Purple acid phosphatase
Purple acid phosphatases (PAPs) are metalloenzymes found in animals, plants and fungi. They possess a binuclear metal centre to catalyse the hydrolysis of phosphate esters (e.g. of sugars or proteins) and anhydrides (e.g. ATP) under acidic conditions. The distinctive purple colour of these enzymes is due to a metal to ligand charge transfer from a tyrosine phenolate to a chromophoric Fe(III). The cornerstone of the active site of PAP is the presence of two metal ions; Fe(III) is always present in the chromophoric site, while the second site can be occupied by a redox active Fe(II/III) in mammals or a Zn(II) or Mn(II) in plants.
Crystal structures of human, pig, rat, and plant PAPs have been determined and show that the amino acid ligands of the metal ions are completely conserved across plant and animal PAPs, but there are some differences in the identities of the residues that line the active site.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P80366
 (3.1.3.2)
(3.1.3.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Phaseolus vulgaris (Kidney bean)

- PDB
-
4kbp
- KIDNEY BEAN PURPLE ACID PHOSPHATASE
(2.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.21.10
 (see all for 4kbp)
(see all for 4kbp)
- Cofactors
- Iron(3+) (1), Zinc(2+) (1), Water (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.3.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
On the basis of structural studies with bound phosphate and tungstate (inhibitor), and the observed inversion of the phosphorous configuration during catalysis, an SN2-type mechanism is proposed for PAP. The substrate phosphate is bound to the Me(II) ion via one of the non-esterified oxygen atoms and oriented by His202 and His296 (numbering for kidney bean enzyme) for in-line attack of an Fe(III)-bound hydroxide ion from a position opposite the esterified oxygen. These residues and the metal ions are presumed to stabilise the pentaco-ordinate transition state. Tentatively, His296 may then act as a general acid to protonate the leaving group, followed by the attack of a water molecule on the Fe(III) atom to release the inorganic phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (4kbp) | ||
| His322, His229 | His295A, His202A | Help stabilise the negatively charged intermediates and transition states. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His323 | His296A | General acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| His352, Asp191, Asp162, Tyr194 | His325A, Asp164A, Asp135A, Tyr167A | Form the iron binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp191, Asn228, His313, His350 | Asp164A, Asn201A, His286A, His323A | Form the zinc binding site | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Klabunde T et al. (1996), J Mol Biol, 259, 737-748. Mechanism of Fe(III) – Zn(II) Purple Acid Phosphatase Based on Crystal Structures. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0354. PMID:8683579.
- Feder D et al. (2012), Chem Biol Drug Des, 80, 665-674. Identification of Purple Acid Phosphatase Inhibitors by Fragment-Based Screening: Promising New Leads for Osteoporosis Therapeutics. DOI:10.1111/cbdd.12001. PMID:22943065.
- Anand A et al. (2012), Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 167, 2174-2197. A Molecular Description of Acid Phosphatase. DOI:10.1007/s12010-012-9694-8. PMID:22684363.
- Schenk G et al. (2012), Acc Chem Res, 45, 1593-1603. Binuclear Metallohydrolases: Complex Mechanistic Strategies for a Simple Chemical Reaction. DOI:10.1021/ar300067g. PMID:22698580.
- Schenk G et al. (2005), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 102, 273-278. Phosphate forms an unusual tripodal complex with the Fe-Mn center of sweet potato purple acid phosphatase. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0407239102. PMID:15625111.
- Sträter N et al. (1995), Science, 268, 1489-1492. Crystal structure of a purple acid phosphatase containing a dinuclear Fe(III)-Zn(II) active site. PMID:7770774.

Step 1. Metal activated water attacks the phosphate in a nucleophilic addition, resulting in a pentavalent transition state, which collapses to release the alcohol group, which gains a proton from His296.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His202A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His296A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp135A | metal ligand |
| Asp164A | metal ligand |
| Tyr167A | metal ligand |
| His325A | metal ligand |
| Asn201A | metal ligand |
| His286A | metal ligand |
| His323A | metal ligand |
| His296A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His295A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His202A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His296A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp135A | metal ligand |
| Asp164A | metal ligand |
| Tyr167A | metal ligand |
| His325A | metal ligand |
| Asn201A | metal ligand |
| His286A | metal ligand |
| His323A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His202A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His295A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His296A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp135A | metal ligand |
| Asp164A | metal ligand |
| Tyr167A | metal ligand |
| His325A | metal ligand |
| Asn201A | metal ligand |
| His286A | metal ligand |
| His323A | metal ligand |
| His296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion
Step 4. The metal coordinated water is now deprotonated by the leaving phosphate group, regenerating the active site. In the product release step, another water enters the active site, displacing the phosphate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp135A | metal ligand |
| Asp164A | metal ligand |
| Tyr167A | metal ligand |
| His325A | metal ligand |
| Asn201A | metal ligand |
| His286A | metal ligand |
| His323A | metal ligand |
| His296A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His295A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His202A | electrostatic stabiliser |

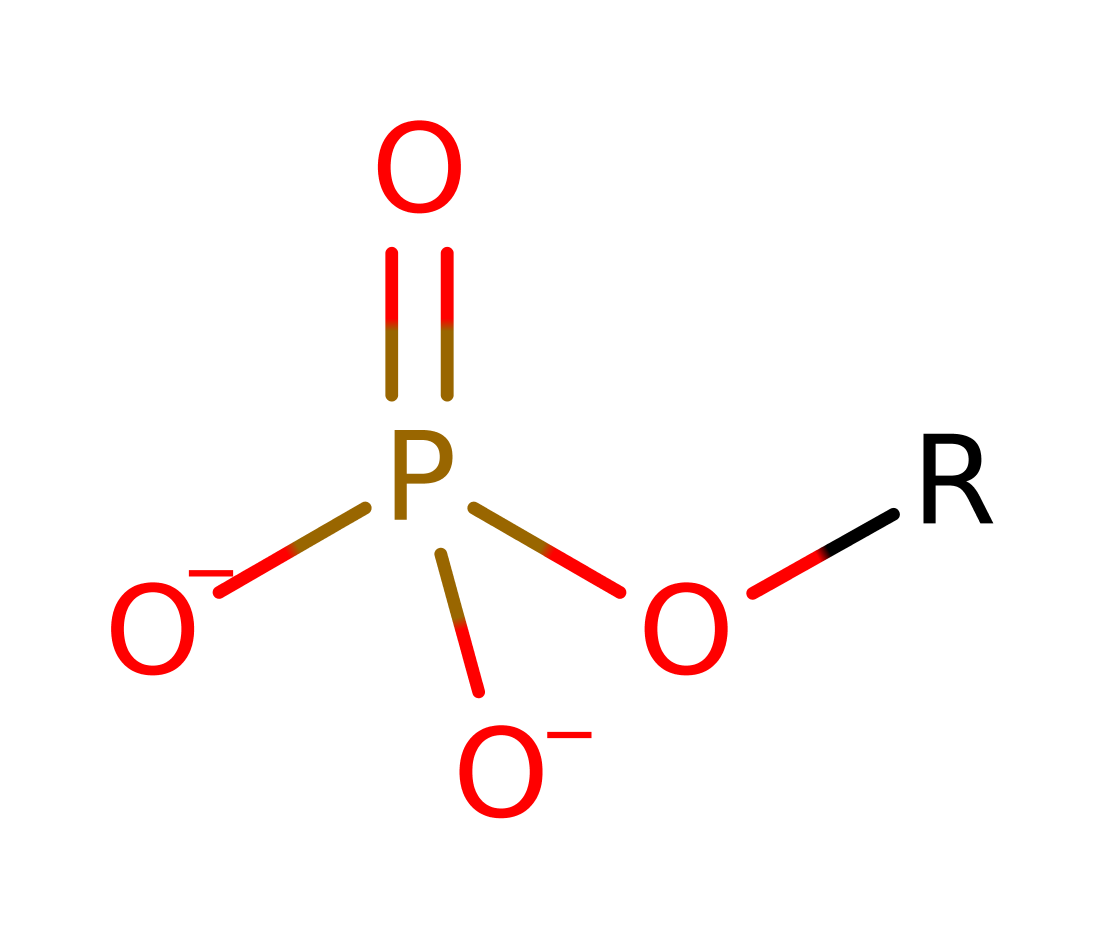

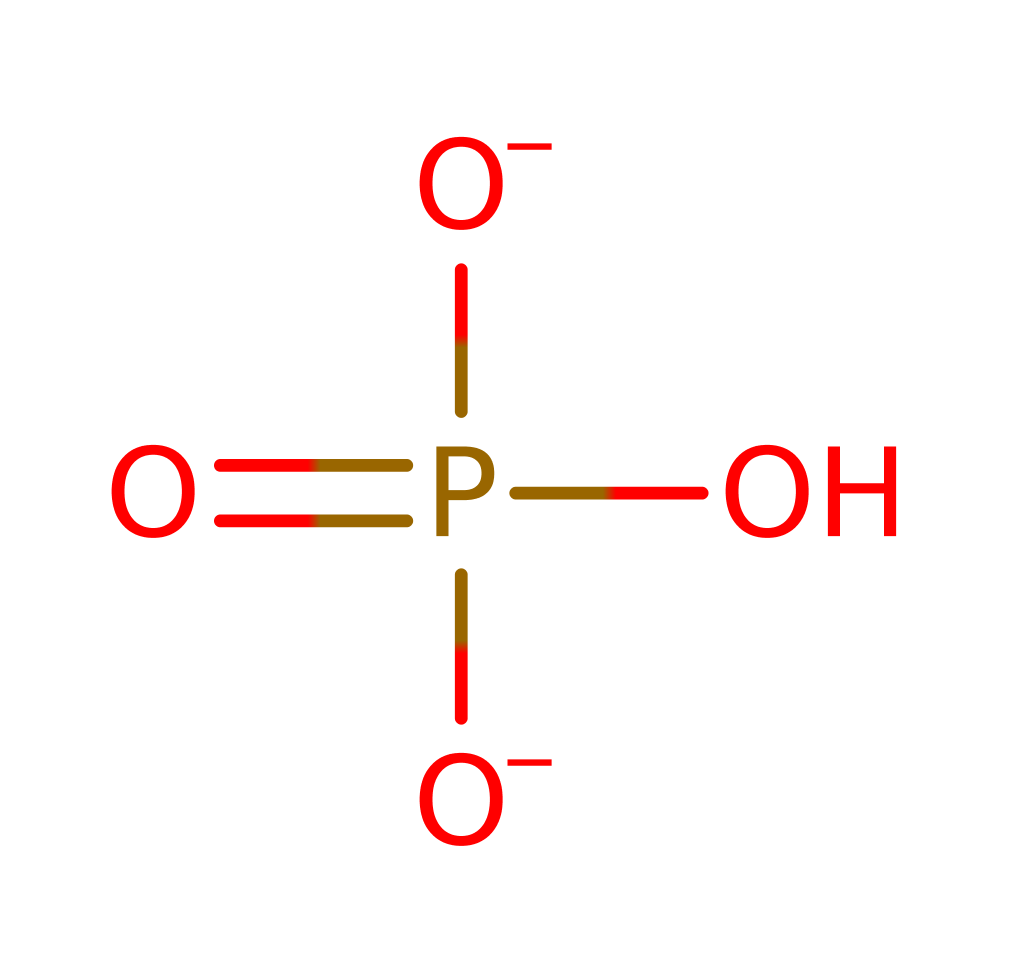


 Download:
Download: