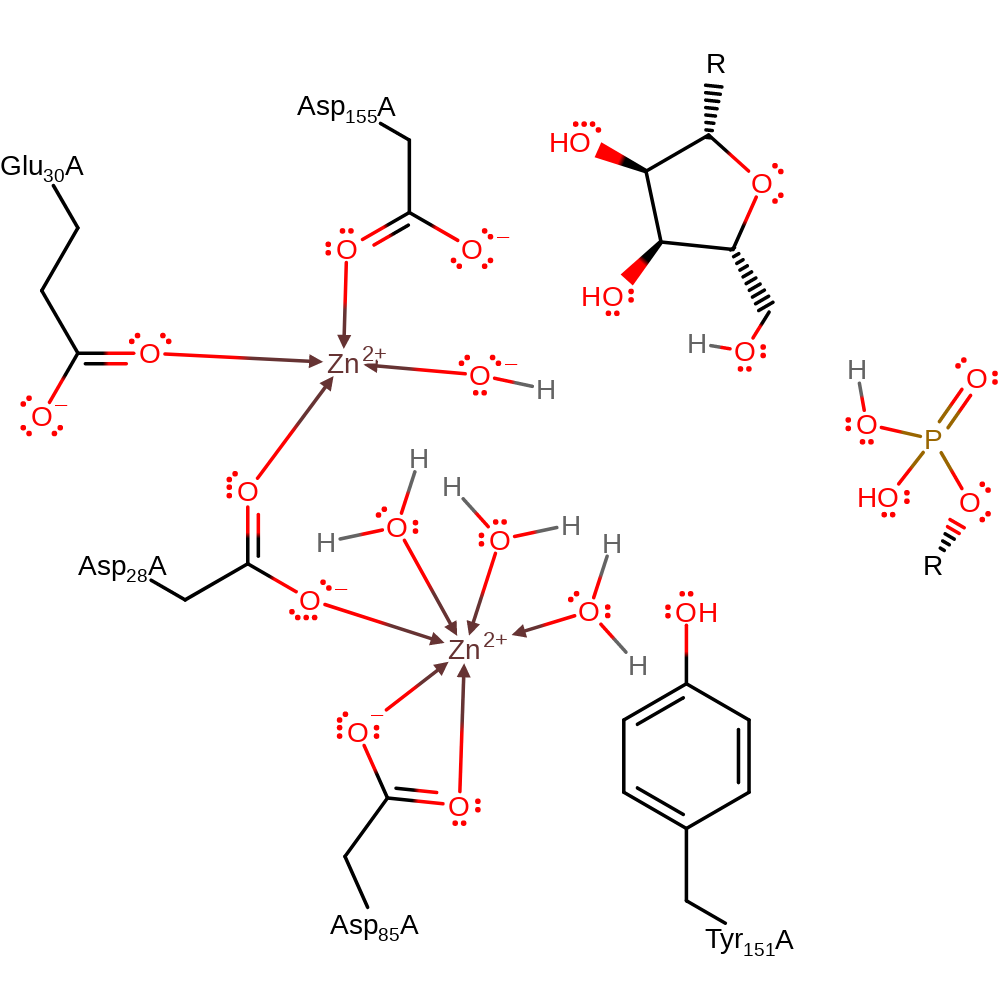
This enzyme can convert a tRNA precursor into a mature tRNA. The activated water, coordinated to one of the active site Zn cations attacks at the pentavalent 5' phosphorous centre. The 3' hydroxyl group deprotonates a water molecule, regenerating the Zn hydroxide centre.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1yt3) | ||
| Asp28 | Asp28A | Acts as a bidentate ligand between the zinc binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Asp155 | Asp155A | Positioned in exo-site 3, implicated in stabilising and directing the nucleophile. Also forms part of the zinc 1 binding site. | attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr151 | Tyr151A | Positioned in exo-site 3, implicated in stabilising and directing the nucleophile | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu30 | Glu30A | Forms part of the zinc 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp85 | Asp85A | Forms part of the zinc 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation, proton transfer, coordination, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Zuo Y et al. (2005), Structure, 13, 973-984. Crystal Structure of Escherichia coli RNase D, an Exoribonuclease Involved in Structured RNA Processing. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2005.04.015. PMID:16004870.
- Yang W (2011), Q Rev Biophys, 44, 1-93. Nucleases: diversity of structure, function and mechanism. DOI:10.1017/s0033583510000181. PMID:20854710.
- Phillips S et al. (2003), RNA, 9, 1098-1107. Contribution of domain structure to the RNA 3' end processing and degradation functions of the nuclear exosome subunit Rrp6p. DOI:10.1261/rna.5560903. PMID:12923258.
- Steitz TA et al. (1993), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 90, 6498-6502. A general two-metal-ion mechanism for catalytic RNA. DOI:10.1073/pnas.90.14.6498. PMID:8341661.

Step 1. The hydroxide ion, coordinated to one of the active site Zn cations attacks at the pentavalent 5' phosphorous centre.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp155A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr151A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp155A | metal ligand |
| Glu30A | metal ligand |
| Asp28A | metal ligand |
| Asp85A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation
Step 2. The 3' hydroxyl group deprotonates a water molecule, regenerating the Zn hydroxide centre.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp155A | electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction |
| Tyr151A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp155A | metal ligand |
| Glu30A | metal ligand |
| Asp28A | metal ligand |
| Asp85A | metal ligand |




 Download:
Download: