6-deoxyerythronolide-B synthase
Thioesterase domain of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase, a polyketide synthase, catalyses the cyclisation and release of 6-deoxyerythronolide B via lactonisation. 6-deoxyerythronolide B is the macrocyclic core of the antibiotic erythromycin
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
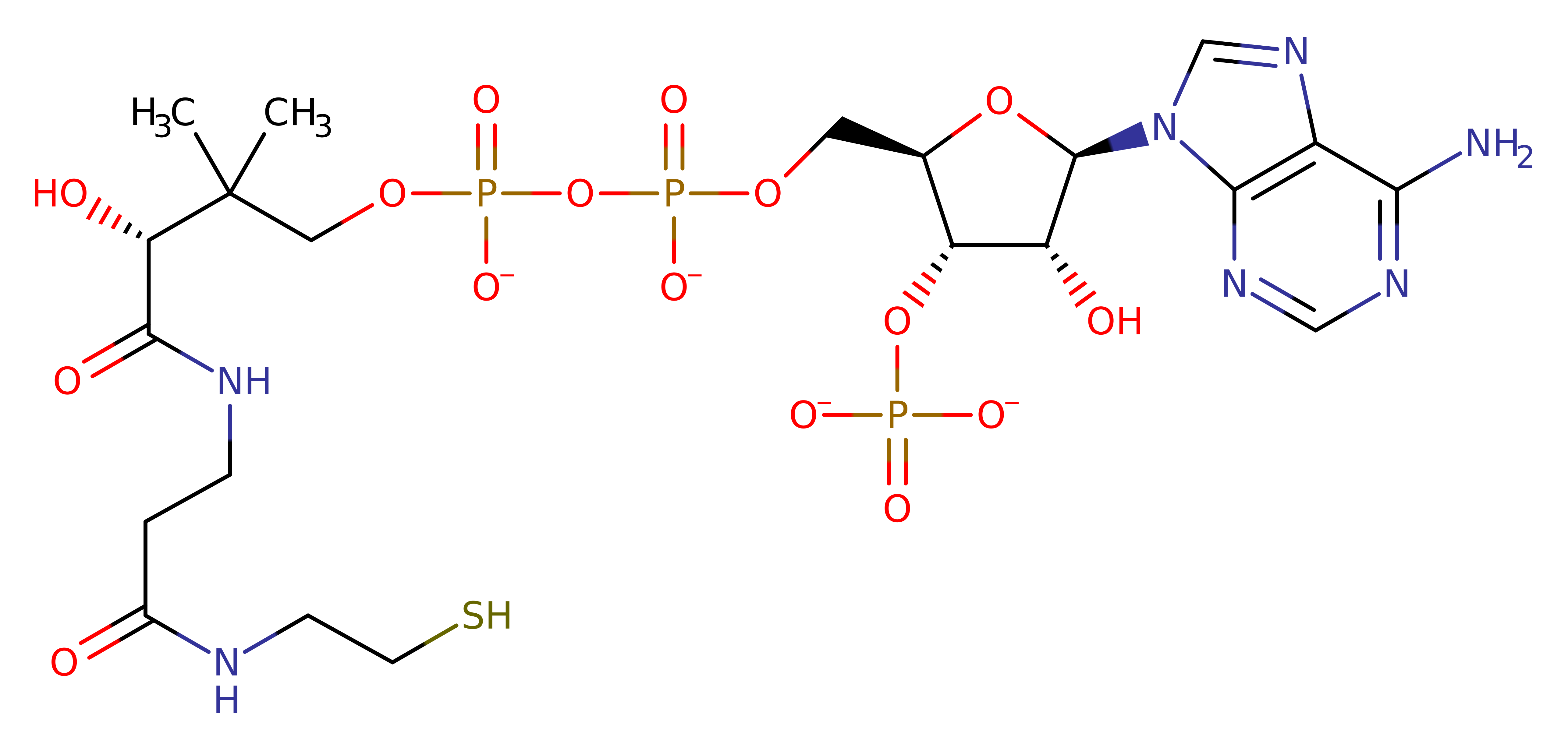
Q03133
 (2.3.1.94)
(2.3.1.94)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharopolyspora erythraea (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1kez
- Crystal Structure of the Macrocycle-forming Thioesterase Domain of Erythromycin Polyketide Synthase (DEBS TE)
(2.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1kez)
(see all for 1kez)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.94)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic triad consists of Asp169, His259 and Ser142. His259, stabilised by Asp-169, acts as a base that deprotonates Ser-142, as it attacks the ACP6-bound thioester substrate, to yield an acyl-O-serine intermediate. The NH of Ala-143 may serve as the oxyanion stabilising residue. The enzyme-bound intermediate is subsequently attacked by a hydroxyl group on the polyketide chain.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1kez) | ||
| His3148 | His259A | It deprotonates Ser 142 to allow its nucleophilic attack of thioester substrate to yield an acyl-O-serine intermediate. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp3058 | Asp169A | It alters the pKa of His 259 and stabilise it for the deprotonation of Ser 142 | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala3032 (main-N) | Ala143A (main-N) | Its backbone NH lines the oxyanion hole and acts as a hydrogen bond donor to the C1 carbonyl | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser3031 | Ser142A | It nucleophilically attacks the thioester substrate upon deprotonation by His 259. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Tsai SC et al. (2001), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 98, 14808-14813. Crystal structure of the macrocycle-forming thioesterase domain of the erythromycin polyketide synthase: Versatility from a unique substrate channel. DOI:10.1073/pnas.011399198. PMID:11752428.
- Robbins T et al. (2016), Curr Opin Struct Biol, 41, 10-18. Structure and mechanism of assembly line polyketide synthases. DOI:10.1016/j.sbi.2016.05.009. PMID:27266330.
- Chen X et al. (2016), ACS Catal, 6, 4369-4378. Theoretical Studies on the Mechanism of Thioesterase-Catalyzed Macrocyclization in Erythromycin Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1021/acscatal.6b01154.
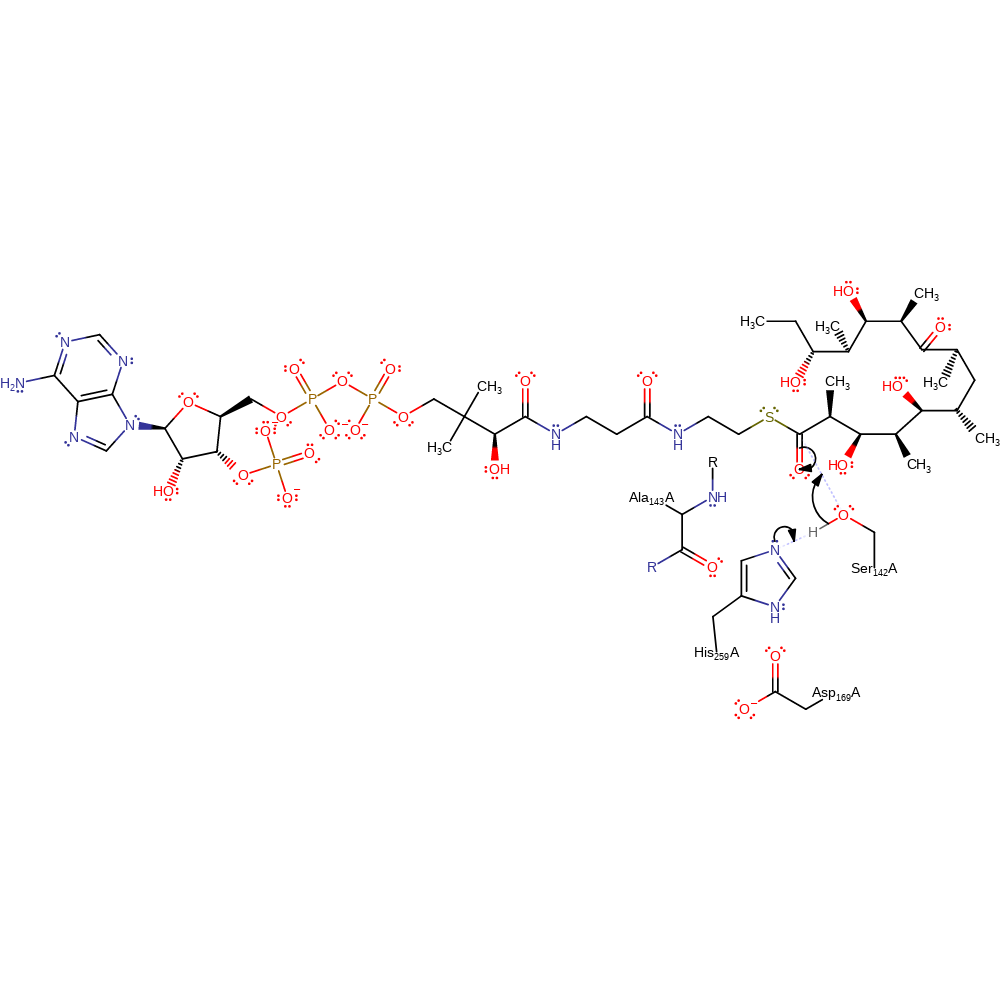
Step 1. His259 deprotonates Ser142 which activates it for nucleophilic attack on the C1 carbonyl carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser142A | covalently attached |
| Ala143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp169A | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| His259A | proton acceptor |
| Ser142A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. The oxyanion collapse resulting in the elimination of CoA which will accept a proton from the C13 OH
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp169A | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| Ser142A | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton transfer
Step 3. The deprotonated C11 oxygen then nucleophilically attacks the C1 carbonyl carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp169A | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| Ser142A | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation
Step 4. The oxyanion intiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the acyl-enzyme bond and the released Ser142 will then accept a proton from His259.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala143A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp169A | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| Ser142A | proton acceptor |
| His259A | proton donor |
| Ser142A | nucleofuge |


 Download:
Download: