Phosphorylase kinase
Eukaryotic protein kinases catalyse the transfer of ATP-gamma phosphate to serine, threonine and tyrosine residues on specific target proteins. The family of protein kinases represents one of the largest protein superfamilies, and structures of active kinases show similar conformations in key regions involved in ATP and protein substrate recognition domains. Phosphorylase kinase, the first protein kinase to be discovered, catalyses the phosphorylation of a single serine residue, Ser14 of inactive phosphorylase B (GPb). Phosphorylation converts the protein to active glycogen phosphorylase A (GPa), which catalyses glycogen degredation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00518
 (2.7.11.1, 2.7.11.19, 2.7.11.26)
(2.7.11.1, 2.7.11.19, 2.7.11.26)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)

- PDB
-
2phk
- THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A PHOSPHORYLASE KINASE PEPTIDE SUBSTRATE COMPLEX: KINASE SUBSTRATE RECOGNITION
(2.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.510.10
 (see all for 2phk)
(see all for 2phk)
- Cofactors
- Manganese(2+) (1), Magnesium(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.11.19)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
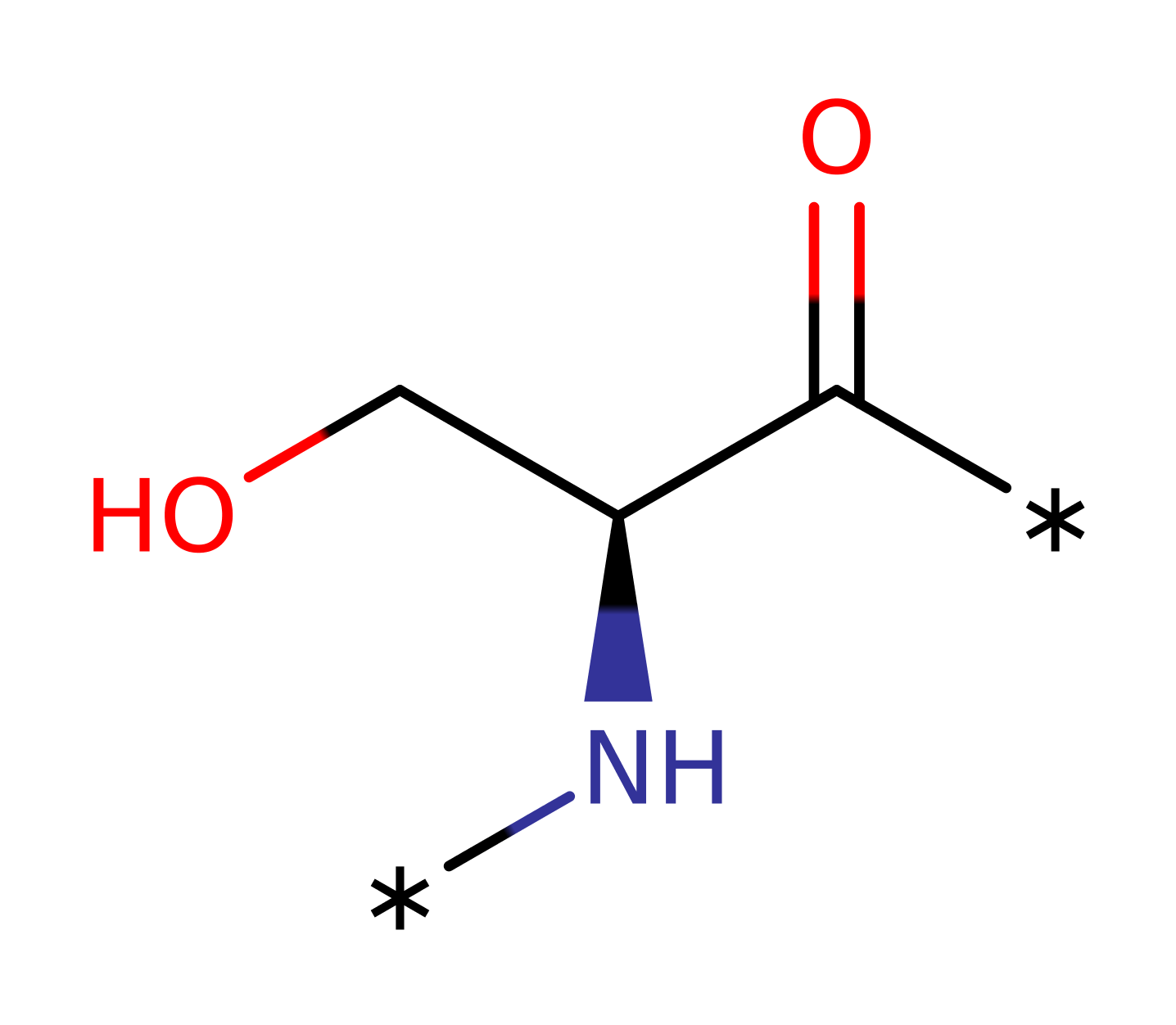
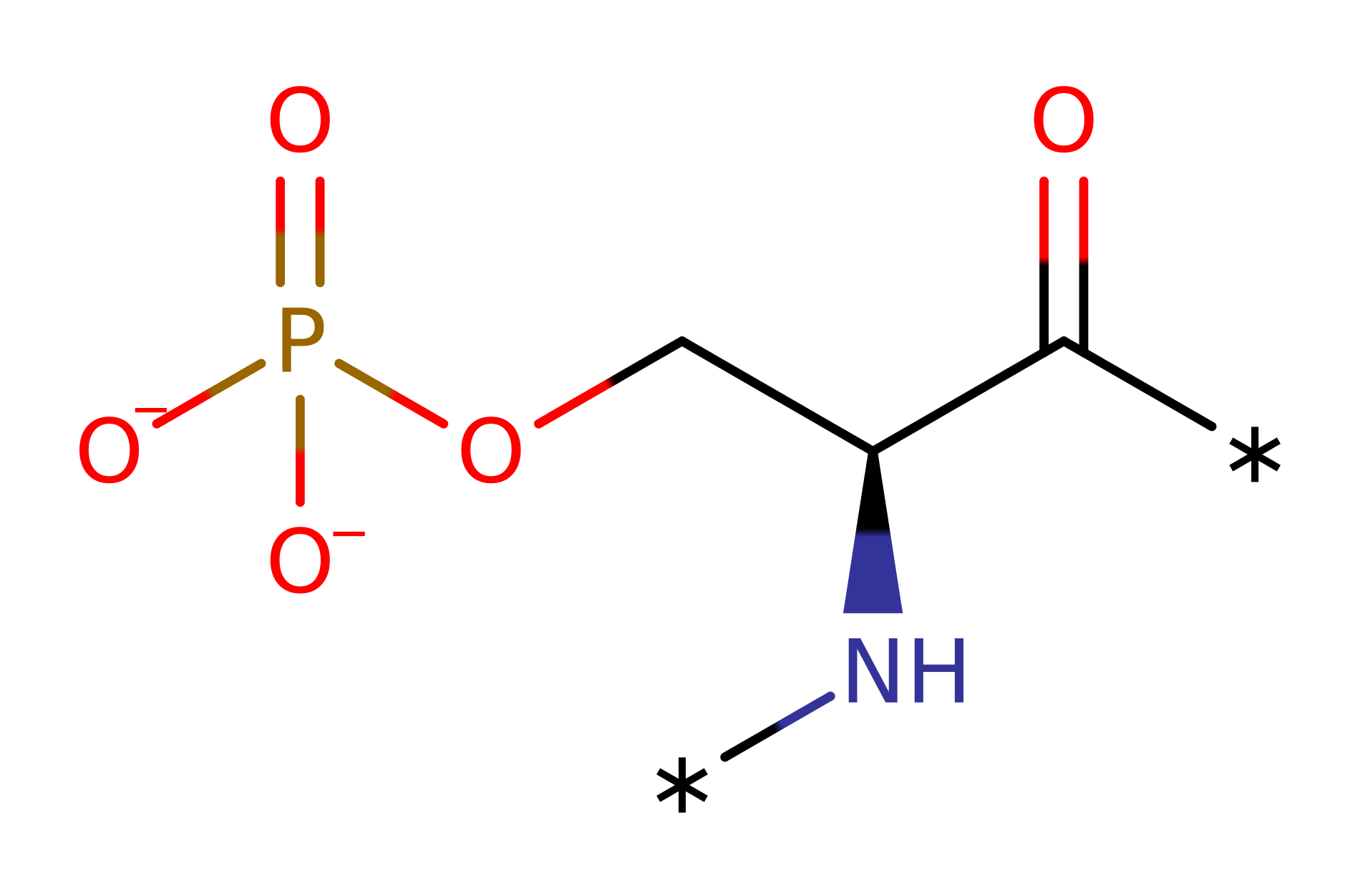
Asp149 deprotonates the protein substrate hydroxyl group, initiating nucleophilic attack upon the gamma-phosphate of ATP in a substitution reaction that eliminates ADP. The phosphorylated protein deprotonates Asp149 [PMID:10545198].
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2phk) | ||
| Lys152 | Lys151(138)A | Transition state stabiliser. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr187 | Thr186(173)A | Activates Asp149. | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp150 | Asp149(136)A | Acts as a general acid/base catalyst. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asn155, Asp168 | Asn154(141)A, Asp167(154)A | Bind the Mg(II) ions. Asp168 binds both, Asp154 binds one only. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Skamnaki VT et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 14718-14730. Catalytic mechanism of phosphorylase kinase probed by mutational studies. DOI:10.2210/pdb1ql6/pdb. PMID:10545198.
- Lowe ED et al. (1997), EMBO J, 16, 6646-6658. The crystal structure of a phosphorylase kinase peptide substrate complex: kinase substrate recognition. DOI:10.1093/emboj/16.22.6646. PMID:9362479.
- Owen DJ et al. (1995), Structure, 3, 467-482. Two structures of the catalytic domain of phosphorylase kinase: an active protein kinase complexed with substrate analogue and product. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00180-0. PMID:7663944.

Step 1. Asp149 deprotonates the protein substrate hydroxyl group, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the gamma-phosphate of ATP in a substitution reaction that eliminates ADP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp149(136)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys151(138)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr186(173)A | hydrogen bond donor, activator |
| Asp167(154)A | metal ligand |
| Asn154(141)A | metal ligand |
| Asp149(136)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp149(136)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys151(138)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr186(173)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp167(154)A | metal ligand |
| Asn154(141)A | metal ligand |
| Asp149(136)A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: