Isomaltulose synthase
Isomaltulose synthase (PalI), also known as sucrose isomerase, catalyses the isomerisation of sucrose to produce isomaltulose (alpha-D-glucosylpyranosyl-1,6-D-fructofuranose) and trehalulose (alpha-D-glucosylpyranosyl-1,1-D-fructofuranose) as the main products with residual amounts of glucose and fructose isomaltulose and trehalulose, two functional isomers of sucrose, have been suggested as non-cariogenic alternatives to sucrose and are widely used in health products and the food industry.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q8KR84

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Klebsiella sp. LX3 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1m53
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ISOMALTULOSE SYNTHASE (PALI) FROM KLEBSIELLA SP. LX3
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.80
 (see all for 1m53)
(see all for 1m53)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.4.99.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glu295 protonates the oxygen atom of the glycosidic link, in concert with the nucleophile Asp241 attacking at C1, yielding a molecule of fructose and a glucose-enzyme complex. Sucrose then attacks at C1 with the C6 hydroxyl group, displacing Asp241 to form Isomatulose.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1m53) | ||
| Glu295 | Glu295(267)A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton donor |
| Asp241 | Asp241(213)A | Forms a covalent linkage with the sugar. | nucleofuge, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formedReferences
- Zhang D et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 35428-35434. Isomaltulose Synthase (PalI) of Klebsiella sp. LX3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE AND IMPLICATION OF MECHANISM. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m302616200. PMID:12819210.

Step 1. There is nucleophilic attack from Asp 241 on the C1 atom of the glucose component, this is in concert with oxygen of the glycosidic link being protonated by Glu 295. This results in the link being broken in an SN2 reaction and an enzyme bound intermediate being formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu295(267)A | proton donor |
| Asp241(213)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer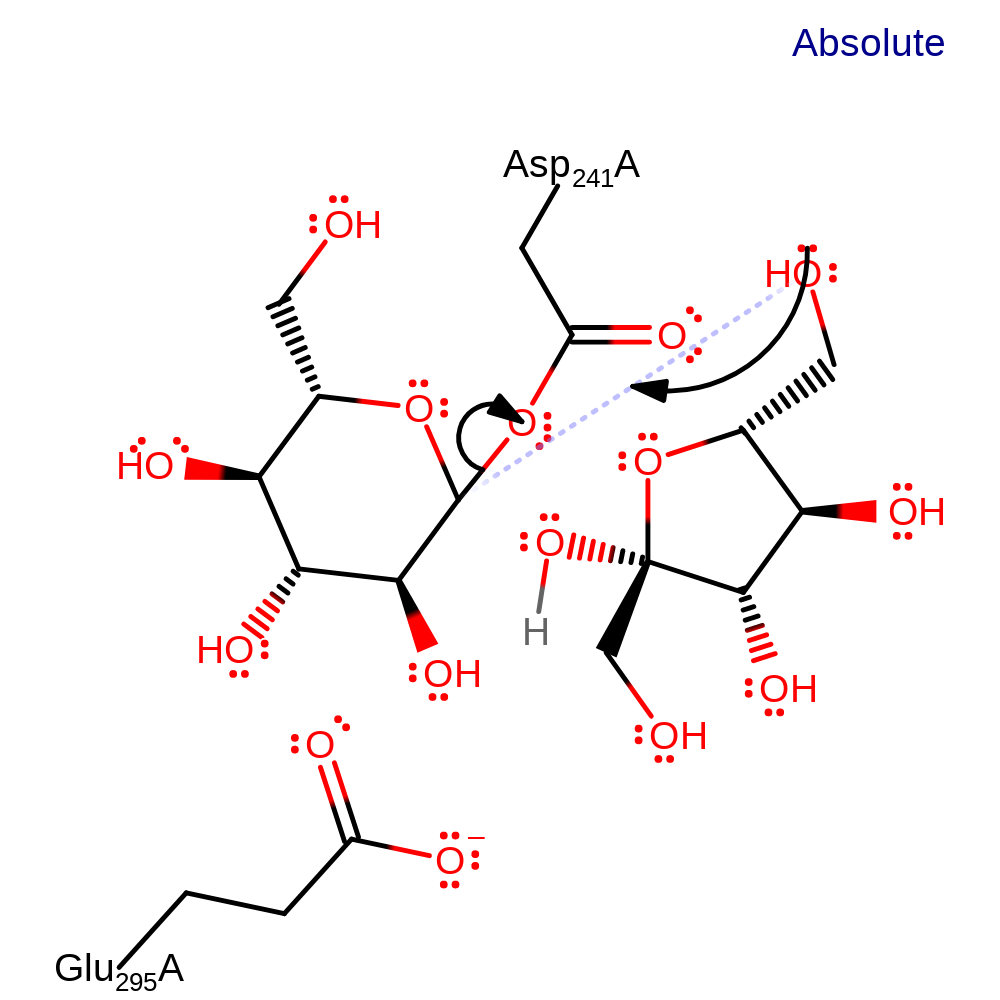
Step 2. There is a second SN2 reaction where C6 hydroxyl of the fructose attacks C1 of the Asp-glucose intermediate. This results in a new glycosidic linkage and the formation of Isomaltulose.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp241(213)A | nucleofuge |


 Download:
Download: