2-hydroxymuconate tautomerase
2-hydroxymuconate tautomerase is also known as 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase (4-OT). Converts 2-hydroxymuconate to the alpha-beta-unsaturated ketone, 2-oxo-3-hexenedioate [PMID:1339435]. This enzyme forms part of a bacterial metabolic pathway that oxidatively catabolises toluene, o-xylene, 3-ethyltoluene, and 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene into intermediates of the citric acid cycle.
4-OT has only 62 residues in each chain, making it one of the smallest enzyme subunits known [PMID:12051677]. In solution, however, the enzyme forms a hexamer of six identical subunits, so the active site may be formed by amino acid residues from several subunits [PMID:8547259].
The rate of catalysis approaches the diffusion-controlled limit. The gene for the enzyme is carried by the TOL plasmid in Pseudomonas putrida, and is involved in the catabolism of aromatic carbon sources. This entry represents a group of 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerases found in Pseudomonas [PMID:1339435] and other species of bacteria and archaea.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q01468
 (5.3.2.6)
(5.3.2.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas putida (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1bjp
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF 4-OXALOCROTONATE TAUTOMERASE INACTIVATED BY 2-OXO-3-PENTYNOATE AT 2.4 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.429.10
 (see all for 1bjp)
(see all for 1bjp)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.2.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The N-terminal proline, is thought to act as a catalytic base (the only known enzyme for which this is the case). Arg39 and Arg11 are thought to stabilise the binding of the carboxylate groups on the substrate and Arg39 may also play a role in altering the pKa of Pro1.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bjp) | ||
| Arg40, Arg62 | Arg39B, Arg61B(BB) | Stabilises the transition states and reactive intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe51 | Phe50B(BB) | Activates the substrate. | activator, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Pro2 (N-term) | Pro1A(AB) (N-term) | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, polar/non-polar interaction |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Whitman CP (2002), Arch Biochem Biophys, 402, 1-13. The 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase family of enzymes: how nature makes new enzymes using a β–α–β structural motif. DOI:10.1016/s0003-9861(02)00052-8. PMID:12051677.
- van der Meer JY et al. (2016), Nat Commun, 7, 10911-. Using mutability landscapes of a promiscuous tautomerase to guide the engineering of enantioselective Michaelases. DOI:10.1038/ncomms10911. PMID:26952338.
- Huddleston JP et al. (2014), Arch Biochem Biophys, 564, 189-196. Identification and characterization of new family members in the tautomerase superfamily: Analysis and implications. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2014.08.019. PMID:25219626.
- Terrell CR et al. (2013), Arch Biochem Biophys, 537, 113-124. Structural and kinetic characterization of two 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerases in Methylibium petroleiphilum strain PM1. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2013.06.016. PMID:23831510.
- Wu P et al. (2012), J Phys Chem B, 116, 6889-6897. Catalytic Mechanism of 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase: Significances of Protein–Protein Interactions on Proton Transfer Pathways. DOI:10.1021/jp212643j. PMID:22417185.
- Ruiz-Pernía JJ et al. (2009), J Am Chem Soc, 131, 2687-2698. Critical Role of Substrate Conformational Change in the Proton Transfer Process Catalyzed by 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase. DOI:10.1021/ja8087423. PMID:19199636.
- Kasai D et al. (2009), J Bacteriol, 191, 6758-6768. Uncovering the Protocatechuate 2,3-Cleavage Pathway Genes. DOI:10.1128/jb.00840-09. PMID:19717587.
- Sevastik R et al. (2007), Bioorg Chem, 35, 444-457. Quantum chemical modeling of enzymatic reactions: The case of 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase. DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2007.08.003. PMID:17904194.
- Tuttle T et al. (2007), J Phys Chem B, 111, 7665-7674. Substrate Orientation in 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase and Its Effect on QM/MM Energy Profiles. DOI:10.1021/jp0685986. PMID:17567166.
- Wang SC et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 11919-11929. Kinetic and Stereochemical Analysis of YwhB, a 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase Homologue inBacillus subtilis: Mechanistic Implications for the YwhB- and 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase-Catalyzed Reactions†. DOI:10.1021/bi701231a. PMID:17902707.
- Tuttle T et al. (2006), J Phys Chem B, 110, 19685-19695. Understanding the Enzymatic Activity of 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase and Its Mutant Analogues: A Computational Study. DOI:10.1021/jp0634858. PMID:17004838.
- Azurmendi HF et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 7725-7737. Half-of-the-Sites Binding of Reactive Intermediates and Their Analogues to 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase and Induced Structural Asymmetry of the Enzyme†. DOI:10.1021/bi0502590. PMID:15909987.
- Cisneros GA et al. (2004), Biochemistry, 43, 6885-6892. The Protein Backbone Makes Important Contributions to 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase Enzyme Catalysis: Understanding from Theory and Experiment†. DOI:10.1021/bi049943p. PMID:15170325.
- Cisneros GA et al. (2003), J Am Chem Soc, 125, 10384-10393. Ab Initio QM/MM Study Shows There Is No General Acid in the Reaction Catalyzed by 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase. DOI:10.1021/ja029672a. PMID:12926963.
- Czerwinski RM et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 1984-1995. The Structural Basis for the Perturbed pKaof the Catalytic Base in 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase: Kinetic and Structural Effects of Mutations of Phe-50†. DOI:10.1021/bi0024714. PMID:11329265.
- Harris TK et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 12343-12357. Kinetic, Stereochemical, and Structural Effects of Mutations of the Active Site Arginine Residues in 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase†. DOI:10.1021/bi991116e. PMID:10493802.
- Soares TA et al. (1999), Biopolymers, 50, 319-328. Docking of 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase substrates: Implications for the catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1002/(sici)1097-0282(199909)50:3<319::aid-bip7>3.0.co;2-8. PMID:10397792.
- Taylor AB et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 14692-14700. Crystal Structure of 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase Inactivated by 2-Oxo-3-pentynoate at 2.4 Å Resolution: Analysis and Implications for the Mechanism of Inactivation and Catalysis†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi981607j. PMID:9778344.
- Stivers JT et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 803-813. Catalytic Role of the Amino-Terminal Proline in 4-Oxalocrotonate Tautomerase: Affinity Labeling and Heteronuclear NMR Studies†. DOI:10.1021/bi951077g. PMID:8547260.
- Subramanya HS et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 792-802. Enzymatic Ketonization of 2-Hydroxymuconate: Specificity and Mechanism Investigated by the Crystal Structures of Two Isomerases†. DOI:10.1021/bi951732k. PMID:8547259.
- Chen LH et al. (1992), J Biol Chem, 267, 17716-17721. 4-Oxalocrotonate tautomerase, an enzyme composed of 62 amino acid residues per monomer. PMID:1339435.

Step 1. The N-terminal proline deprotonates the CH2 of the substrate, initiating double bond rearrangement and forming the enol form of the substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe50B(BB) | activator, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Arg39B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Pro1A(AB) (N-term) | hydrogen bond acceptor, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Arg61B(BB) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pro1A(AB) (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation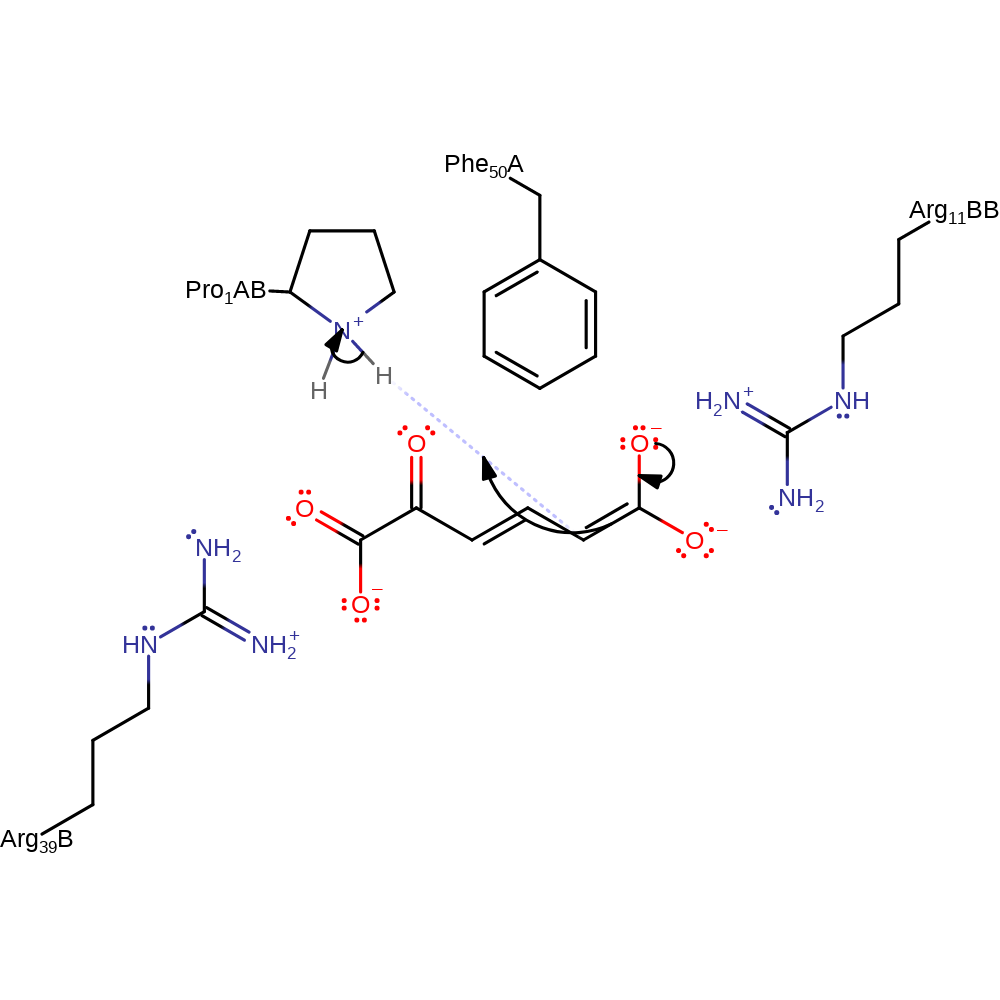
Step 2. The oxyanion collapses back, initiating double bond rearrangement, and the terminal double bond then accepts a proton from the N-terminal proline.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe50B(BB) | polar/non-polar interaction |
| Arg39B | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Pro1A(AB) (N-term) | hydrogen bond donor, polar/non-polar interaction |
| Arg61B(BB) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pro1A(AB) (N-term) | proton donor |
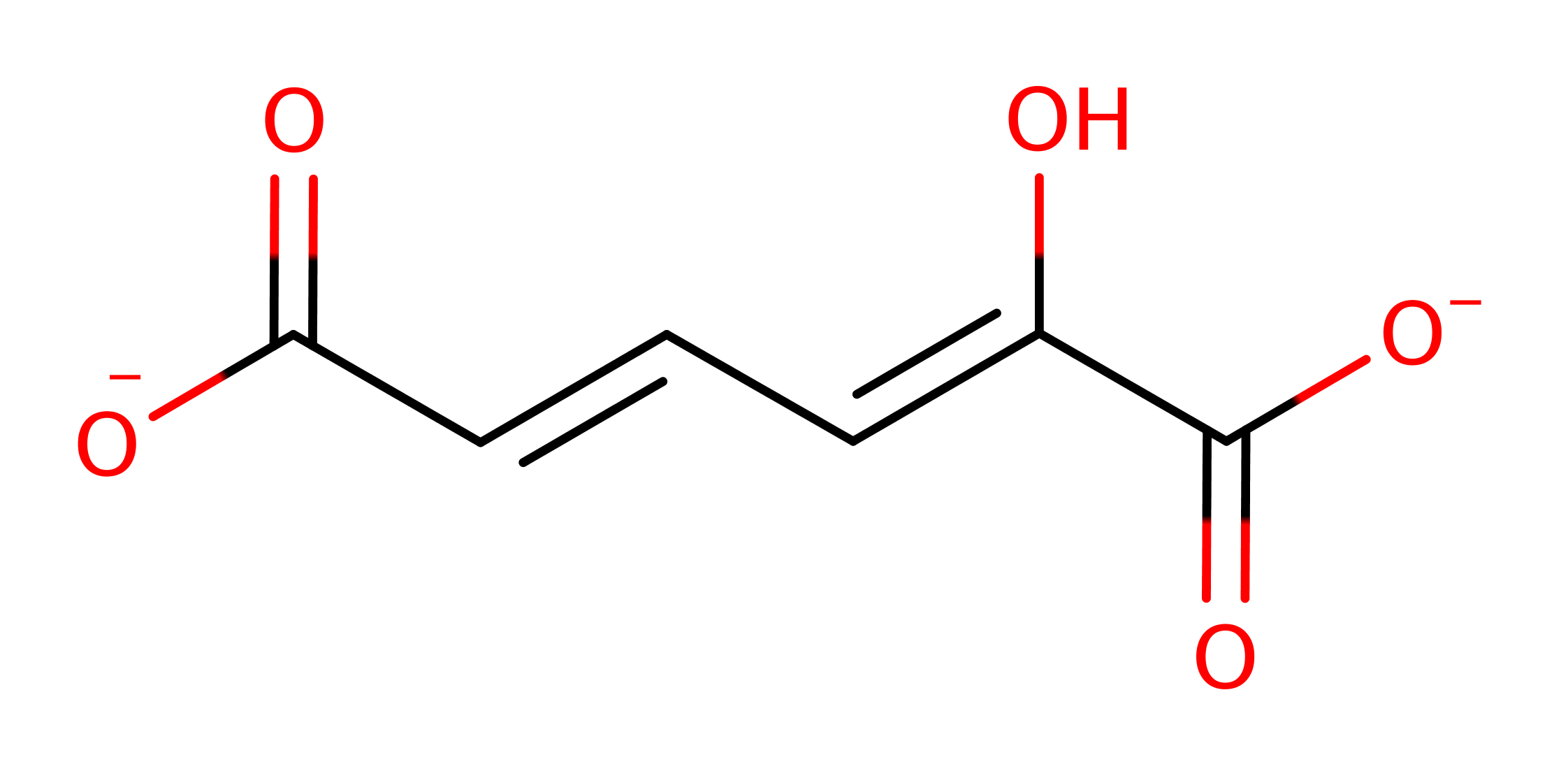

 Download:
Download: