Histone acetyltransferase (GCN5 family)
p300/CBP-associating factor (PCAF) from Homo sapiens is a histone acetyltransferase. It catalyses the transfer of an acetyl group from acetyl-coenzyme A to the epsilon-amino group of specific lysine residues within histone amino termini. The acetylation of histone plays a crucial role in the transcriptional activation of specific target genes, and in transcriptional regulation. Eukaryotic GCN5 acetyltransferases influence diverse biological processes by acetylating histones and non-histone proteins and regulating chromatin and gene-specific transcription as part of multiprotein complexes.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q92830
 (2.3.1.-, 2.3.1.48)
(2.3.1.-, 2.3.1.48)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1z4r
- Human GCN5 Acetyltransferase
(1.74 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.630.30
 (see all for 1z4r)
(see all for 1z4r)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.48)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The hydrophobic residues Phe 563, Phe 568, Ile 571, Val 572, Leu 606, Ile 637 and Tyr 640 raise the pKa of Glu 570, facilitating proton transfer. Glu 570 acts as a general base by abstracting a proton from the N atom of lysine of the substrate histone. This activates the N atom for nucleophilic attack on the C atom of the acetyl carbonyl on acetyl-CoA, forming a negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate. This intermediate is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to the backbone amide of Cys 574. The carbonyl of the acetyl group is reformed, breaking the C-S bond to CoA, leaving the acetyl group covalently bound to the histone.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1z4r) | ||
| Glu575 | Glu575(81)A | Glu 570 acts as a base by deprotonating the N atom of the lysine of the histone substrate. | proton acceptor |
| Phe573, Val577, Ile576, Leu611, Ile642, Tyr645, Phe568 | Phe573(79)A, Val577(83)A, Ile576(82)A, Leu611(117)A, Ile642(148)A, Tyr645(151)A, Phe568(74)A | This hydrophobic residue serves to raise the pKa of Glu 570, facilitating proton transfer. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys579 (main-N) | Cys579(85)A (main-N) | The main chain amide of Cys 574 hydrogen bonds to the negatively charged tetrahedral intermediate, stabilising it. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay, rate-determining step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, bimolecular eliminationReferences
- Clements A et al. (1999), EMBO J, 18, 3521-3532. Crystal structure of the histone acetyltransferase domain of the human PCAF transcriptional regulator bound to coenzyme A. DOI:10.1093/emboj/18.13.3521. PMID:10393169.
- Cortopassi WA et al. (2016), J Mol Graph Model, 67, 69-84. Mechanisms of histone lysine-modifying enzymes: A computational perspective on the role of the protein environment. DOI:10.1016/j.jmgm.2016.04.011. PMID:27258188.
- Dutnall RN et al. (2002), Nat Struct Biol, 9, 888-891. Methyl magic and HAT tricks. DOI:10.1038/nsb1202-888. PMID:12447351.
- Trievel RC et al. (1999), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 96, 8931-8936. Crystal structure and mechanism of histone acetylation of the yeast GCN5 transcriptional coactivator. DOI:10.1073/pnas.96.16.8931. PMID:10430873.

Step 1. Glu570 acts as a general base and abstracts a proton from the histone lysine via a water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu611(117)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile642(148)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Val577(83)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe568(74)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr645(151)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe573(79)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys579(85)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ile576(82)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu575(81)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay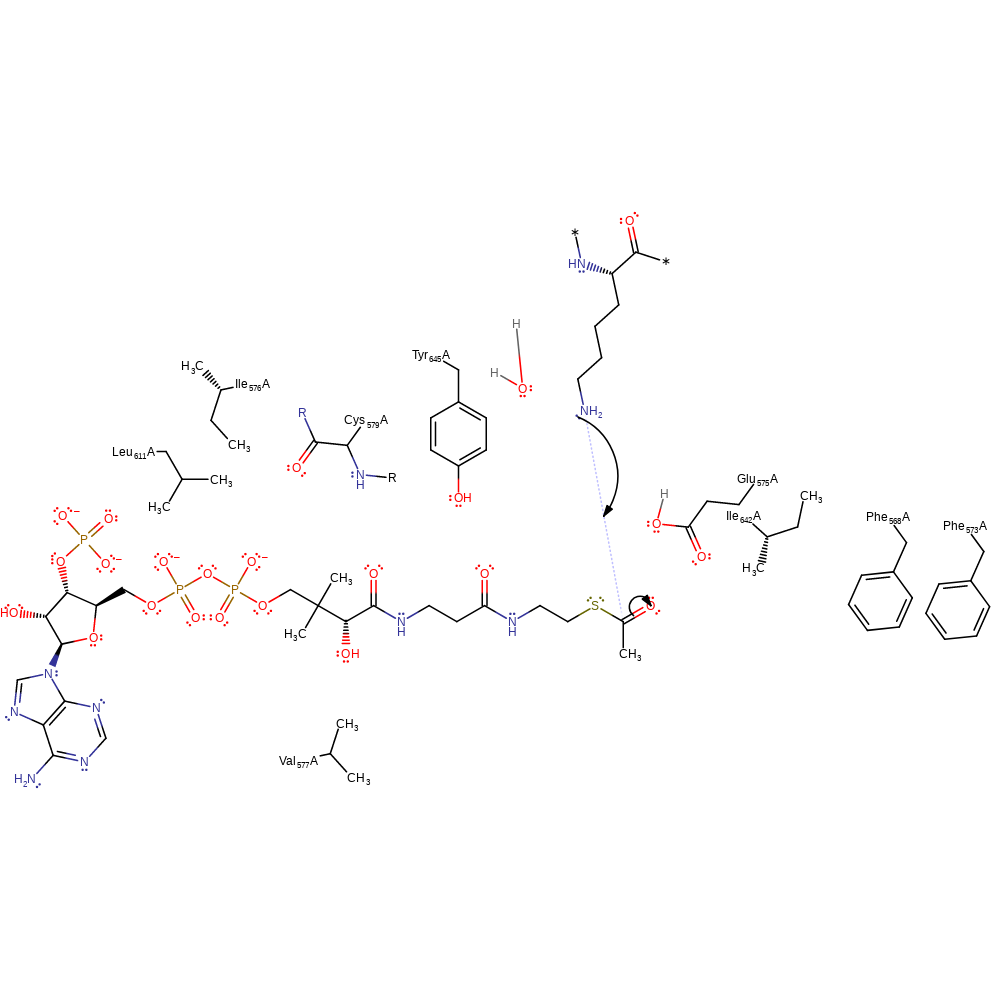
Step 2. Nucleophilic attack by the histone lysine on the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA, forming a negatively charged, tetrahedral intermediate
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
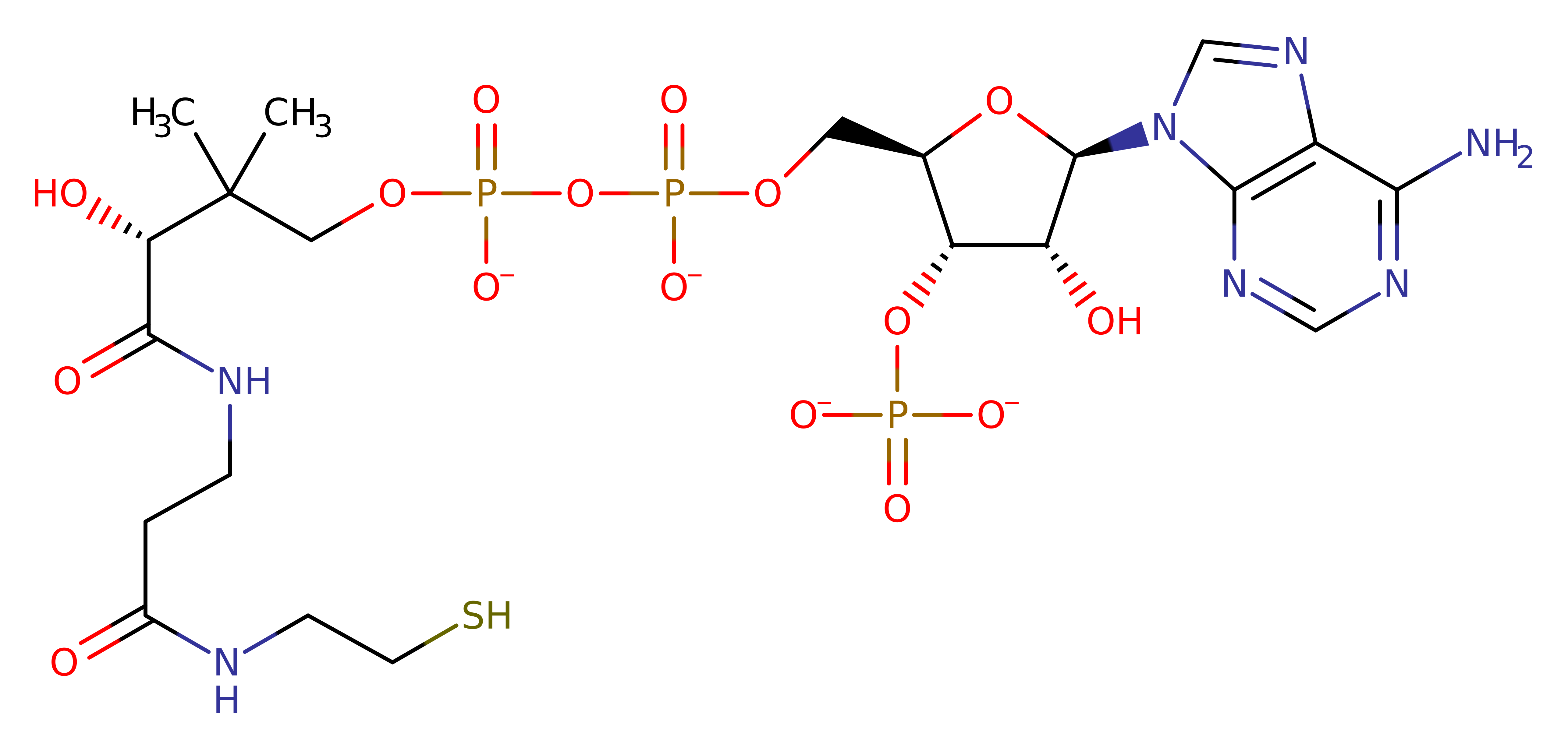
Step 3. The C-S bond to CoA breaks, leaving the acetyl group covalently bound to the histone. The protonation of the sulphur atom is inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|




 Download:
Download: