Ferrochelatase
Ferrochelatase (protoheme ferrolyase) catalyses the terminal step in heme biosynthesis, the insertion of ferrous iron into protoporphyrin IX to form protoheme IX (heme). In eukaryotes, the enzyme is nuclear encoded, synthesised in the cytoplasm, and translocated to the mitochondrion where it is proteolytically processed to its mature size of 42 kDa. Within the mitochondria, ferrochelatase is associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane with the active site facing the mitochondrial matrix.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P22830
 (4.99.1.1)
(4.99.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1hrk
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN FERROCHELATASE
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1400
 (see all for 1hrk)
(see all for 1hrk)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.99.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Fe begins being coordinated to Glu343, His 263 and two water molecules. The bond between Fe and Glu343 is broken, Fe immediately forms a new bond with one of the unprotonated nitrogens of the porphyrin ring. Glu343 deprotonates one of the nitrogens of the porphyrin ring allowing the second Fe-N bond to be formed. One of the water molecules dissociates from Fe. The bond between His263 and Fe breaks allowing the third Fe-N bond to be formed. His263 deprotonates the final nitrogen of the porphyrin ring allowing the fourth Fe-N bond to be formed.The second water molecule dissociates from Fe. Leaving Fe bound to the porphyrin ring.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hrk) | ||
| Arg164, Tyr165 | Arg164(100)A, Tyr165(101)A | Associated with bringing the metal ion in. Mutagenesis has proved lower affinity for iron but not for the porphyrin substrate. | |
| His263, Glu343 | His263(199)A, Glu343(279)A | Primarily a general base to deprotonate the pyrrole ring, the proton is then passed down a proton shuttle. | metal ligand, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
decoordination from a metal ion, coordination, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, proton transfer, overall product formedReferences
- Wang Y et al. (2009), J Inorg Biochem, 103, 1680-1686. QM/MM study of the insertion of metal ion into protoporphyrin IX by ferrochelatase. DOI:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2009.09.013. PMID:19850353.
- Wu J et al. (2016), J Chem Inf Model, 56, 2421-2433. Human Ferrochelatase: Insights for the Mechanism of Ferrous Iron Approaching Protoporphyrin IX by QM/MM and QTCP Free Energy Studies. DOI:10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00216. PMID:27801584.
- Sellers VM et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 9821-9827. Human Ferrochelatase: Characterization of Substrate−Iron Binding and Proton-Abstracting Residues†. DOI:10.1021/bi010012c. PMID:11502175.
- Wu CK et al. (2001), Nat Struct Biol, 8, 156-160. The 2.0 A structure of human ferrochelatase, the terminal enzyme of heme biosynthesis. DOI:10.1038/84152. PMID:11175906.

Step 1. The bond between Fe and Glu343 is broken, Fe immediately forms a new bond with one of the unprotonated nitrogens of the porphyrin ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His263(199)A | metal ligand |
| Glu343(279)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
decoordination from a metal ion, coordination, overall reactant used, rate-determining step
Step 2. Glu343 deprotonates one of the nitrogens of the porphyrin ring allowing the second Fe-N bond to be formed. One of the water molecules dissociates from Fe.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His263(199)A | metal ligand |
| Glu343(279)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, coordination, decoordination from a metal ion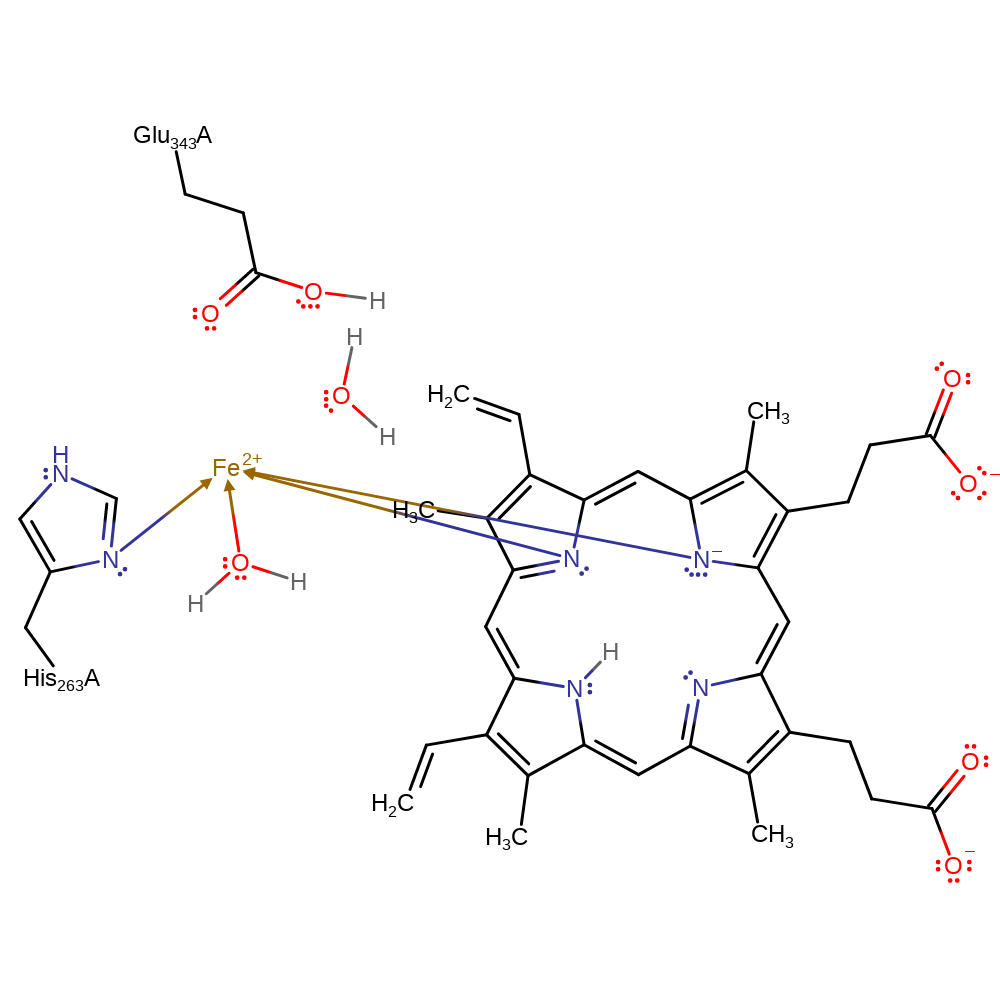
Step 3. The bond between His263 and Fe breaks allowing the third Fe-N bond to be formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His263(199)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
decoordination from a metal ion, coordination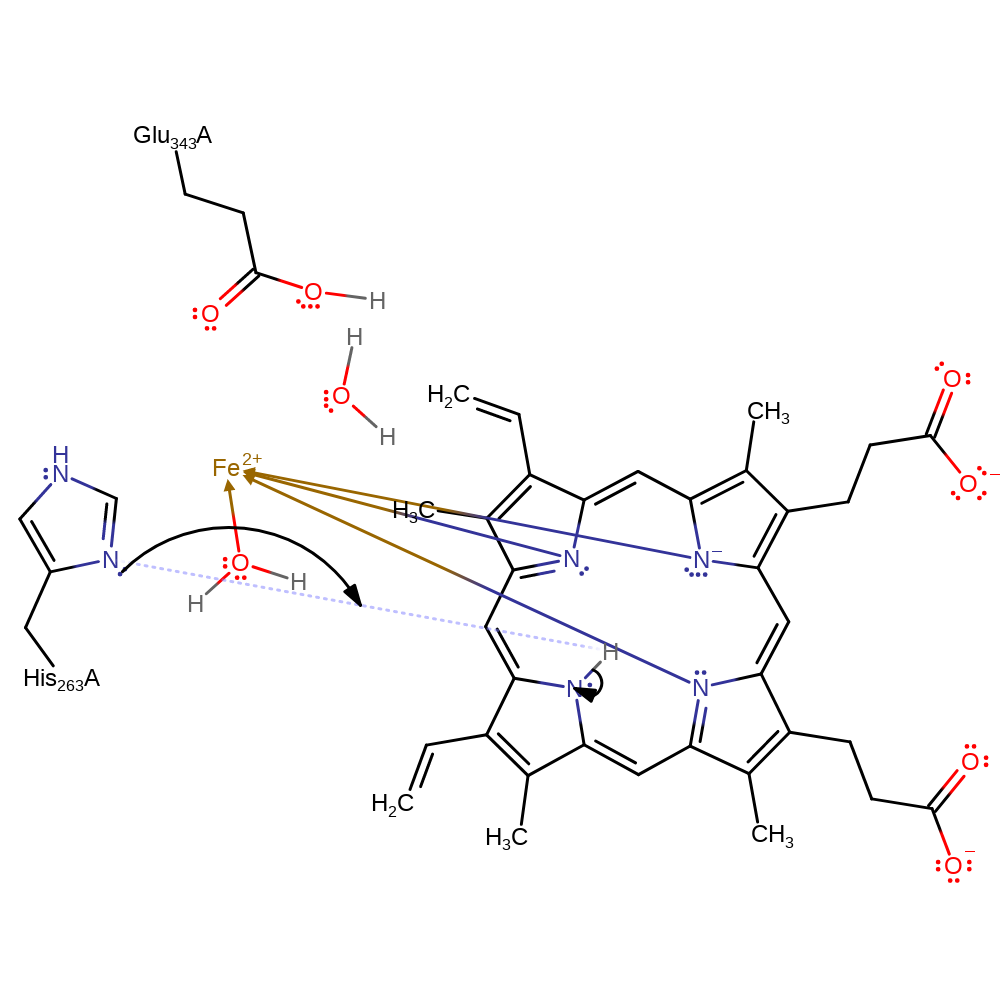
Step 4. His263 deprotonates the final nitrogen of the porphyrin ring allowing the fourth Fe-N bond to be formed.The second water molecule dissociates from Fe.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His263(199)A | proton acceptor |

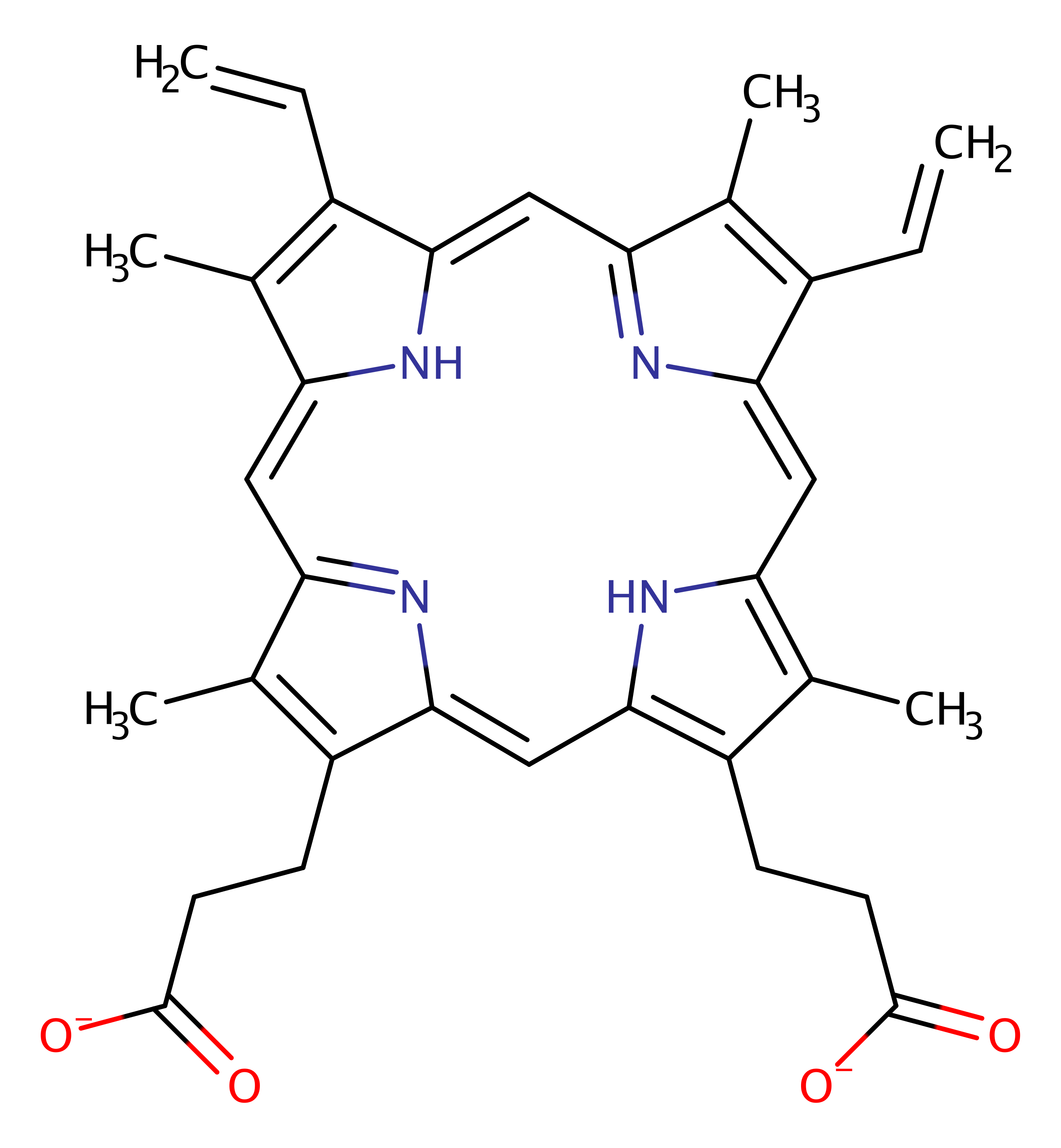
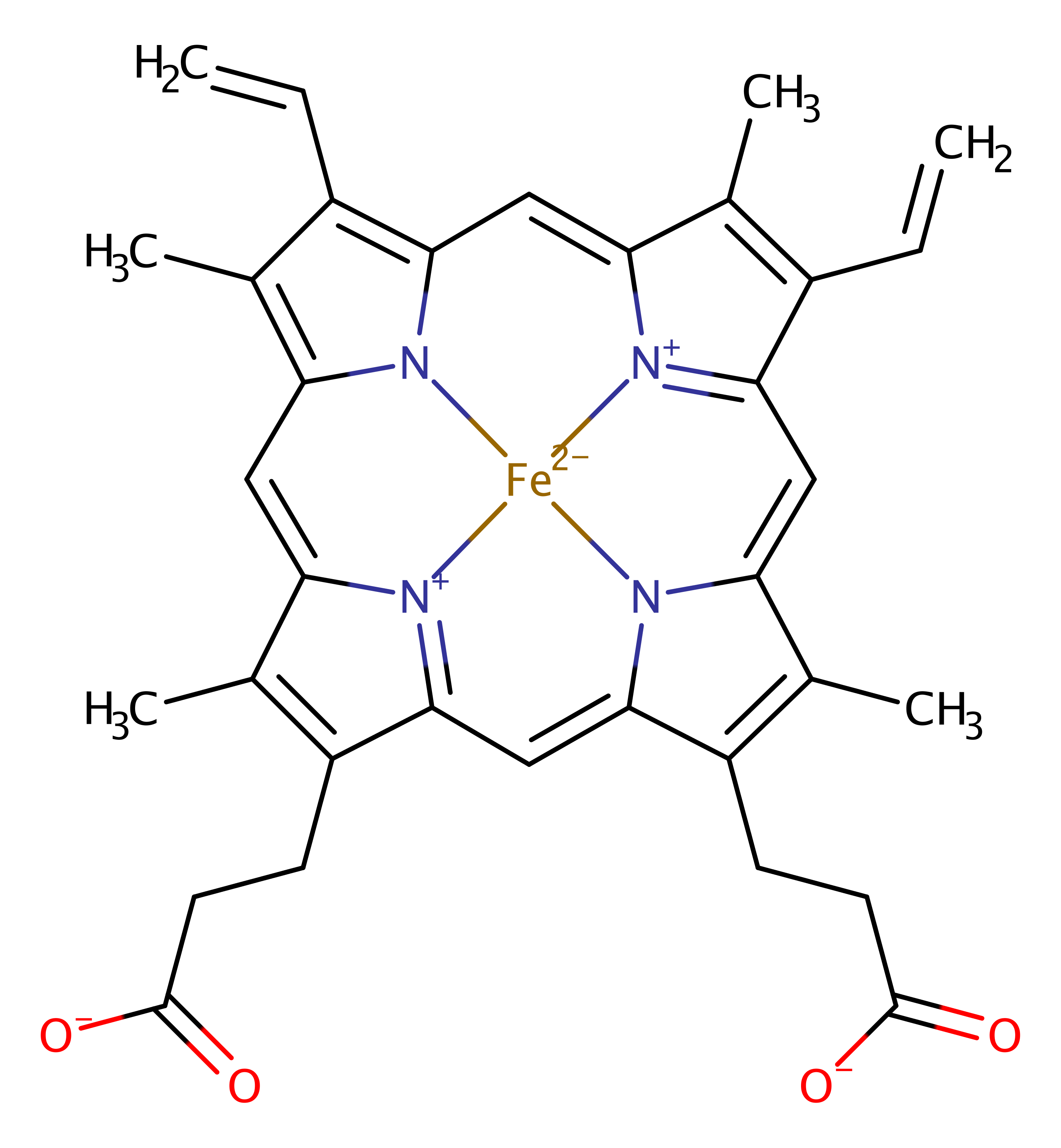

 Download:
Download: