Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase
The allosteric hexameric enzyme from Escherichia coli catalyses the regulatory step of N-acetyl glucosamine catabolism, which consists of the isomerisation and deamination of glucosamine 6-phosphate (GlcN6P) to form fructose 6-phosphate (Fru6P) and ammonia.The enzyme is a hexamer of identical subunits arranged as a dimer of trimers and the allosteric sites appear located in the clefts between the subunits forming the trimers.
Glucosamine-6-phosphate isomerase is activated by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate. Mechanistically, it belongs to the group of aldoseketose isomerases, but its reaction also accomplishes a simultaneous amination/deamination.
The allosteric transition from T to R is generated upon binding of GlcNAc6P at the allosteric site or binding of active-site ligands (GlcN6P, Fru6P, GlcN-ol-6P). An important local conformational change relating allosteric control to catalysis is centred on residue Glu148. Glu148 participates in a proton-relay system that serves to polarise His143. This histidine is essential for the catalytic ring opening of the GlcN6P substrate. The His143 is primarily activated by its interaction with Glu148. The second residue in the His-Glu-Asx triangle appears to be either an Asp or Asn. Interestingly enough, in the work on Escherichia coli, Asn in this position severely disrupts the enzyme's activity.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A759
 (3.5.99.6)
(3.5.99.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dea
- STRUCTURE AND CATALYTIC MECHANISM OF GLUCOSAMINE 6-PHOSPHATE DEAMINASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI AT 2.1 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1360
 (see all for 1dea)
(see all for 1dea)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.99.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Once the ring has been opened, Asp72 deprotonates the carbon to which the amine group is attached in an assisted keto-enol tautomerisation reaction. Then water is added in an electrophlic addition across the C1-C2 pi bond. Ammonia is then eliminated and the final product of the active site is the linear product, which undergoes spontaneous cyclisation.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dea) | ||
| His143 | His143A | Acts as a general acid/base in the enzyme catalysed ring opening reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp72 | Asp72A | Acts as the general acid/base in the latter half of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp141, Glu148 | Asp141A, Glu148A | Involved in modulating the pKa of the general acid/base histidine for the ring opening step. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, decyclisation, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, bimolecular electrophilic addition, deamination, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, cyclisationReferences
- Montero-Morán GM et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 10187-10196. On the Multiple Functional Roles of the Active Site Histidine in Catalysis and Allosteric Regulation ofEscherichia coliGlucosamine 6-Phosphate Deaminase†. DOI:10.1021/bi0105835. PMID:11513596.
- Zhao Y et al. (2014), Phys Chem Chem Phys, 16, 18406-. A QM/MM MD study of the pH-dependent ring-opening catalysis and lid motif flexibility in glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase. DOI:10.1039/c4cp01609b. PMID:25069951.
- Liu C et al. (2008), J Mol Biol, 379, 73-81. Ring-Opening Mechanism Revealed by Crystal Structures of NagB and Its ES Intermediate Complex. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.031. PMID:18436239.
- Lucumí-Moreno A et al. (2005), Arch Biochem Biophys, 442, 41-48. On the functional role of Arg172 in substrate binding and allosteric transition in Escherichia coli glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2005.08.002. PMID:16168949.
- Vincent F et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 19649-19655. Structure and Kinetics of a Monomeric Glucosamine 6-Phosphate Deaminase: MISSING LINK OF THE NagB SUPERFAMILY? DOI:10.1074/jbc.m502131200. PMID:15755726.
- Horjales E et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 527-537. The allosteric transition of glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase: the structure of the T state at 2.3 Å resolution. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80069-0. PMID:10378272.
- Oliva G et al. (1995), Structure, 3, 1323-1332. Structure and catalytic mechanism of glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase from Escherichia coli at 2.1 å resolution. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00270-2. PMID:8747459.
- Altamirano MM et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 1153-1158. Identification of two cysteine residues forming a pair of vicinal thiols in glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase from Escherichia coli and a study of their functional role by site-directed mutagenesis. PMID:1734962.

Step 1. In a ring opening reaction, His143 deprotonates the C1 hydroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His143A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, decyclisation
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, cleaving the C-O bond with concomitant deprotonation of His143 by the newly formed oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation
Step 3. Asp72 deprotonates the carbon to which the amine group is attached.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 4. The newly formed carbanion initiates a double bond rearrangement and deprotonates the Asp72.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 5. In an electrophilic reaction, water is added across the C1-C2 pi bond. The water molecule approaches the re-face of the intermediate (i.e. from the same side as Asp72).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, deamination, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 6. Asp72 deprotonates the newly added hydroxyl group, eliminating ammonia from the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated
Step 7. The released ammonia deprotonates Asp72 to form ammonium and regenerate the enzyme starting state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp72A | proton donor |
Chemical Components

Step 8. The linear product undergoes spontaneous cyclisation outside of the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
reaction occurs outside the enzyme, cyclisationIntroduction
Once the ring has been opened, Asp72 deprotonates the carbon to which the amine group is attached in an assisted keto-enol tautomerisation reaction. Then a cis-enolamine is formed by the deprotonation of the amine group, water then adds to the the activated intermediate. The unstable carbinol ammonium intermediate then eliminates ammonia and the final product of the active site is the linear product, which undergoes spontaneous cyclisation.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dea) | ||
| His143 | His143A | Acts as a general acid/base in the enzyme catalysed ring opening reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Asp72 | Asp72A | Acts as the general acid/base in the latter half of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp141, Glu148 | Asp141A, Glu148A | Involved in modulating the pKa of the general acid/base histidine for the ring opening step. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, decyclisation, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, bimolecular electrophilic addition, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, reaction occurs outside the enzyme, cyclisationReferences
- Oliva G et al. (1995), Structure, 3, 1323-1332. Structure and catalytic mechanism of glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase from Escherichia coli at 2.1 å resolution. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00270-2. PMID:8747459.
- Oliva G et al. (1995), Structure, 3, 1323-1332. Structure and catalytic mechanism of glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase from Escherichia coli at 2.1 å resolution. DOI:10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00270-2.

Step 1. In a ring opening reaction, His143 deprotonates the C1 hydroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Asp72A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor, activator |
| His143A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton relay, decyclisation
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses, cleaving the C-O bond with concomitant deprotonation of His143 by the newly formed oxyanion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, intermediate formation
Step 3. Asp72 deprotonates the carbon to which the amine group is attached.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 4. The newly formed carbanion initiates a double bond rearrangement and deprotonates the Asp72.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 5. The proton from the ammonium group is transferred to the Asp72 carboxylate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 6. cis-enolamine then removes the proton from Asp72 to the position C1 pro-R of the intermediate which rearranges to form fructosimine 6-phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His143A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), proton transfer
Step 7. The imino bond reacts with a water molecule, giving an unstable carbinol ammonium intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His143A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer
Step 8. Asp72 deprotonates the newly added hydroxyl group, eliminating ammonia from the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His143A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp72A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu148A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp141A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp72A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated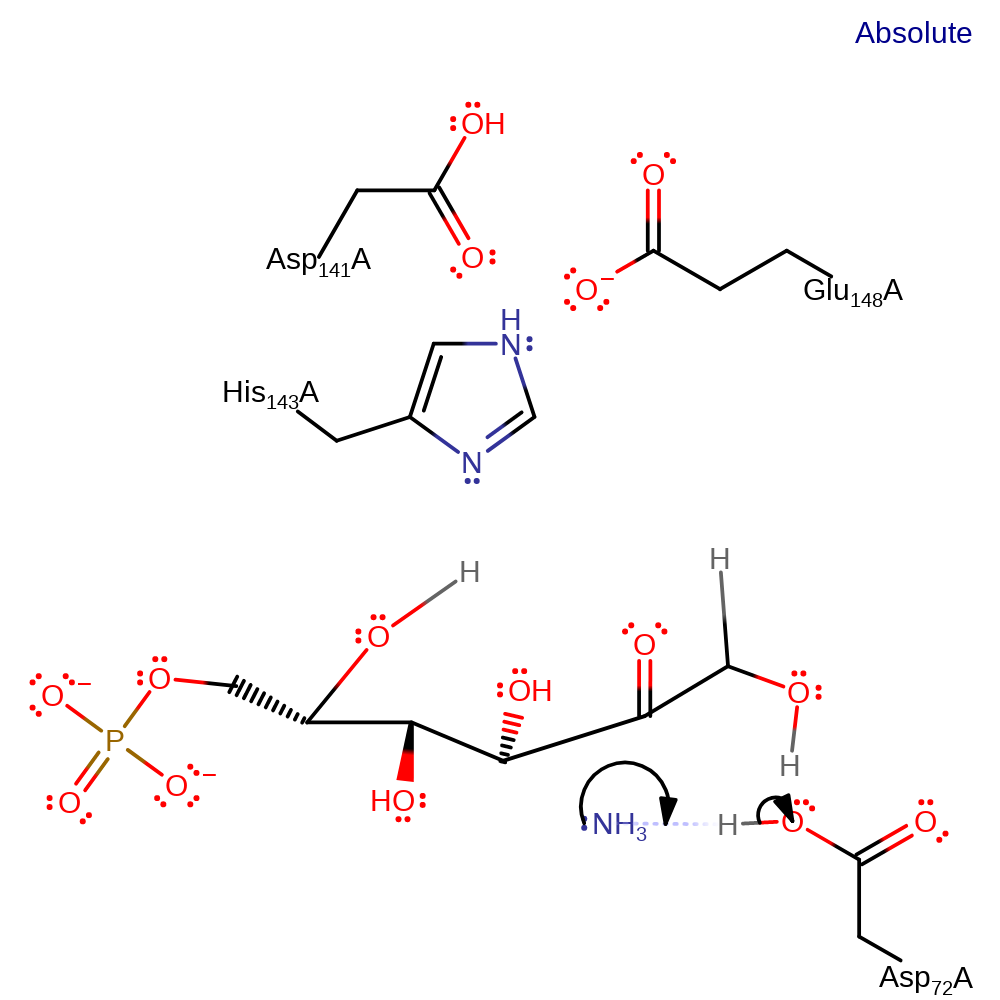
Step 9. The released ammonia deprotonates Asp72 to form ammonium and regenerate the enzyme starting state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp72A | proton donor |
Chemical Components

Step 10. The linear product undergoes spontaneous cyclisation outside of the enzyme active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|




 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: