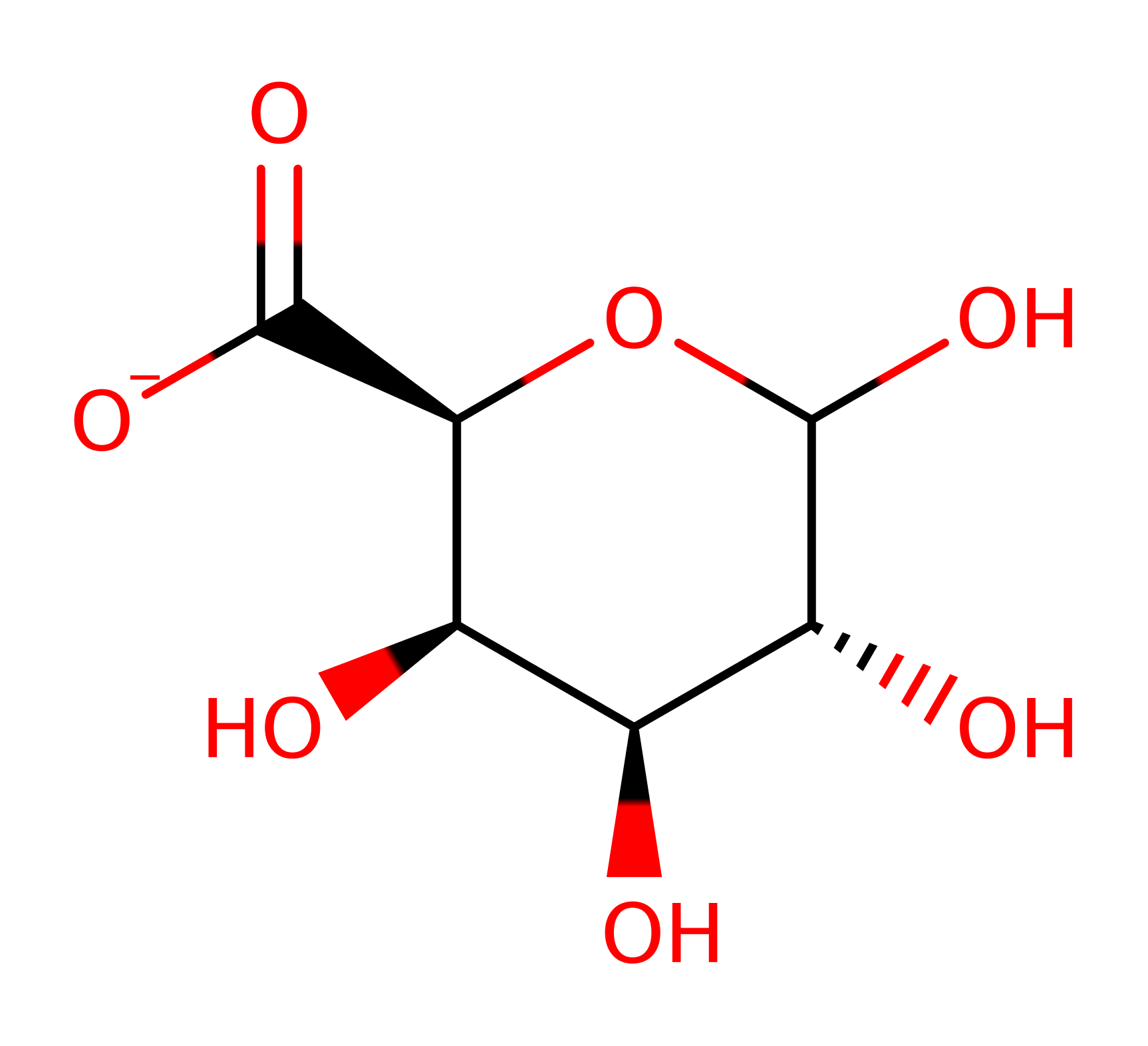
Polygalacturonase
Polygalacturonases hydrolyse the 1,4 linkage of de-esterified pectase. The enzyme belongs to the family 28 of glycosyl hydrolases, catalysing hydrolysis with inversion of stereochemistry at the anomeric carbon
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P26214
 (3.2.1.15)
(3.2.1.15)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1czf
- ENDO-POLYGALACTURONASE II FROM ASPERGILLUS NIGER
(1.68 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.160.20.10
 (see all for 1czf)
(see all for 1czf)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.2.1.15)
+
→
+
Alternative enzyme names: Endo-D-galacturonase, Endo-polygalacturonase, Endogalacturonase, Endopolygalacturonase, Pectin depolymerase, Pectin hydrolase, Pectin polygalacturonase, Pectinase, Pectolase, Poly-alpha-1,4-galacturonide glycanohydrolase, Poly(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonide) glycanohydrolase, Polygalacturonase,
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A hydrolytic water molecule, activated through hydrogen bonding to Asp180 and Asp202 attacks the glycosidic link in a single displacement reaction. The conserved Asp201 acts as a proton donor to the departing glycosidic oxygen. His 223 participates in a proton relay with Asp180, ensuring it is deprotonated to interact with the hydrolytic water.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1czf) | ||
| Asp201 | Asp201A | The residue acts as a general acid towards the departing glycosidic oxygen. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Asp202 | Asp202A | The residue activates the hydrolytic water molecule towards nucleophilic attack at the substrate glycosidic bond through hydrogen bonding. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys258, Arg256 | Lys258A, Arg256A | Modulate and decrease the pKa of the aspartate general acid/base Asp202 | modifies pKa |
| Asp180 | Asp180A | The residue acts as a general base towards the hydrolytic water molecule, activating it towards nucleophilic attack at the glycosidic bond. Interactions with a structurally aligned His223 creates a proton shuttle between the residues, ensuring that Asp202 is deprotonated in the presence of the attacking water molecule. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| His223 | His223A | Crystallographic data and mutagenesis studies have shown His223 to be catalytically essential to the reaction. The residue is thought to act as a proton acceptor from the hydrolytic water via a proton shuttle with Asp180. | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
*PDB label guide - RESx(y)B(C) - RES: Residue Name; x: Residue ID in PDB file;
y: Residue ID in PDB sequence if different from PDB file; B: PDB Chain;
C: Biological Assembly Chain if different from PDB. If label is "Not Found" it means this residue is not found in the reference PDB.
Chemical Components
References
- van Santen Y et al. (1999), J Biol Chem, 274, 30474-30480. 1.68-A Crystal Structure of Endopolygalacturonase II fromAspergillus niger and Identification of Active Site Residues by Site-directed Mutagenesis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.274.43.30474. PMID:10521427.
- Tu T et al. (2016), Sci Rep, 6, 38413-. Probing the role of cation-π interaction in the thermotolerance and catalytic performance of endo-polygalacturonases. DOI:10.1038/srep38413. PMID:27929074.
- Tu T et al. (2015), PLoS One, 10, e0135413-. New Insights into the Role of T3 Loop in Determining Catalytic Efficiency of GH28 Endo-Polygalacturonases. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0135413. PMID:26327390.
- Abbott DW et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 368, 1215-1222. The Structural Basis for Exopolygalacturonase Activity in a Family 28 Glycoside Hydrolase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.083. PMID:17397864.
- Cho SW et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 311, 863-878. The X-ray structure of Aspergillus aculeatus polygalacturonase and a modeled structure of the polygalacturonase-octagalacturonate complex. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4919. PMID:11518536.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp202A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp180A | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Asp201A | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| His223A | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| Arg256A | modifies pKa |
| Lys258A | modifies pKa |