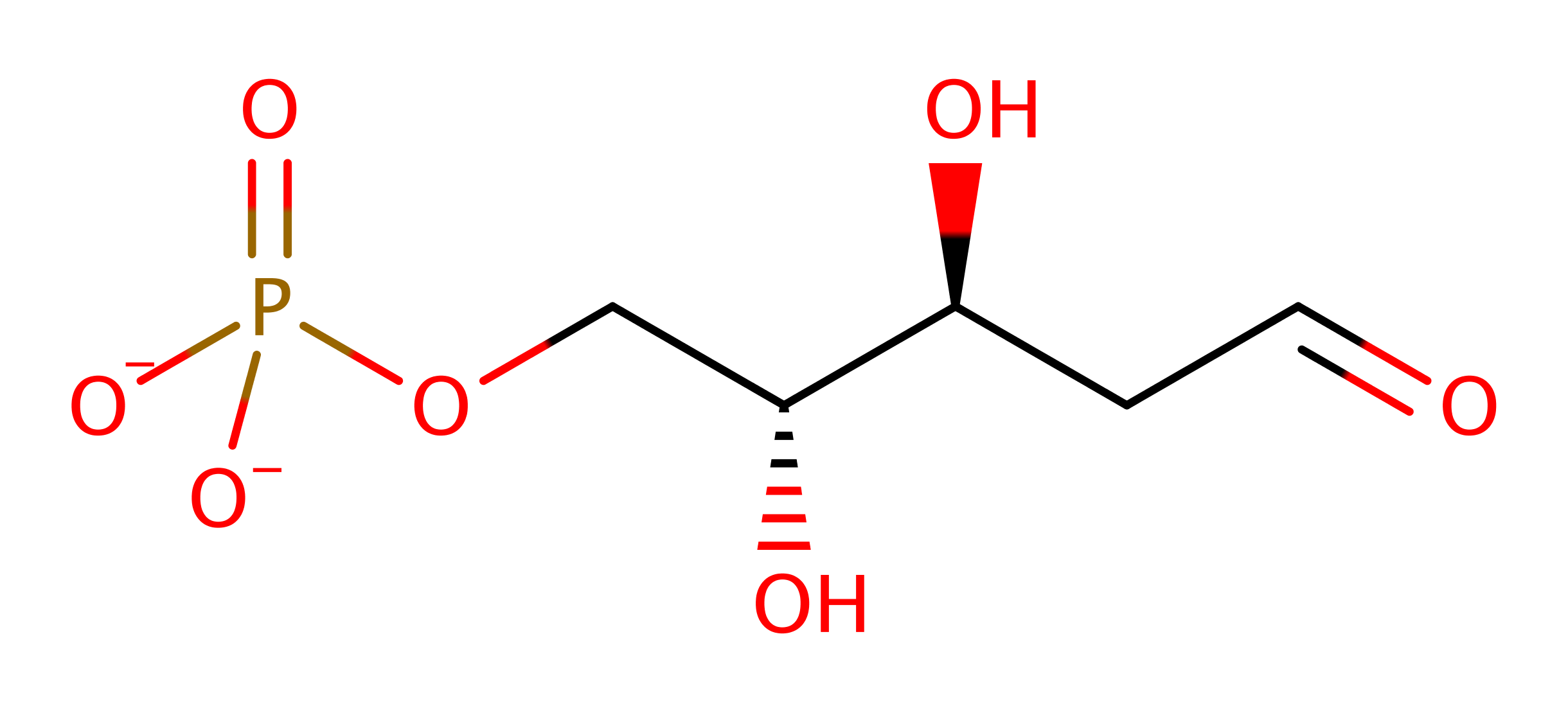
Deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase
The class I aldolase Deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase from Escherichia coli is able to catalyse the formation of DRP from acetaldehyde and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. As such is it a rare form of class I aldolase as it is able to catalyse the condensation between two aldehydes rather than an aldehyde and a ketone.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A6L0
 (4.1.2.4)
(4.1.2.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1p1x
- Comparison of class I aldolase binding site architecture based on the crystal structure of 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase determined at 0.99 Angstrom resolution
(0.99 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.70
 (see all for 1p1x)
(see all for 1p1x)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.2.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
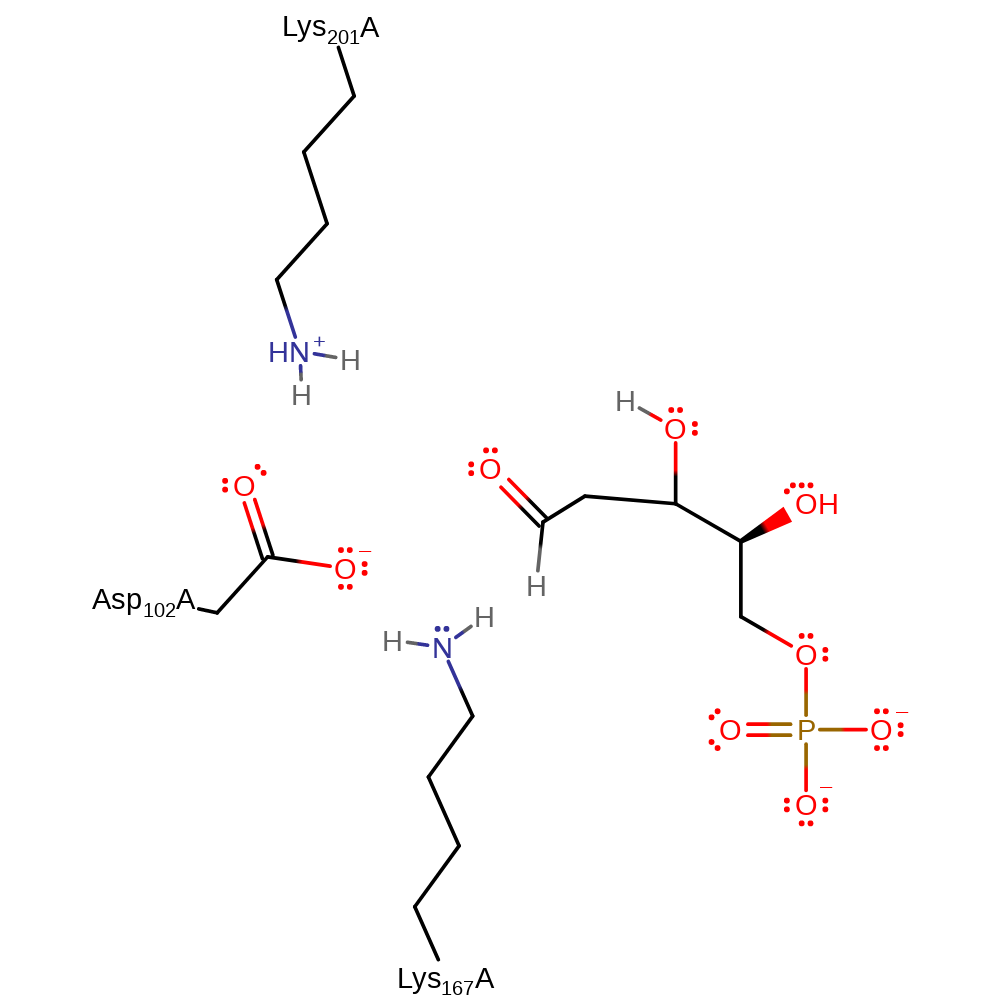
The reaction proceeds via initial nucleophilic attack by Lys 167 on acetaldehyde to form a Schiff base intermediate; deprotonation of the Lys 167 by Asp 102 facilitates this. Subsequent deprotonation of the C2 of the acetaldehyde by a Lys 201 activated water molecule (Wat29) results in the production of a nucleophilic carbon centre which attacks the G3P molecule to form the linear form of the product, DRP.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1p1x) | ||
| Asp102 | Asp102(103)A | Activates Lys 167 towards nucleophilic attack so that Schiff base intermediate can be formed. Also acts to protonate and deprotonate the Lys 167 in order to allow collapse of the Schiff base intermediate. Furthermore, activates water as part of proton relay system with Lys 201. | proton relay, increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Lys167 | Lys167(168)A | Attacks electrophilic carbon centre to form Schiff base intermediate. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, electron pair acceptor, electron pair donor |
| Lys201 | Lys201(202)A | Activates water to allow it to act as a general acid base for deprotonation at C2 of the Schiff base intermediate. Also activates Lys 167 towards nucleophilic attack. | proton relay, increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intramolecular elimination, schiff base formed, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol), aldol addition, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Heine A et al. (2001), Science, 294, 369-374. Observation of Covalent Intermediates in an Enzyme Mechanism at Atomic Resolution. DOI:10.1126/science.1063601. PMID:11598300.
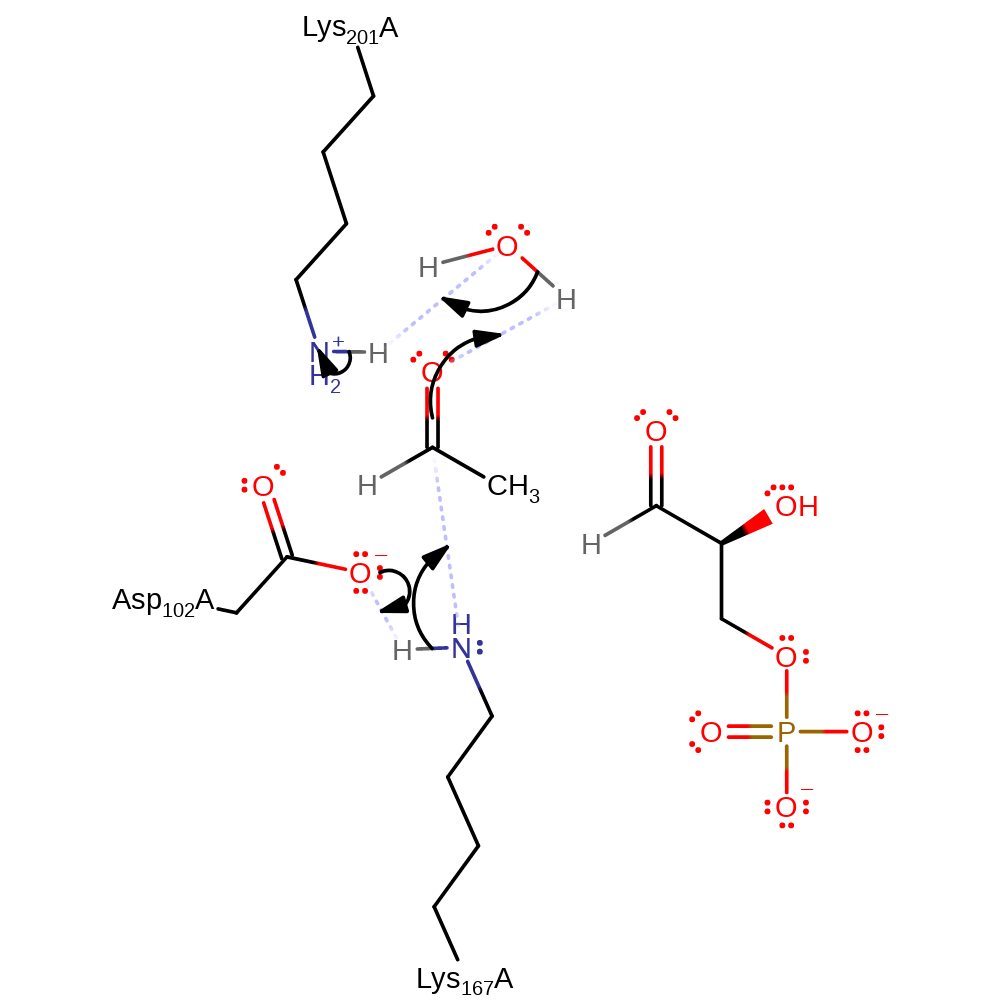
Step 1. Asp102 deprotonates Lys167, this activates the amine group for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of acetaldehyde, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The carbonyl oxygen is protonated by Lys201 via a water molecule .
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys167(168)A | covalently attached |
| Asp102(103)A | increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor |
| Lys167(168)A | proton donor |
| Lys201(202)A | proton donor |
| Lys167(168)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used
Step 2. Water is eliminated and a Schiff base intermediate is formed. This elimination is aided by general acid/base catalysis from Asp102 and Lys201.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys167(168)A | covalently attached, electron pair donor |
| Lys201(202)A | proton donor |
| Lys167(168)A | proton donor |
| Asp102(103)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular elimination, schiff base formed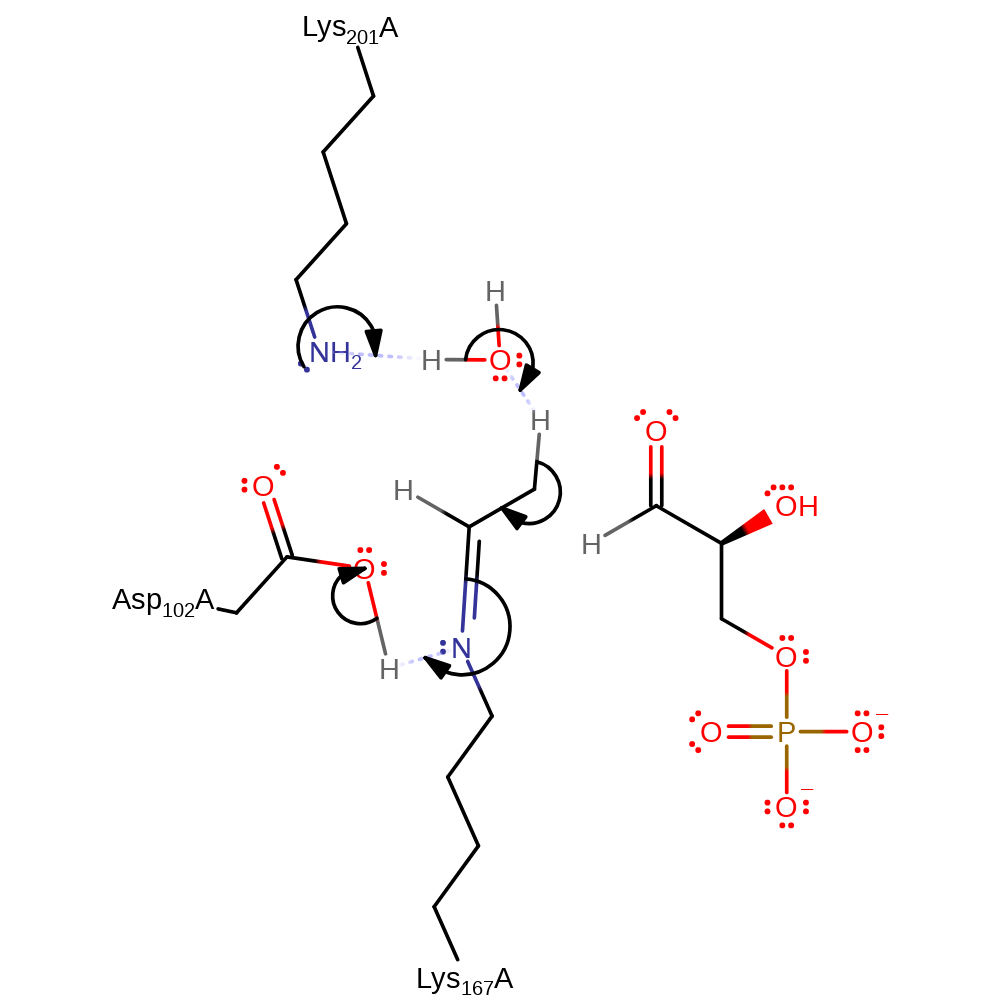
Step 3. The schiff base tautomerizes via acid/base catalysis to form a nucleophilic C=C bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys167(168)A | covalently attached |
| Lys201(202)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys167(168)A | proton acceptor, electron pair acceptor |
| Asp102(103)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted tautomerisation (not keto-enol)
Step 4. The C=C bond performs a nucleophilic attack upon the carbonyl carbon of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in an aldol addition. Which is again assisted by acid/base catalysis.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys167(168)A | covalently attached |
| Asp102(103)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys167(168)A | proton donor |
| Lys201(202)A | proton donor |
| Lys167(168)A | electron pair donor |
Chemical Components
aldol addition, proton transfer, schiff base formed
Step 5. A hydrolytic water performs a nucleophilic attack upon the the schiff base, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The water is activated by deprotonation from Lys201.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys201(202)A | increase nucleophilicity |
| Lys167(168)A | covalently attached, proton acceptor |
| Asp102(103)A | proton acceptor |
| Lys201(202)A | proton donor |
| Asp102(103)A | proton donor, proton relay |
| Lys201(202)A | proton relay |
| Lys167(168)A | electron pair acceptor |
| Lys201(202)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer
Step 6. Lys167 is cleaved from the substrate forming the product and regenerating the enzyme in its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp102(103)A | proton donor |
| Lys167(168)A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| Lys201(202)A | proton acceptor |
 Download:
Download: