Choline O-acetyltransferase
Choline acetyltransferase synthesises the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from choline in neurones and other cell types. It catalyses the reversible transfer of an acetyl group between acetyl CoA and choline, and belongs to the choline/carnitine acyltranserase family which also includes enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
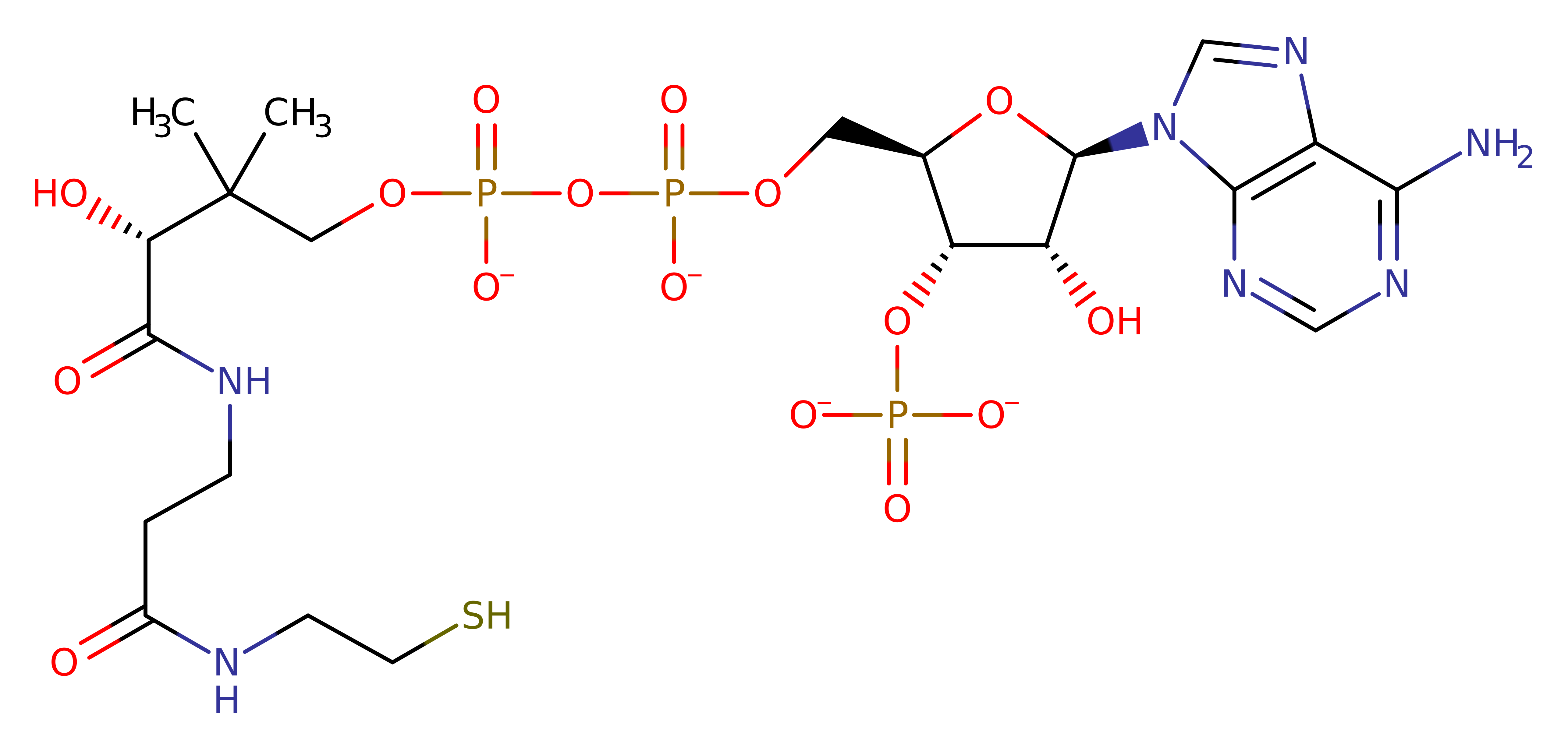
P32738
 (2.3.1.6)
(2.3.1.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)

- PDB
-
1q6x
- Crystal structure of rat choline acetyltransferase
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.559.40
 3.30.559.70
3.30.559.70  (see all for 1q6x)
(see all for 1q6x)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His 334 acts as a general base to remove the proton from the choline OH group as the oxygen attacks the carbonyl of acetyl CoA. The resulting tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate is stabilised by Ser 550. Collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate releases CoA which is protonated by the His 334. Tyr 95 and Pro 108 function to stabilise the unprotonated form of His 334 N-epsilon so that it can act as a general base in the first step of the reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1q6x) | ||
| Tyr95, Pro108 | Tyr95A, Pro108A | Steric packing with His 334 forces the His 334 to adopt a strained conformation with an intraresidue hydrogen bond between N-delta and its carbonyl oxygen. This is proposed to position N-epsilon and stabilise its non-protonated, nucleophilic state. | |
| His334 | His334A | Acts as a general base, extracting a proton from the attacking hydroxyl group of choline. Later protonates the departing sulphydryl group of CoA. | |
| Ser550 | Ser550A | Hydrogen bonding from side chain OH stabilises the tetrahedral intermediate/transition state. |
Chemical Components
References
- Jogl G et al. (2003), Cell, 112, 113-122. Crystal Structure of Carnitine Acetyltransferase and Implications for the Catalytic Mechanism and Fatty Acid Transport. DOI:10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01228-x. PMID:12526798.
- Kim AR et al. (2006), Biochemistry, 45, 14621-14631. Substrate binding and catalytic mechanism of human choline acetyltransferase. DOI:10.1021/bi061536l. PMID:17144655.
- Cai Y et al. (2004), EMBO J, 23, 2047-2058. Choline acetyltransferase structure reveals distribution of mutations that cause motor disorders. DOI:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600221. PMID:15131697.
- Wu D et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 13159-13165. Structure of Human Carnitine Acetyltransferase: MOLECULAR BASIS FOR FATTY ACYL TRANSFER. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m212356200. PMID:12562770.