Phosphoglycerate mutase (2,3-diphosphoglycerate-dependent)
Phosphoglycerate mutase (EC:5.4.2.11) from vertebrates, platyhelminths, mollusks, annelids, crustaceans, insects, algae, fungi, yeast and some bacteria (particularly Gram-negative) interconverts 2-phosphoglycerate and 3-phosphoglycerate via a transiently phosphorylated active site histidine. This histidine is phosphorylated by a 2,3-diphosphoglyerate cofactor. The enzyme has no requirement for metal ions and also catalyses, slowly, the reactions of EC 5.4.2.4, bisphosphoglycerate mutase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00950
 (5.4.2.11)
(5.4.2.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
1qhf
- YEAST PHOSPHOGLYCERATE MUTASE-3PG COMPLEX STRUCTURE TO 1.7 A
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1240
 (see all for 1qhf)
(see all for 1qhf)
- Cofactors
- (2r)-2,3-diphosphoglyceric acid (1), Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.4.2.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The substrate/cofactor initially binds with its phospho group favorably hydrogen bonded by His8, Arg59. The phosphohistidine intermediate would result from the nucleophilic attack of His8 on the phospho group, with accompanying transfer of a proton from Glu86 to the dephosphorylated product. This proton transfer is likely water-mediated. Formation of the catalytically active, protonated form of Glu86 would be promoted by the proximity of the substrate's phospho group. The phosphohistidine intermediate would be stabilised through hydrogen bonding interactions with Arg59. Dephosphorylation of this intermediate would be ccomplished through a water-mediated nucleophilic attack of the now deprotonated Glu86
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qhf) | ||
| His9 | His8A | Forms a tele-phosphohistidine intermediate. | covalent catalysis |
| Glu87 | Glu86A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton shuttle (general acid/base), proton donor |
| Arg60, His182 | Arg59A, His181A | Acts to stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
References
- Bond CS et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 316, 1071-1081. Mechanistic implications for Escherichia coli cofactor-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase based on the high-resolution crystal structure of a vanadate complex. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2002.5418. PMID:11884145.
- Wang Y et al. (2006), J Biol Chem, 281, 39642-39648. Seeing the Process of Histidine Phosphorylation in Human Bisphosphoglycerate Mutase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m606421200. PMID:17052986.
- Wang Y et al. (2005), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 331, 1207-1215. Crystal structure of human B-type phosphoglycerate mutase bound with citrate. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.243. PMID:15883004.
- Wang Y et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 39132-39138. Crystal Structure of Human Bisphosphoglycerate Mutase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m405982200. PMID:15258155.
- Rigden DJ et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 315, 1129-1143. Structure and mechanism of action of a cofactor-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase homolog from Bacillus stearothermophilus with broad specificity phosphatase activity. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5290. PMID:11827481.
- Rigden DJ et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 286, 1507-1517. Sulphate ions observed in the 2.12 Å structure of a new crystal form of S. cerevisiae phosphoglycerate mutase provide insights into understanding the catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.2566. PMID:10064712.
- White MF et al. (1992), Eur J Biochem, 207, 709-714. Development of a mutagenesis, expression and purification system for yeast phosphoglycerate mutase. Investigation of the role of active-site His181. PMID:1386023.

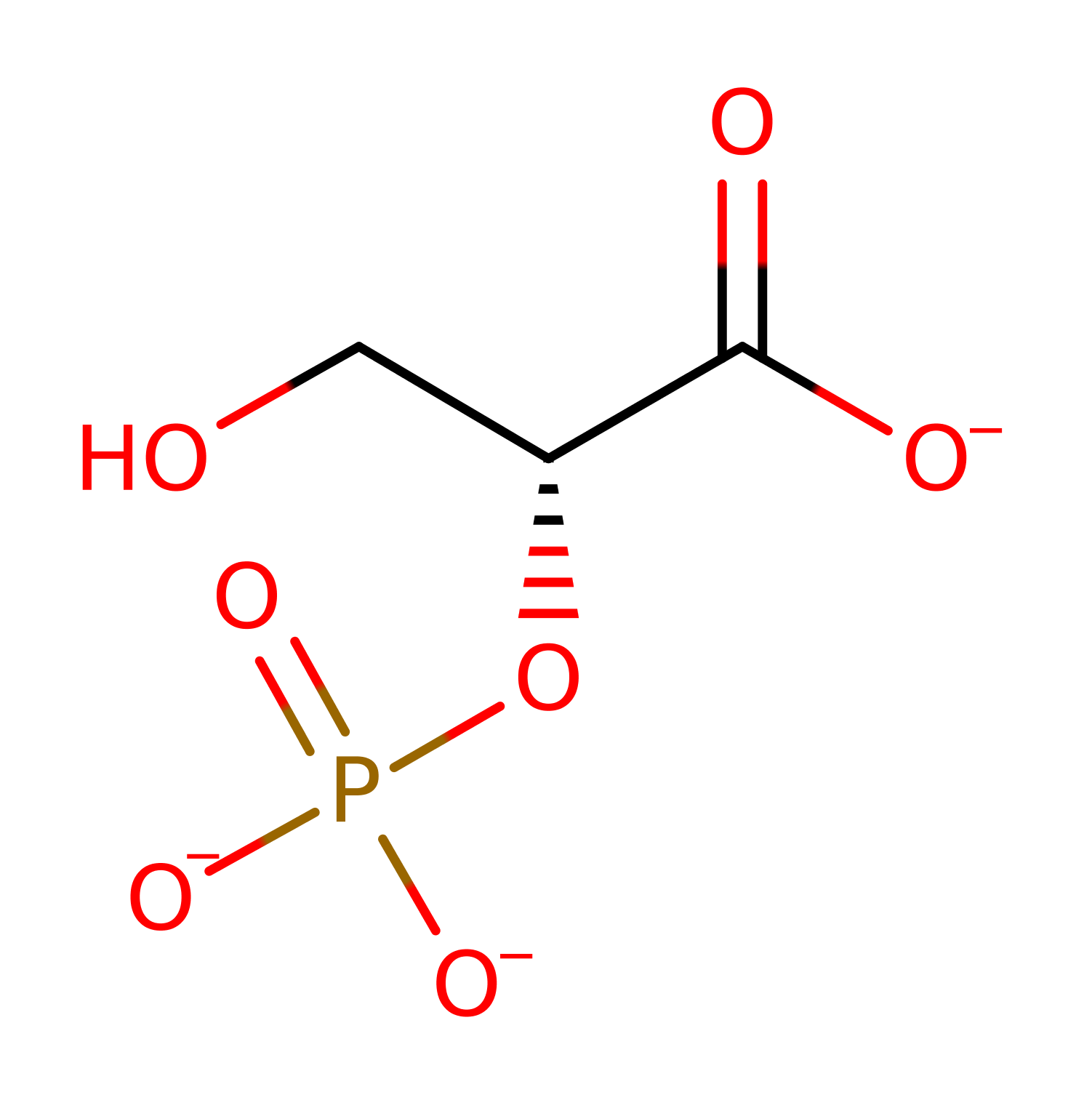
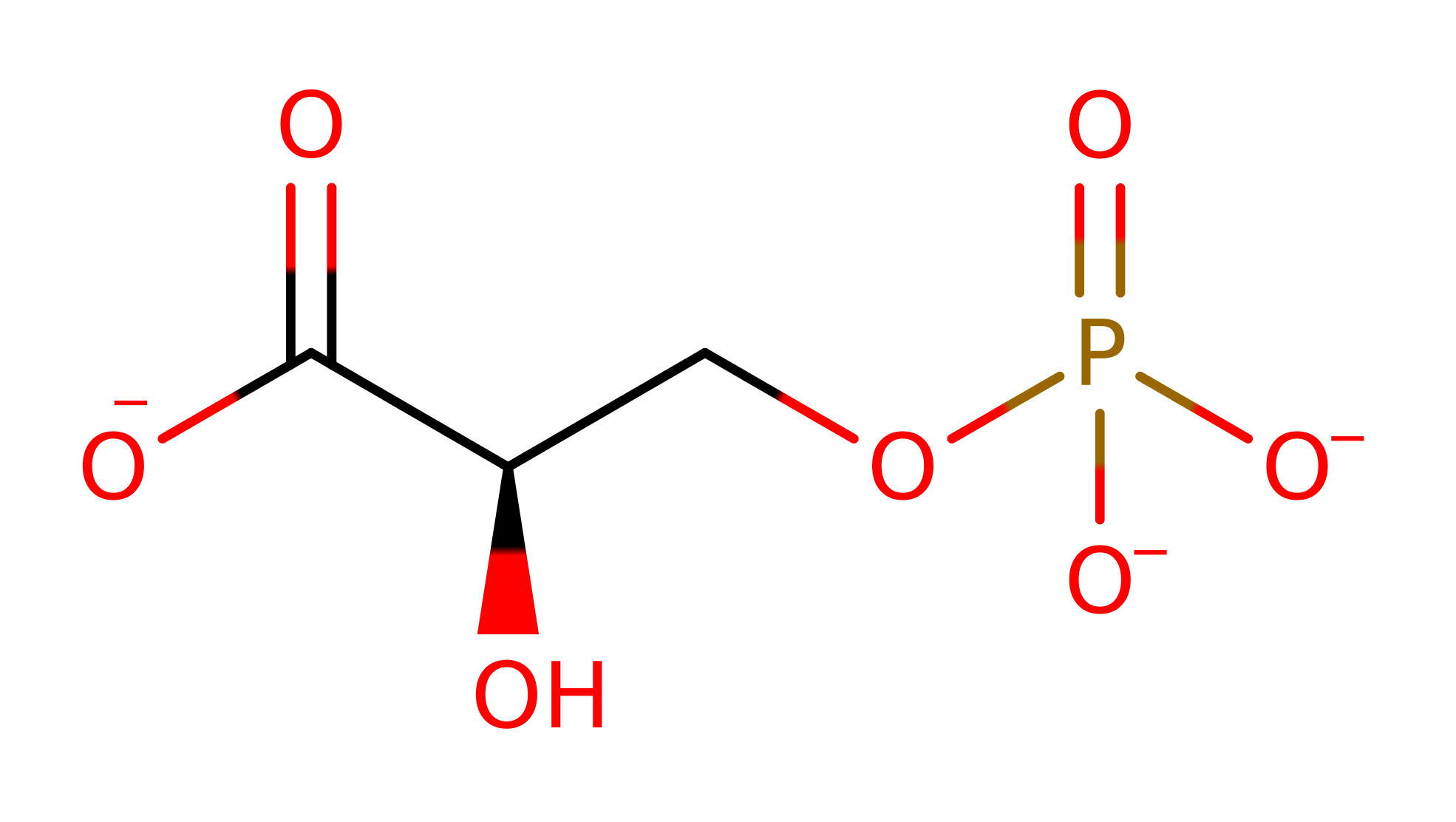
Step 1. His8 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the 2,3-BPG cofactor, which eliminates 2-phosphoglycerate, which is protonated via a proton relay through a water molecule and Glu86.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu86A | proton shuttle (general acid/base) |
| His8A | covalent catalysis |
| Arg59A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His181A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu86A | proton donor |