Aspartate racemase (CT type)
Catalyses the unidirectional L to R isomerisation of aspartate using a dibase (asymmetrical) mechanism.
Reference Protein
- Sequence
-
A0A0H3JGH6
 (5.1.1.3, 5.1.1.13)
(5.1.1.3, 5.1.1.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Bacteria)

Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In a mechanism analagous to the canonical two cysteine mechanism (see MACiE entry 1), the first Cys (197) base deprotonates the substrate, and the L to R isomerisation is completed by the subsequent deprotonataion of the Thr (83) residue.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | ||
| Ser14 | Activates Cys197 | increase basicity |
| Thr83 | Acts as the general acid in the reprotonation step of the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys197 | Acts as the general base in the initial proton abstraction of the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transferReferences
- Liu X et al. (2016), FEBS Lett, 590, 1262-1269. Crystal structure and molecular mechanism of an aspartate/glutamate racemase fromEscherichia coliO157. DOI:10.1002/1873-3468.12148. PMID:27001440.
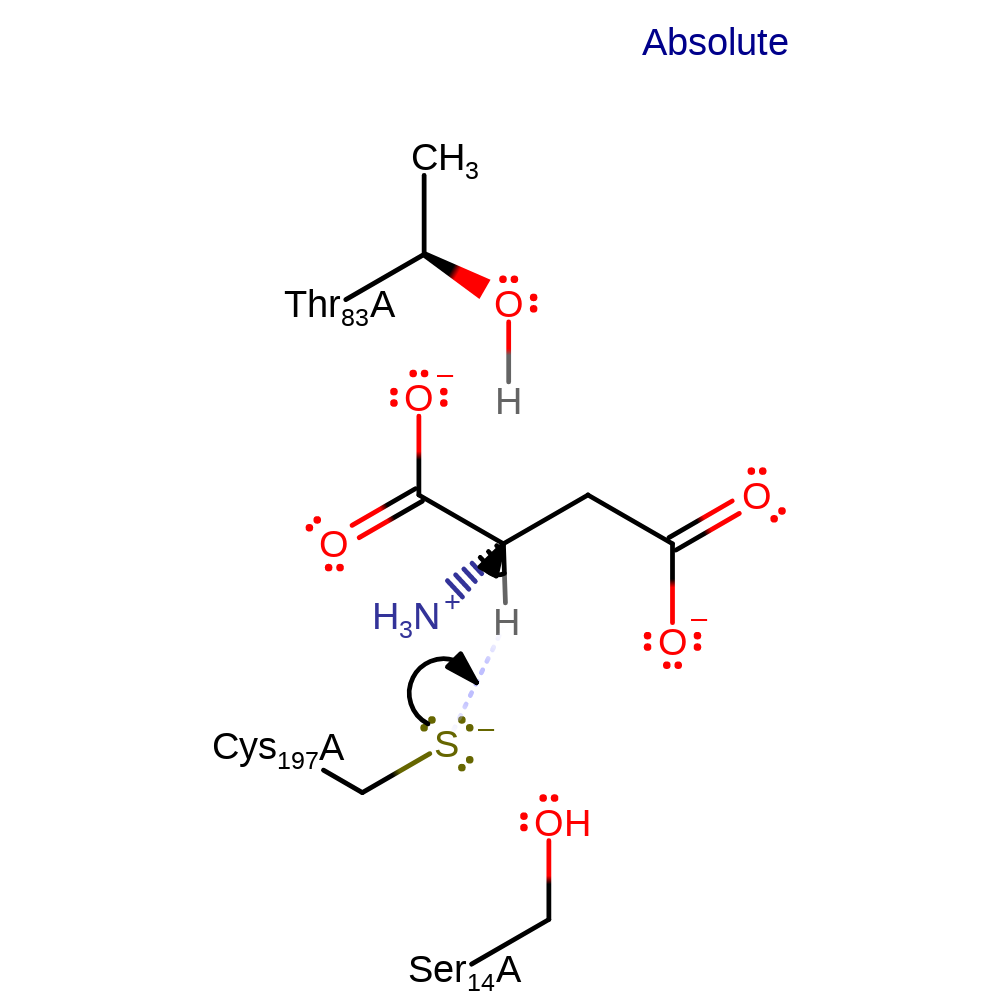
Step 1. Cys thiolate deprotonates the substrate, generating a negatively charged intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser14A | increase basicity |
| Cys197A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer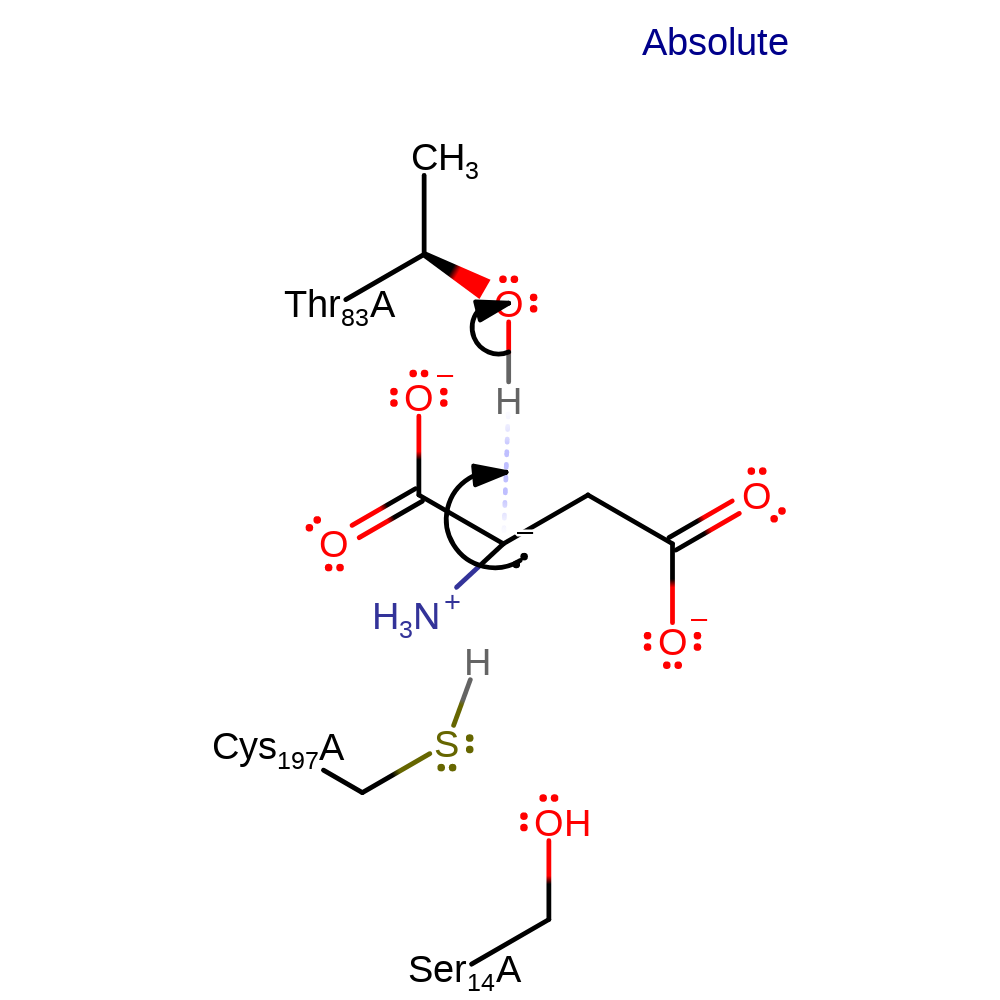
Step 2. The negatively charged intermediate deprotonates Thr83 to generate the opposite enatiomer.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr83A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser14A | increase basicity |
| Thr83A | proton acceptor |
| Cys197A | proton donor |

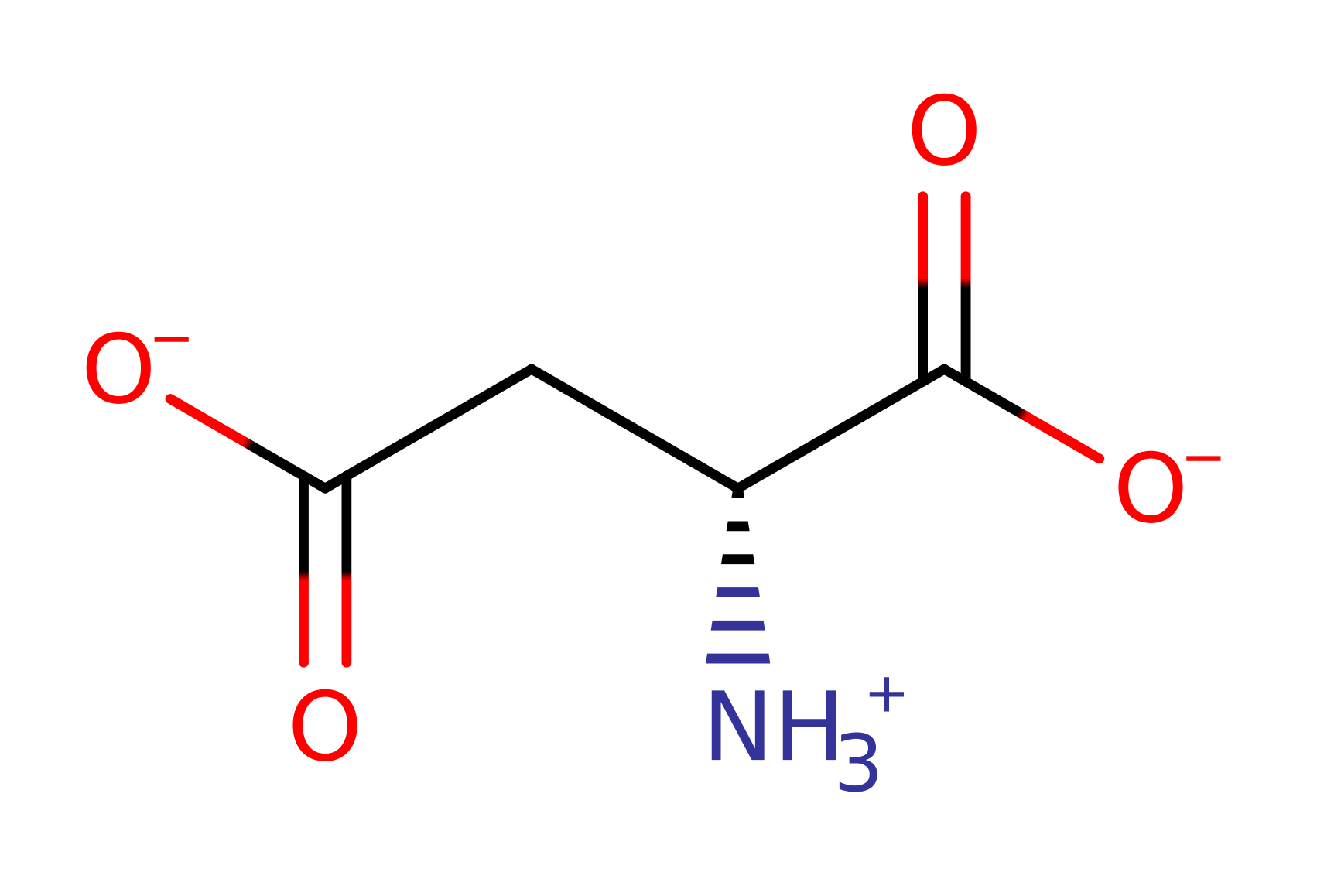

 Download:
Download: