1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA synthase
Naphthoate synthase (MenB, also known as 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA synthase) is involved in the synthesis of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoate, a branch point metabolite leading to the biosynthesis of menaquinone (vitamin K2, in bacteria), phylloquinone (vitamin K1 in plants), and many plant pigments. The coenzyme A group is subsequently removed from the product by 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-CoA hydrolase (EC:3.1.2.28). It is a member of the crotonase superfamily.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P9WNP5
 (4.1.3.36)
(4.1.3.36)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1q51
- Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis MenB in Complex with Acetoacetyl-Coenzyme A, a Key Enzyme in Vitamin K2 Biosynthesis
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.12.10
 3.90.226.10
3.90.226.10  (see all for 1q51)
(see all for 1q51)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.3.36)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The C7 carboxylate group abstracts the pro-2S proton. The resulting enolate oxyanion is stabilised in the oxyanion hole formed by the backbone amides of Gly105 and Gly161. The intramolecular proton transfer in the previous step increases the electrophilicity of the protonated carboxylate, allowing the attack of a C=C bond to the C atom of the carboxylate. The C7 tetrahedral intermediate formed is stabilised by oxyanion hole formed by the two Tyr residues. The tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate, aided by surrounding hydrogen bond network, collapses through an internal elimination producing a molecule of water. The intermediate tautomerises to produce 1,4-dihydroxy-2-napthoyl-CoA with the aid of Asp185 and Ser190. Inferred step to return the enzyme to its native state, involving reprotonation of Tyr287' by a hydronium ion
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1q51) | ||
| Tyr287 | Tyr287D | Tyr115A and Tyr287B play a central role in orientating the OSB C7 carboxylate group so that it can abstract the pro-2S proton. These two residues also form an oxyanion hole that stabilises the C7 tetrahedral intermediate formed during the course of the reaction. Tyr287B also acts as a general acid/base in the elimination of water. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, polar interaction, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Gly105 (main-N), Gly161 (main-N) | Gly105A (main-N), Gly161A (main-N) | The oxyanion hole formed by the backbone amides of Gly105 and Gly161 binds the carbonyl group adjacent to the CoA and stabilise the reactive intermediate and transition states formed at that position. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr115 | Tyr115A | Tyr115A and Tyr287B play a central role in orientating the OSB C7 carboxylate group so that it can abstract the pro-2S proton. These two residues also form an oxyanion hole that stabilises the C7 tetrahedral intermediate formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Asp185, Ser190 | Asp185A, Ser190A | Although the exact role of these residues is unknown, they are thought to be essential for the tautomerisation reaction that occurs in step 4. They have been shown simply as activating here, but they could act as general acid/bases. | activator |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, intramolecular electrophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, keto-enol tautomerisation, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate terminated, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Li HJ et al. (2011), Biochemistry, 50, 9532-9544. Mechanism of the Intramolecular Claisen Condensation Reaction Catalyzed by MenB, a Crotonase Superfamily Member. DOI:10.1021/bi200877x. PMID:21830810.
- Sun Y et al. (2013), PLoS One, 8, e63095-. Structural basis of the induced-fit mechanism of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl coenzyme A synthase from the crotonase fold superfamily. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0063095. PMID:23658663.
- Song H et al. (2012), Sci China Chem, 55, 98-105. Characterization of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl-coenzyme A synthase (MenB) in phylloquinone biosynthesis of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. DOI:10.1007/s11426-011-4448-y.
- Truglio JJ et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 42352-42360. Crystal Structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis MenB, a Key Enzyme in Vitamin K2 Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m307399200. PMID:12909628.
- Holden HM et al. (2001), Acc Chem Res, 34, 145-157. The crotonase superfamily: divergently related enzymes that catalyze different reactions involving acyl coenzyme a thioesters. PMID:11263873.

Step 1. Tyr115 and Tyr287' play a central role in orientating the OSB C7 carboxylate group so that it can abstract the pro-2S proton. The resulting enolate oxyanion is stabilised in the oxyanion hole formed by the backbone amides of Gly105 and Gly161 [PMID:21830810].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly105A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly161A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr115A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Tyr287D | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The intramolecular proton transfer in the previous step increases the electrophilicity of the protonated carboxylate, allowing the attack of a C=C bond to the C atom of the carboxylate. The C7 tetrahedral intermediate formed is stabilised by oxyanion hole formed by the two Tyr residues [PMID:21830810].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly105A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly161A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr115A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Tyr287D | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate formation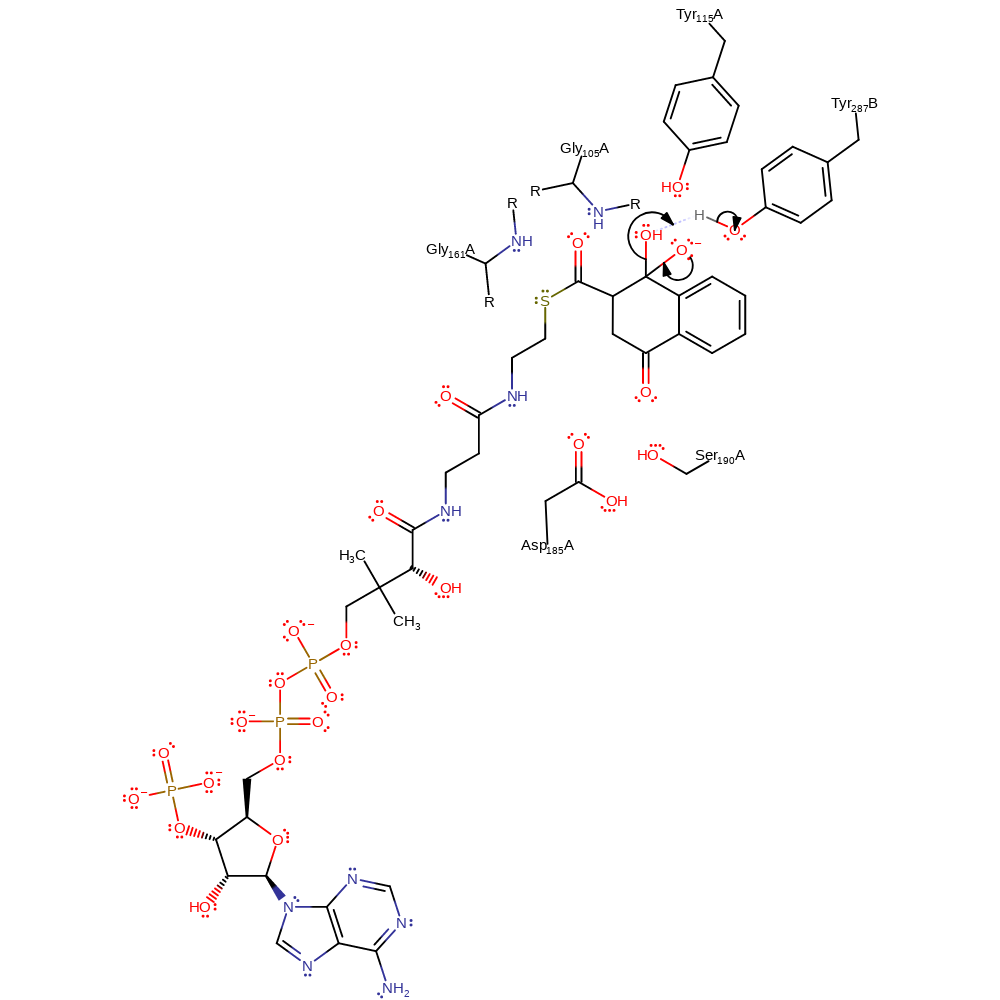
Step 3. The tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate, aided by surrounding hydrogen bond network, collapses through an internal elimination producing a molecule of water
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly105A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly161A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr115A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr287D | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 4. The intermediate tautomerises to produce 1,4-dihydroxy-2-napthoyl-CoA with the aid of Asp185 and Ser190
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly105A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly161A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr115A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr287D | polar interaction |
| Asp185A | activator |
| Ser190A | activator |
Chemical Components
keto-enol tautomerisation, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed
Step 5. Inferred step to return the enzyme to its native state, involving reprotonation of Tyr287' by a hydronium ion
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr287D | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |

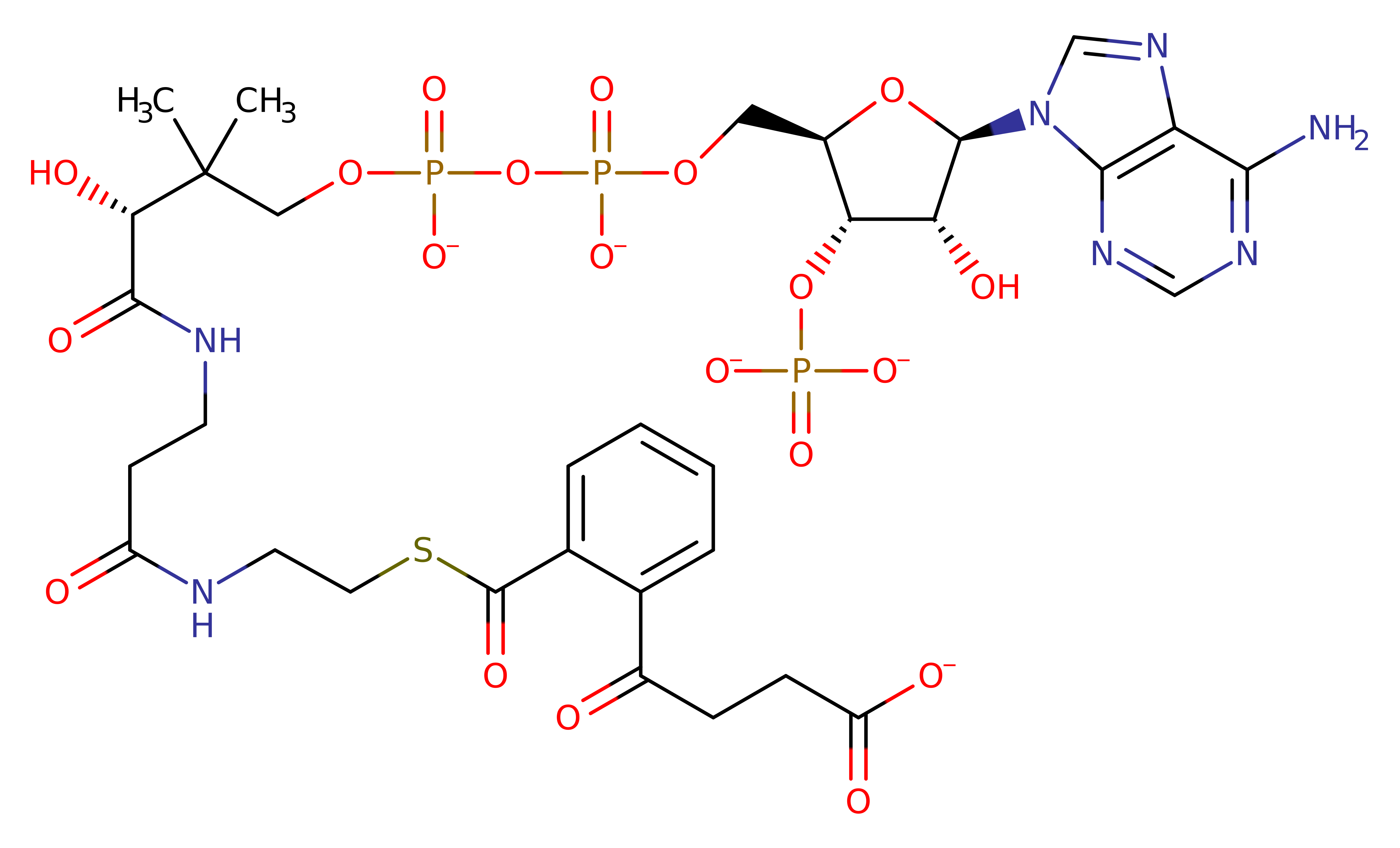

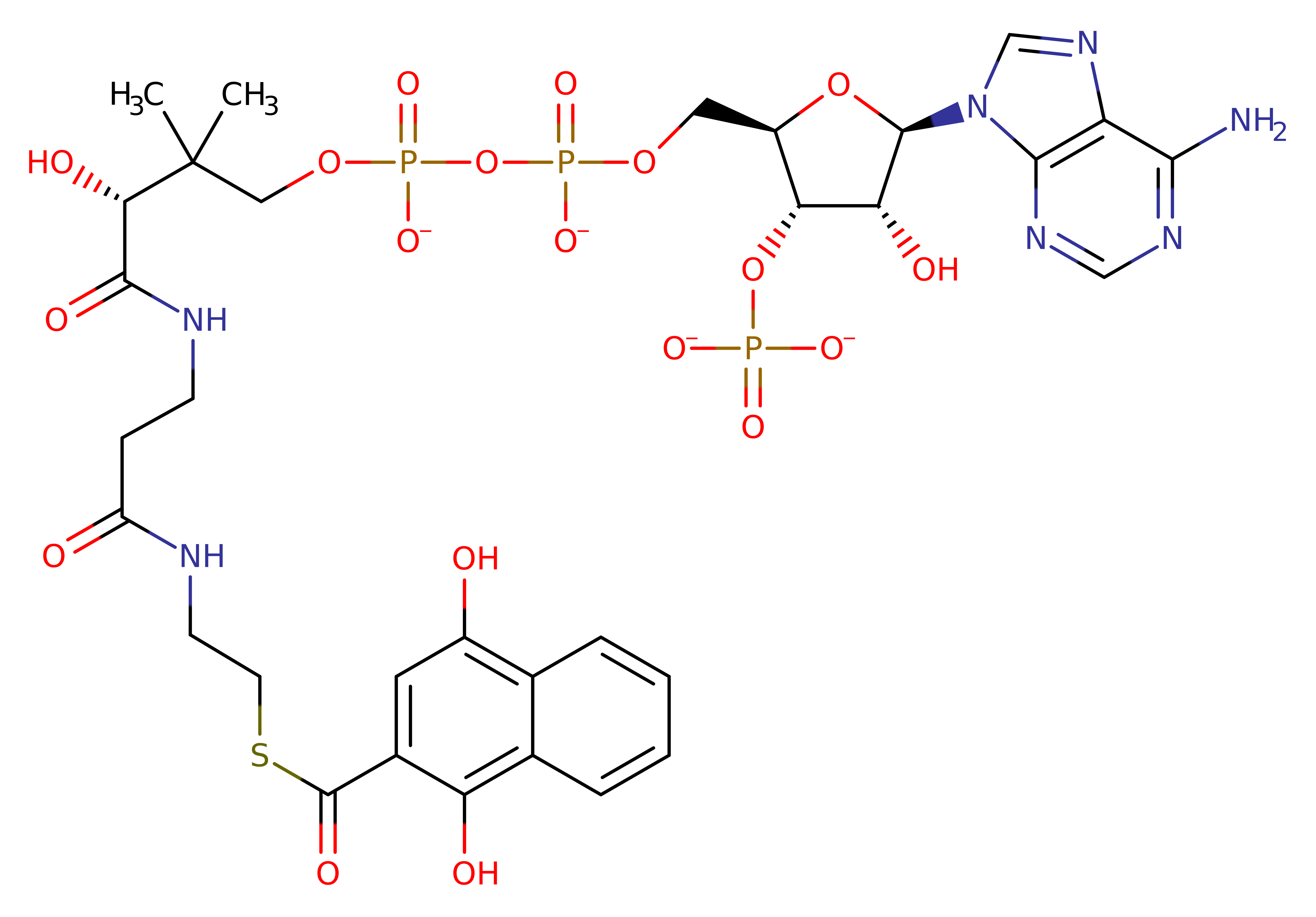
 Download:
Download: