Aspartate carbamoyltransferase
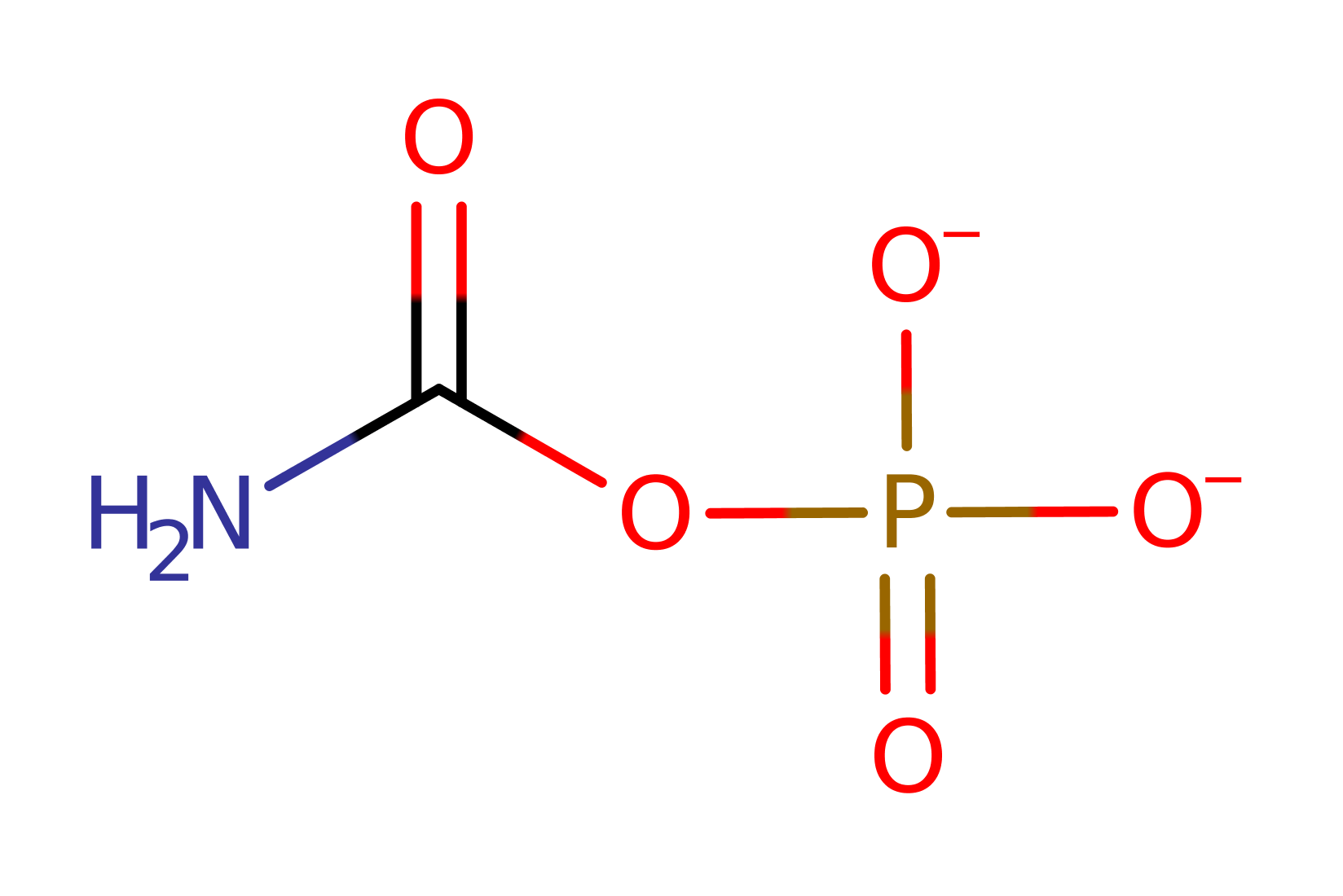
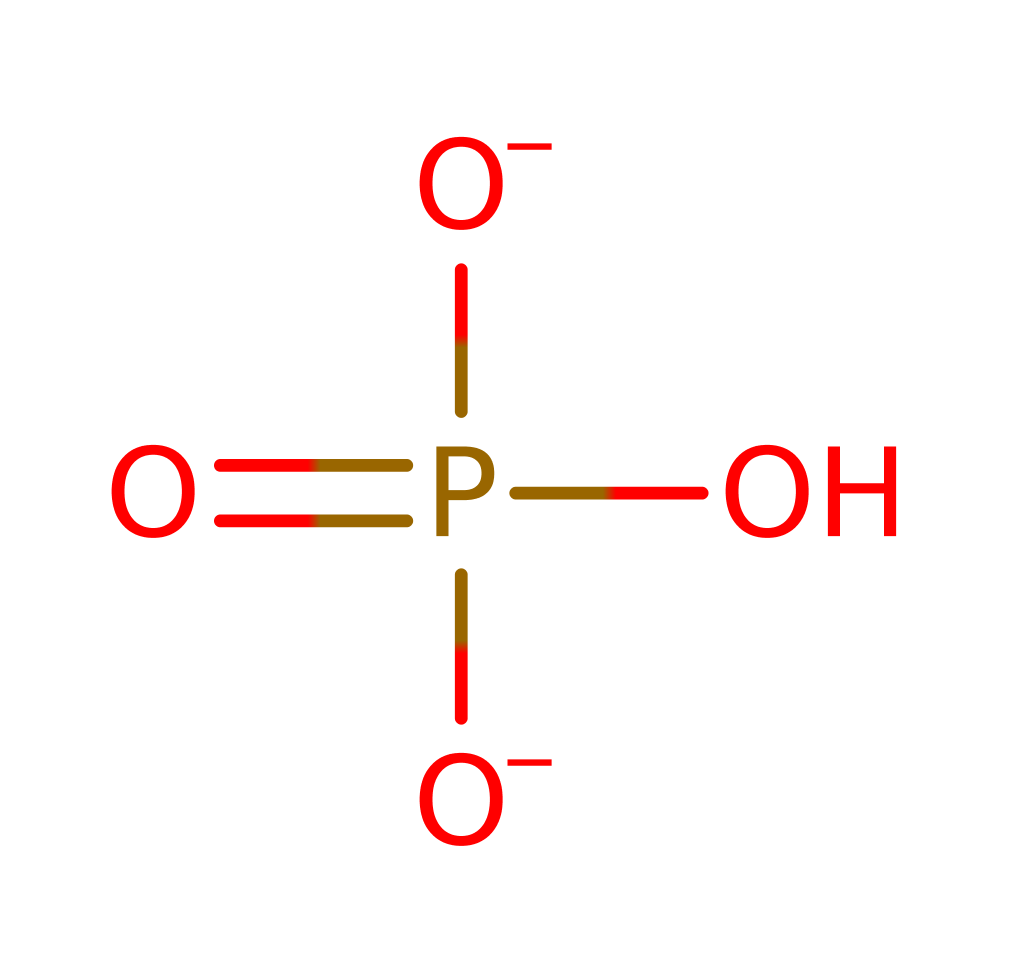
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase catalyses the formation of N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate and inorganic phosphate from carbamoyl phosphate and L-aspartate. In many prokaryotes such as E. coli this reaction is the committed step in pyrimidine biosynthesis.
The E. coli protein exits as a heterododecamer (2C3:3R2) of six catalytic PyrB chains organized as two trimers (C3), and six regulatory PyrI chains organized as three dimers (R2). The PyrI chain is involved in the allosteric regulation of the catalytic reaction and binds one zinc ion. E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase is feedback inhibited by CTP and by UTP in the presence of CTP.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P0A786
 (2.1.3.2)
(2.1.3.2)
P0A7F3
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1at1
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURES OF PHOSPHONOACETAMIDE LIGATED T AND PHOSPHONOACETAMIDE AND MALONATE LIGATED R STATES OF ASPARTATE CARBAMOYLTRANSFERASE AT 2.8-ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION AND NEUTRAL P*H
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1370
 (see all for 1at1)
(see all for 1at1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.3.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Lysine deprotonates the amino group of aspartate to activate it as a nucleophile. Three other residues interact with the carbonyl oxygen of the carbamoyl phosphate, enhancing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon for attack by aspartate. An arginine residue stabilises the developing negative charge of the oxygen as the phosphate leaving group is expelled.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1at1) | ||
| Arg55 | Arg54A | Stabilises the developing negative charge of the oxygen as the phosphate leaving group is expelled. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr56, His135, Arg106 | Thr55A, His134A, Arg105A | Enhances electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon. | increase electrophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys85 | Lys84A(AA) | Deprotonates the amino group of aspartate. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
Chemical Components
References
- Lipscomb WN et al. (2012), Acc Chem Res, 45, 444-453. Structure and Mechanisms of Escherichia coli Aspartate Transcarbamoylase. DOI:10.1021/ar200166p. PMID:22011033.
- Kantrowitz ER (2012), Arch Biochem Biophys, 519, 81-90. Allostery and cooperativity in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2011.10.024. PMID:22198283.
- Peterson AW et al. (2012), Biochemistry, 51, 4776-4778. A Second Allosteric Site inEscherichia coliAspartate Transcarbamoylase. DOI:10.1021/bi3006219. PMID:22667327.
- West JM et al. (2008), J Mol Biol, 384, 206-218. Time Evolution of the Quaternary Structure of Escherichia coli Aspartate Transcarbamoylase upon Reaction with the Natural Substrates and a Slow, Tight-Binding Inhibitor. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.022. PMID:18823998.
- Macol CP et al. (2001), Nat Struct Biol, 8, 423-426. Direct structural evidence for a concerted allosteric transition in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase. DOI:10.1038/87582. PMID:11323717.
- Jin L et al. (1999), Proteins, 37, 729-742. Insights into the mechanisms of catalysis and heterotropic regulation ofEscherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase based upon a structure of the enzyme complexed with the bisubstrate analogueN-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate at 2.1 ? DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(19991201)37:4<729::aid-prot21>3.0.co;2-f. PMID:10651286.
- Stebbins JW et al. (1989), Biochemistry, 28, 2592-2600. Three residues involved in binding and catalysis in the carbamyl phosphate binding site of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase. PMID:2659074.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys84A(AA) | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Arg54A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr55A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg105A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His134A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr55A | increase electrophilicity |
| Arg105A | increase electrophilicity |
| His134A | increase electrophilicity |